Human Anatomy Lab Exercises Tissues Recognition and Function

Loose connective tissue, adipose

Blood

Bone

Cardiac muscle

Connective tissue loose, areolar

Dense connective tissue, elastic

Dense connective tissue, elastic

Dense connective tissue, regular

Cartilage: elastic

Fibrocartilage

Cartilage: hyaline

Dense connective tissue, irregular

Stratified squamous epithelium

Nervous tissue

Pseudostratified columnar epithelium

Dense connective tissue, reticular

Simple columnar epithelium

Simple cuboidal epithelium

Simple squamous epithelium
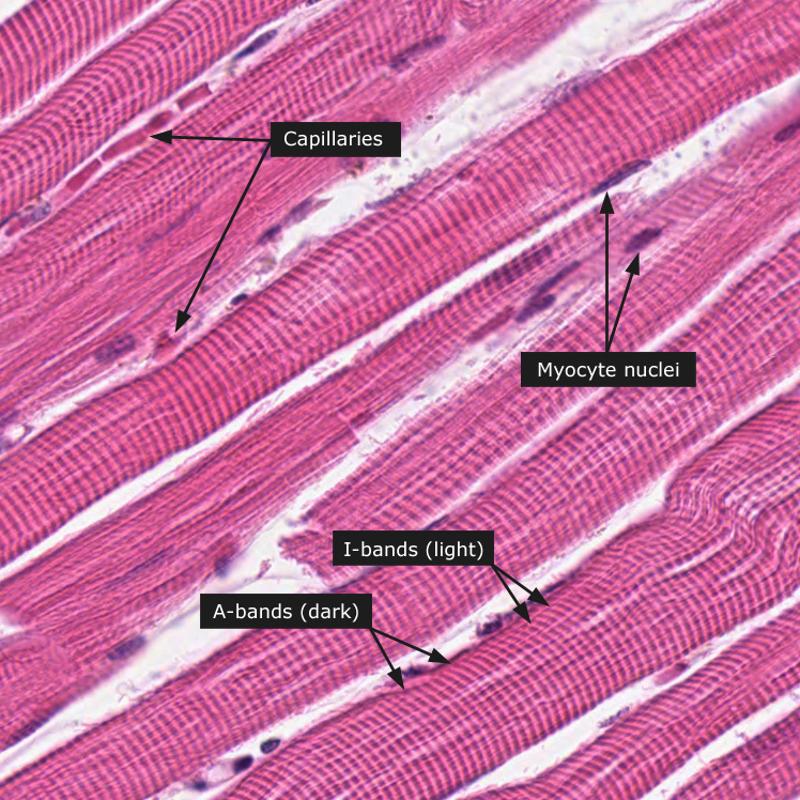
Skeletal muscle

Smooth muscle

Stratified cuboidal epithelium

Stratified columnar epithelium

Transitional epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium
Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration where protection is not important
Secretes lubricating substances in the serosae
Stratified squamous epithelium
Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasions
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Secretion and absorption
Transitional epithelium
Stretches readily and permits distention of urinary organ by contained urine
Simple columnar epithelium
Absorption, secretion of mucus and enzymes
Ciliated type propels mucus
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
1. Secretion, particularly of mucus
2. Propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
Loose connective tissue, areolar
1. Wraps and cushions organs
2. Phagocytizes bacteria
3. Plays an important role in inflammation
4. Holds and conveys tissue fluids
Loose connective tissue, adipose
1. Provides reserve fuel
2. Insulates against heat loss
3. Supports and protects organs
Dense connective tissue, regular
1. Attaches muscles to bones or muscles to muscles
2. Attaches bones to bones
3. Withstands great tensile strength when force is applied in one direction
Dense connective tissue, irregular
1. Withstands tension exerted in many directions
2. Provides structural strength
Dense connective tissue, reticular
1. Fibers form soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
Dense connective tissue, elastic
1. Allows recoil of tissue after stretching
2. Maintains pulsatile flow of blood through the arteries
3. Aids in passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
Cartilage: hyaline
1. Supports and reinforces
2. Has resilient cushioning properties
3. Resists compressive stress
Cartilage: elastic
Maintains shape of structure while allowing great flexibility
Fibrocartilage
Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
Bone
1. Supports and protects (by enclosing)
2. Provides levers for muscles to act on
3. Stores calcium, minerals, and fat
4. Marrow for blood cell formation
Blood
Transport of respiratory gases, wastes, and other substances
Skeletal muscle
1. Voluntary movement
2. Locomotion
3. Manipulation of environment
4. Facial expression
5. Voluntary control
Smooth muscle
1. Propels substances or objects (foodstuffs urine, baby) along internal passageways
2. Involuntary control
Cardiac muscle
1. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation
2. Involuntary control
Nervous tissue - Neurons
Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands) which control their activity
Neuroglial cells or Neuroglia
1. Maintains homeostasis
2. Forms myelin
3. Provides support and protection for neurons