Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy Lab Exercises Tissues Recognition and Function
front 1  | back 1 Loose connective tissue, adipose |
front 2  | back 2 Blood |
front 3  | back 3 Bone |
front 4  | back 4 Cardiac muscle |
front 5  | back 5 Connective tissue loose, areolar |
front 6  | back 6 Dense connective tissue, elastic |
front 7  | back 7 Dense connective tissue, elastic |
front 8  | back 8 Dense connective tissue, regular |
front 9  | back 9 Cartilage: elastic |
front 10  | back 10 Fibrocartilage |
front 11  | back 11 Cartilage: hyaline |
front 12  | back 12 Dense connective tissue, irregular |
front 13  | back 13 Stratified squamous epithelium |
front 14  | back 14 Nervous tissue |
front 15  | back 15 Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
front 16  | back 16 Dense connective tissue, reticular |
front 17  | back 17 Simple columnar epithelium |
front 18  | back 18 Simple cuboidal epithelium |
front 19  | back 19 Simple squamous epithelium |
front 20 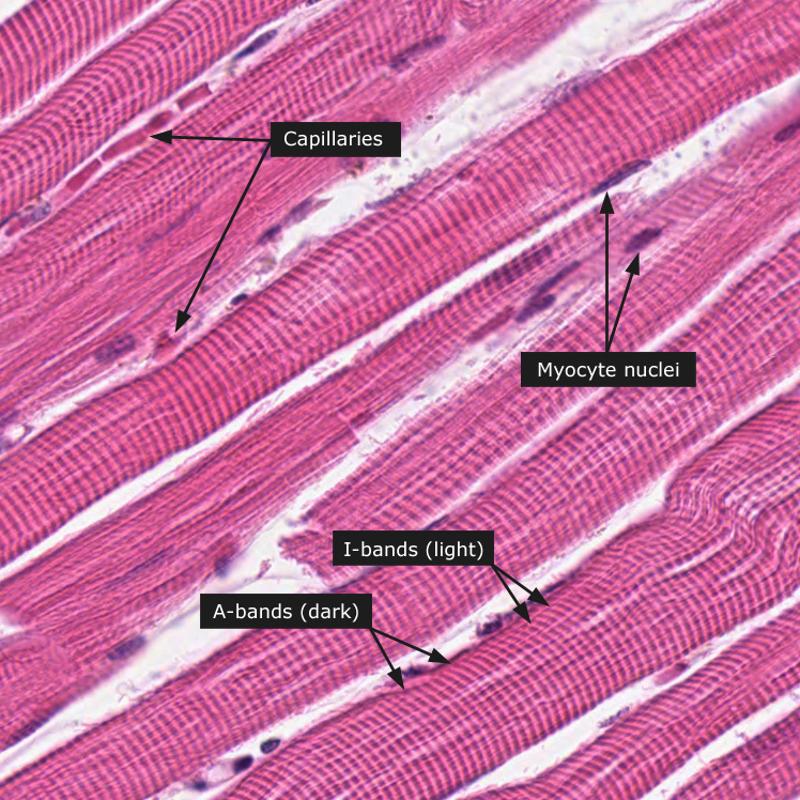 | back 20 Skeletal muscle |
front 21  | back 21 Smooth muscle |
front 22  | back 22 Stratified cuboidal epithelium |
front 23  | back 23 Stratified columnar epithelium |
front 24  | back 24 Transitional epithelium |
front 25 Simple squamous epithelium | back 25 Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration where protection is not important Secretes lubricating substances in the serosae |
front 26 Stratified squamous epithelium | back 26 Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasions |
front 27 Simple cuboidal epithelium | back 27 Secretion and absorption |
front 28 Transitional epithelium | back 28 Stretches readily and permits distention of urinary organ by contained urine |
front 29 Simple columnar epithelium | back 29 Absorption, secretion of mucus and enzymes Ciliated type propels mucus |
front 30 Pseudostratified columnar epithelium | back 30 1. Secretion, particularly of mucus 2. Propulsion of mucus by ciliary action |
front 31 Loose connective tissue, areolar | back 31 1. Wraps and cushions organs 2. Phagocytizes bacteria 3. Plays an important role in inflammation 4. Holds and conveys tissue fluids |
front 32 Loose connective tissue, adipose | back 32 1. Provides reserve fuel 2. Insulates against heat loss 3. Supports and protects organs |
front 33 Dense connective tissue, regular | back 33 1. Attaches muscles to bones or muscles to muscles 2. Attaches bones to bones 3. Withstands great tensile strength when force is applied in one direction |
front 34 Dense connective tissue, irregular | back 34 1. Withstands tension exerted in many directions 2. Provides structural strength |
front 35 Dense connective tissue, reticular | back 35 1. Fibers form soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages |
front 36 Dense connective tissue, elastic | back 36 1. Allows recoil of tissue after stretching 2. Maintains pulsatile flow of blood through the arteries 3. Aids in passive recoil of lungs following inspiration |
front 37 Cartilage: hyaline | back 37 1. Supports and reinforces 2. Has resilient cushioning properties 3. Resists compressive stress |
front 38 Cartilage: elastic | back 38 Maintains shape of structure while allowing great flexibility |
front 39 Fibrocartilage | back 39 Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock |
front 40 Bone | back 40 1. Supports and protects (by enclosing) 2. Provides levers for muscles to act on 3. Stores calcium, minerals, and fat 4. Marrow for blood cell formation |
front 41 Blood | back 41 Transport of respiratory gases, wastes, and other substances |
front 42 Skeletal muscle | back 42 1. Voluntary movement 2. Locomotion 3. Manipulation of environment 4. Facial expression 5. Voluntary control |
front 43 Smooth muscle | back 43 1. Propels substances or objects (foodstuffs urine, baby) along internal passageways 2. Involuntary control |
front 44 Cardiac muscle | back 44 1. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation 2. Involuntary control |
front 45 Nervous tissue - Neurons | back 45 Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands) which control their activity |
front 46 Neuroglial cells or Neuroglia | back 46 1. Maintains homeostasis 2. Forms myelin 3. Provides support and protection for neurons |