Microbiology Fall 2016 Study Guide Lab Exam 1
What are the standard things you do upon arriving to class each day, before the activity starts?
decontaminate work surface with disinfectant
what are some of the standard things you do before leaving class each day?
decontaminate work surface with disinfectant
what needs to be written on each plate or test tube?
your name, name of organism, and date it was innoculated
where do we dispose of broken glass and old prepared slides?
broken glass container
where do we dispose of old Petri plates?
autoclaveable containers: Sharps container or orange biohazard bag
What are some of the objects that are regularly flamed to avoid contamination with unwanted bacteria?
inoculating loop and top of glass tube
what is the power of the ocular lens?
10x
what is the power of the four objective lenses on our microscope?
4x, 10x, 40x, 100x
what is the equation to calculate total magnification?
ocular lens x objective lense
what is the purpose of immersion oil
to increase the resolving power of a microscope
which objective lens requires immersion oil?
100x
why do we go through the effort of fusing the bacteria of the smear.
to kill the bacteria and to make sure it sticks to the slide, so when we stain, it's there
what are the three things we flamed during the preparation of smear
inoculating loop, top of test tube, and slide to heat fix
why to we flame these objects?
to avoid contamination and to make sure the bacteria stick to the slide
what is a wet mount?
organism on a slide in a drop of liquid, organism is still alive, requires coverslip
what is the advantage of using a wet mount instead of a smear?
the organisms are alive
why do we stain microorganisms?
some are transparent; to be able to see them in contrast
how is a simple stain different from a differential stain?
simple stains color the everything on the slide, differential stains color only certain types of cells
what are the names of the two simple stains we used in our lab?
safranin and methylene blue
when are simple stains used in differential staining protocol?
as a counterstain
what are the four basic steps of a differential stain?
- primary stain
- mordant
- decolorizer
- counterstain
For gram staining what is the primary stain ?
crystal violet
For gram staining what is the mordant
gram's iodine
For gram staining what is the decolorizer?
acetone or alcohol
For gram staining what is the counterstain?
safranin
For gram staining which of the chemicals used in the staining procedure that we did in lab does not match the lab book?
alcohol/acetone
what color is gram positive cells at the end of the stain?
purple
what color is the gram negative cells at the end of the stain?
pink
what is the structural difference between gram - and gram + cells?
gram - has two plasma membrane and one thin cell wall
gram + have a thick cell wall
what shape and color is the bacteria of Staphylococcus aureus
cocci, purple
what shape and color is the bacteria of Bacillus brevis
bacili, purple
what shape and color is the bacteria of Escherichia coli
bacili, pink

Gram + and Gram - staining
For spore staining, what is the primary stain?
malachite green
For spore staining, what is the mordant
steam
For spore staining, what is the decolorizer?
water
For spore staining, what was the counterstain ?
safranin
For spore staining, what are the two general of common spore formers?
Bacillus and Clostridium
Where do spore-forming bacteria commonly grow?
survive environmental conditions that are not favorable
what color are the endospore at the end of the stain?
