CHEM 23: Statistics and Data Handling in Analytical Chemistry
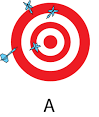
low accuracy, low precision

low accuracy, high precision

high accuracy, low preicison

high accuracy, high precision
accuracy
agreement between a measured value and the accepted true value, how close would it be to the actual value
ways to express accuracy
absolute error and relative error
absolute error formula
measured value – true value
relative error formula
((measured value - true value)/(true value)) x 100%
precision
degree of agreement between replicate measurements of the same quantity
determinate errors
determinable and that presumably can be either avoided or corrected
instrumental errors
faulty equipment
example of instrumental error
uncalibrated glassware
operative errors
personal errors
example of operative error
mathematical error in calculation, misread of menisicus
errors of the method
wrong method for an experiment
example of error of the method
coprecipitation of impurities
indeterminate errors
accidental or random errors
what does indeterminate error show in a distribution?
bell curve or normal distribution
significant figures
the number of digits necessary to express the results of a measurement consistent with the measured precision
significant figure rule in addition and subtraction
use least significant decimal place
significant figure rule in multiplication and division
use least significant figures