Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy and Physiology 2 Wiley Chapter 29
front 1 Fertilization normally occurs within which structure? | back 1 Fallopian tube |
front 2 Which of the following is a series of functional changes that sperm go through when they are in the female reproductive tract? | back 2 capacitation |
front 3 The fusion of the male nucleus and the female pronucleus results in which developmental stage? | back 3 zygote |
front 4 Which of the following is the part of the blastocyst that promotes implantation and produces hCG? | back 4 trophoblast |
front 5 Which of the following is the portion of the endometrium that lies between the embryo and the stratum basale? | back 5 decidua basalis |
front 6 Which of the following develops from the epiblast and carries a protective fluid? | back 6 Amnion |
front 7 Which of the following will become the primary structure for exchange of material between the mother and the fetus? | back 7 chorionic villi of the placenta |
front 8 During development, each somite may differentiate into a ___ that forms connective tissue. | back 8 dermatome |
front 9 Which of the following is the connection between the placenta and the embryo? | back 9 umbilical cord |
front 10 How many pairs of pharangyeal arches form in the future head and neck region during the fourth week? | back 10 5 |
front 11 Gastrulation occurs at approximately which point after fertilization? | back 11 During third week of embryonic period |
front 12 What exam is performed between 14-16 weeks of gestation and is used to detect genetic abnormalities? | back 12 Amniocentesis |
front 13 CVS is taking cells from where? | back 13 Chorion |
front 14 Which hormone is secreted by nonpregnant women from neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus? | back 14 CRH |
front 15 During pregnancy, stroke volume can increase by | back 15 30% |
front 16 Labor cannot take place until all of which hormone's effects are diminished? | back 16 Progesterone |
front 17 Which of the following is the time from the onset of labor to complete dilation of the cervix? | back 17 stage of dilation |
front 18 Involution is | back 18 When the uterus decreases in size |
front 19 What connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava in infants? | back 19 ductus venosus |
front 20 Which is the effector when oxytocin stimulates milk ejection? | back 20 myoepithelial cells |
front 21 Which principle hormone releases milk into the mammary glands? | back 21 oxytocin |
front 22 Which of the following is a permanent heritable change in an allele? | back 22 mutation |
front 23 When phenotype can be drastically different depending on whether the gene is inherited from the mother or father it is called- | back 23 genomic imprinting |
front 24 An example of incomplete dominance is | back 24 Sickle-cell disease |
front 25 If one parent has type A blood and one parent has type B blood, what blood type is possible for their child? | back 25 all of these choices |
front 26 If a child has type B blood and the mother has type B blood, what is the possible phenotype of the father? | back 26 B, O, A, or AB |
front 27 Chromosome #15 is considered | back 27 an autosome |
front 28 A Barr body | back 28 is an inactivated X chromosome |
front 29 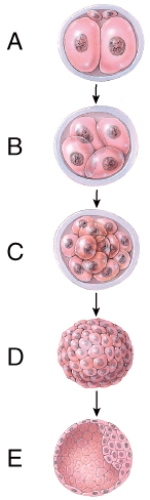 Which represents the morula stage? | back 29 C) C |
front 30  Which one represents the blastocyst stage? | back 30 E |
front 31  What does figure "A" represent? | back 31 cleavage of zygote |
front 32 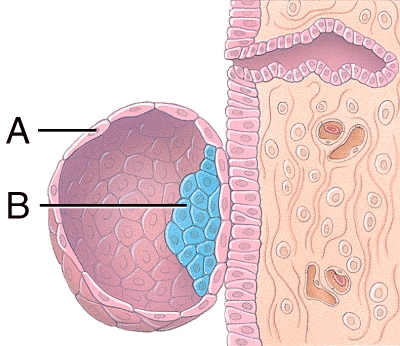 What is line "A" pointing to? | back 32 trophoblast |
front 33  What happens 3-4 days after fertilization? | back 33 C) C |
front 34  What stage happens 6 days after fertilization? | back 34 E) E |
front 35 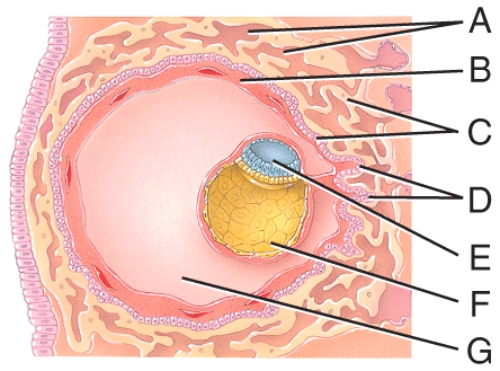 Which structure was formerly called the blastocyst cavity? | back 35 D) F |
front 36  This is composed of the syncytiotrophoblast and the cytotrophoblast. | back 36 C) C |
front 37  Where is the amniotic cavity? | back 37 A) E |
front 38  Which cells are derived from the yolk sac and form a connective tissue layer? | back 38 B) B |
front 39 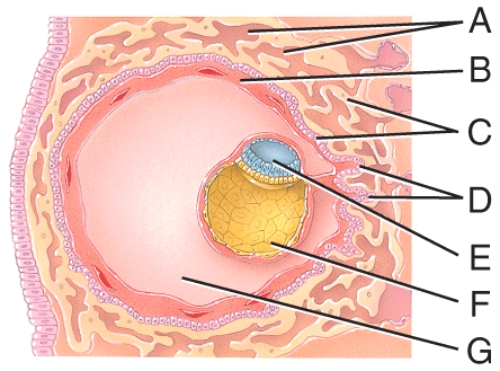 What is line "G" pointing to? | back 39 none of these |
front 40 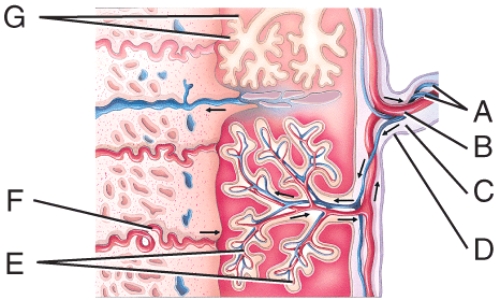 What is like "G" pointing to in this figure? | back 40 chorionic villi |
front 41 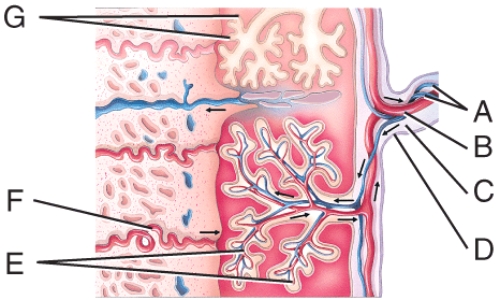 Where are the fetal blood vessels in the figure? | back 41 C) E |
front 42  What is line "F" pointing to in the figure? | back 42 maternal endometrial arteriole |
front 43 Which condition listed is a malpractice in which the fetal buttocks or lower limbs present into the material pelvis? | back 43 breech presentration |