green
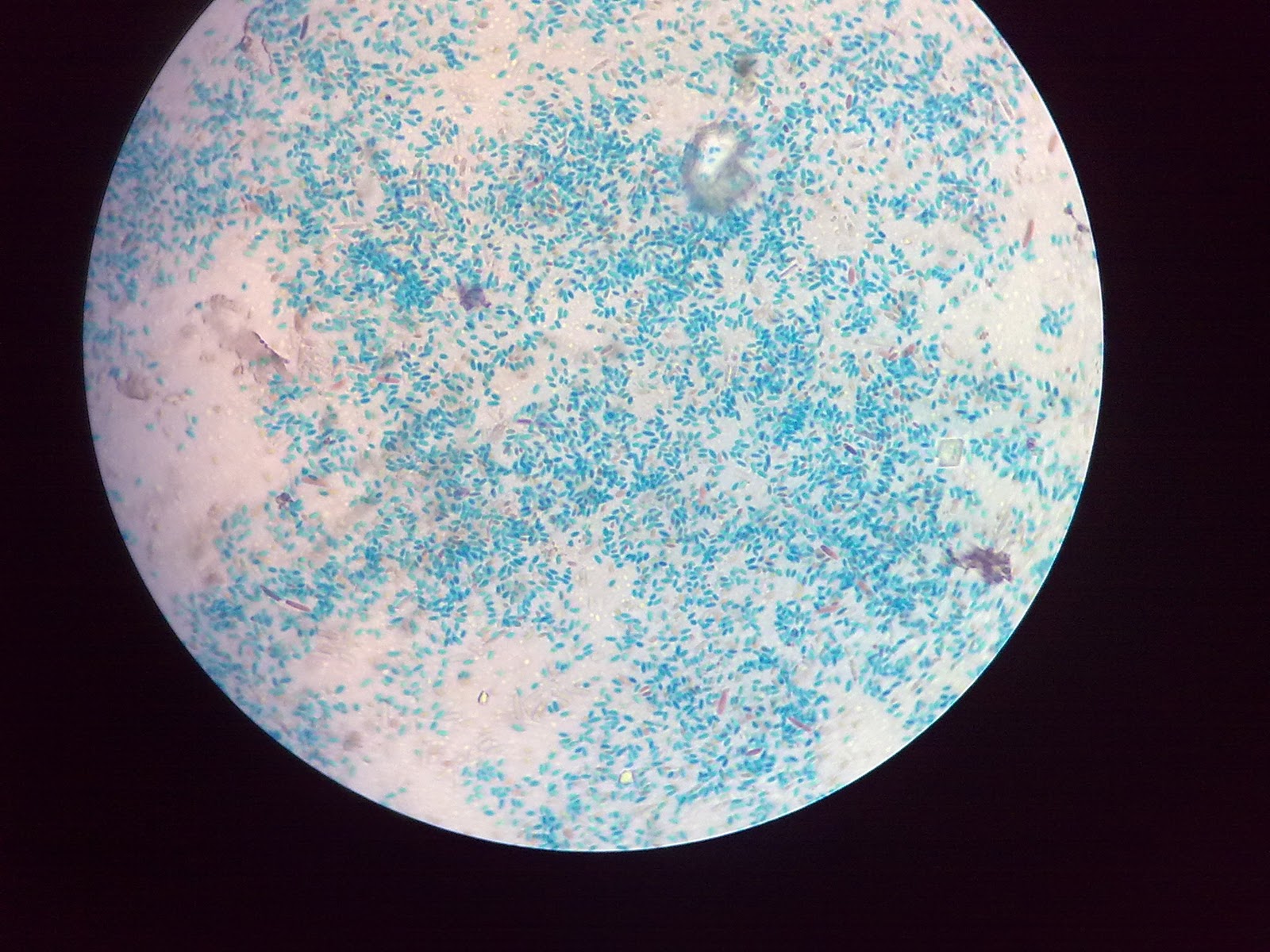
Spore staining
why do bacteria form endospore?
spore are produced when conditions become unfavorable
what appear pink at the end of the spore stain?
the vegetative cells
For acid-fast staining what is the primary stain ?
basic fuchsin
For acid-fast staining what is the mordant
steam
For acid-fast staining what is the decolorizer?
acid alcohol
For acid-fast staining what is the counterstain?
methylene blue
For acid-fast staining what chemical was used for the primary stain in our lab ?
carbol fuchsin
What color are the acid fast positive cells at the end of the stain?
metallic shiny red
what is the genus of the organism that was used as a acid-fast negative control?
Staphylococcus
Acid-fast staining
For capsule staining how is the basis of a negative stain different from the other staining protocols ?
The background is dark and the cells are clear.
how is the fixing step for the capsule stain different from the other staining protocols that we performed so far in lab?
it is chemically fixed with acid alcohol. and not heat fixed
For capsule staining what is the primary stain?
congo red stain
For capsule staining what is the purpose of acid alcohol?
fixing the smear on the slide
For capsule staining what is the secondary stain ?
carbol fuchsin
For capsule staining what is the genus of the organism that was used in class for this stain?
Klebsiella
For capsule staining what color is the capsule at the end of the procedure?
mostly clear or colorless
For capsule staining what color is the background?
purple/grey/red
how does the presence of a capsule affect the pathogenicity of a bacterium?
the capsule shield from immune response

Capsule Staining