front 44 Which condition listed is a developmental abnormality due to mechanical forces that mold a part of the fetus over a prolonged period of time? | back 44 deformation |
front 45 Clubfeet is an example of which condition listed? | back 45 deformation |
front 46 Which condition listed is also called morning sickness? | back 46 emesis gravidarum |
front 47 Which condition is listed as a sex chromosome aneuploidy, usually due to trisomy XXY? | back 47 Klinefelter's syndrome |
front 48 A deficiency in corticotropin-releasing hormone could lead to the development of ___ in the newborn | back 48 respiratory distress syndrome |
front 49 The hormone associated with a change in gait of pregnant woman in the later stages of pregnancy is | back 49 relaxin |
front 50 A neural tube defect in the developing fetus may be detected by measuring the levels of which of the following substances? | back 50 maternal alpha-fetoprotein |
front 51 Which of the following may be associated with anencephaly and a higher risk of ectopic pregnancies? | back 51 all of these |
front 52 During pregnancy, a malfunction during which weeks might leak to a breech presentation at birth? | back 52 30-34 weeks |
front 53 If one was able to view the developing embryo and fetus, at which stage of the pregnancy would the gender of the baby be distinguishable for the first time? | back 53 9-12 weeks |
front 54 Which condition listed is a sex chromosome aneuploidy, caused by the presence of a single X chromosome designated XO? | back 54 Turner's syndrome |
front 55 A teratogen induced developmental defect resulting in characteristics facial features is associated with | back 55 fetal alcohol syndrome |
front 56 Which condition listed results from an infection originating in the birth canal following child birth and affects the mother's endometrium? | back 56 puerperal fever |
front 57 Which condition listed is a sex chromosome aneuploidy characterized by at least 3 X chromosomes (XXX)? | back 57 Metafemale syndrome |
front 58 Which of the terms below describes the development of an organism from an undifferentiated cell? | back 58 epigenesis |
front 59 Which of the terms below includes all structures that develop from a zygote: the embryo, the embryonic placenta and its associated membranes? | back 59 conceptus |
front 60 Which of the terms below describes the beginning or first discernible indication of the development of an organ or structure? | back 60 primordium |
front 61 Which of the terms below describes the chromosomal characteristic of an individual presented as a systemic arrangement of pairs of metaphase chromosomes arranged by size? | back 61 karyotype |
front 62 What is the term used to describe the age of an embryo or fetus calculated from the presumed first day of the last normal menstruation period? | back 62 gestational age |
front 63 In an individual who is heterozygous for a certain gene, the dominant allele is responsible for that person having the trait of polydactyly. What is the masked, recessive trait in this individual? | back 63 normal digits |
front 64 In an individual who is heterozygous for a certain gene, the dominant allele is responsible for that person having diabetes insipidos. What is the masked recessive trait in this individual? | back 64 normal digits |
front 65 In an individual who is heterozygous for a certain gene, the dominant allele gives Huntington's disease. What is the masked, recessive trait in this individual? | back 65 normal nervous system |
front 66 In an individual who is heterozygous for a certain gene, the dominant allele gives normal skin pigmentation. What is the masked, recessive trait in this individual? | back 66 albinism |
front 67 Which hormone causes release of milk into the mammary ducts via the milk ejection reflex? | back 67 oxytocin |
front 68 The principle hormone in promoting milk production | back 68 prolactin |
front 69 Which of the following is a function of the hormone corticotropin-releasing hormone? | back 69 establish the timing of birth |
front 70 Which of the following is a noninvasive prenatal test? | back 70 AFP |
front 71 When are the primary germ layers established during pregnancy? | back 71 third week of development |
front 72 Which of the following structures are produced from the endoderm? | back 72 gametes |
front 73 Endoderm gives rise to which of these structures? | back 73 gonads |
front 74 Which of the following is NOT produced from the mesoderm? | back 74 melanocytes |
front 75 Which of the following are major potential teratogens that affect embryonic development? | back 75 all of thse |
front 76 The period of prenatal development would include | back 76 all of these |
front 77 In the process of fertilization, the sperm will fertilize the | back 77 secondary oocyte |