Anatomy of the Arteries of the Trunk - Lecture 5
Define the difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation
Pulmonary circulation is this which involves the SVC, IVC, RA, RV, Pulmonary trunk and pulmonary arteries in which deoxygenated blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation
Systemic circulation involves the pulmonary veins, LA, LV and aorta, in which oxygenated blood is distributed around the rest of the body, including the hear itself
Describe what an anastomoses is and the types that occur

Anatomoses
- A continuity between 2 larger vessels that allows blood to bypass the capillaries
- Close when there is an increased demand for oxygenation/provision of nutrients to a tissue area (as in the case of alimentary anatomoses)
Types
- Artery - Artery
- Such as Inferior and Superior epigastric arteries
- Ductus arteriosus from the pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aorta within the fetus
- Vein - vein
- Cardiac veins have an extensive network
- Artery - vein
- Erectile tissue in penis
- Alimentary mucous membrane
Briefly outline what a portal system is
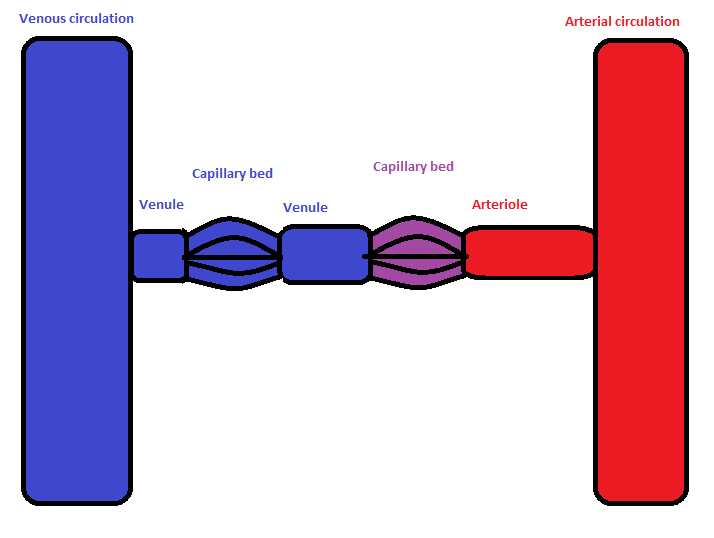
A portal system is where a vein or arteriole connect two capillary networks, one capillary bed drains into another
This occurs in the hepatic portal system in which the hepatic portal veins connect capillaries of the intestine to liver sinusoids (capillaries)
The efferent arteriole in the kidney glomerulus, drains glomerular capillaries of the kidney into peritubular capillaries around cortical renal tubes
What is meant by a vasa vasorum
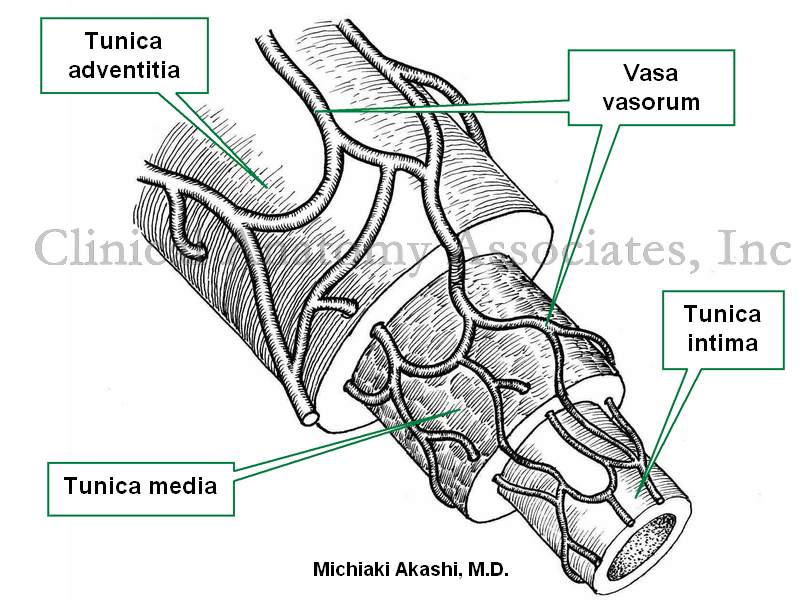
The connection of blood vessels that surround larger blood vessels (such as arteries) and supply the vascular smooth arterial muscle with blood
Seen as a tracery of fine purple thread on the outer surface of arteries
The arterial blood within the vasa vasorum is from the artery itself (vasa vasorum internae)
Venous drainage occurs back into the artery
Undergo pathological changes in réponse to infection, artherosclerosis or injury
Why don't arteries have valves

In the arterial system there is enough +ve pressure to prevent back flow of blood
Valves only occur at the pulmonary and aortic valve, though these are needed to allow proper systole to occur
Veins have valves as at times there can be -ve pressure within them which would cause a back flow of blood
Describe the function and location of the pulmonary veins are arteries

R.Pulmonary artery
- Posterior to aortic arch and SVC
- Anterior to trachea and bronchi
L.Pulmonary artery
- Anterior to descending aorta and L.principle bronchus
- Connects to inferior arch of aorta via ligamentum arteriosum
Pulmonary veins
- 2 from each lung drain into LA
- No valves present
Describe the branches that arise from the ascending aorta
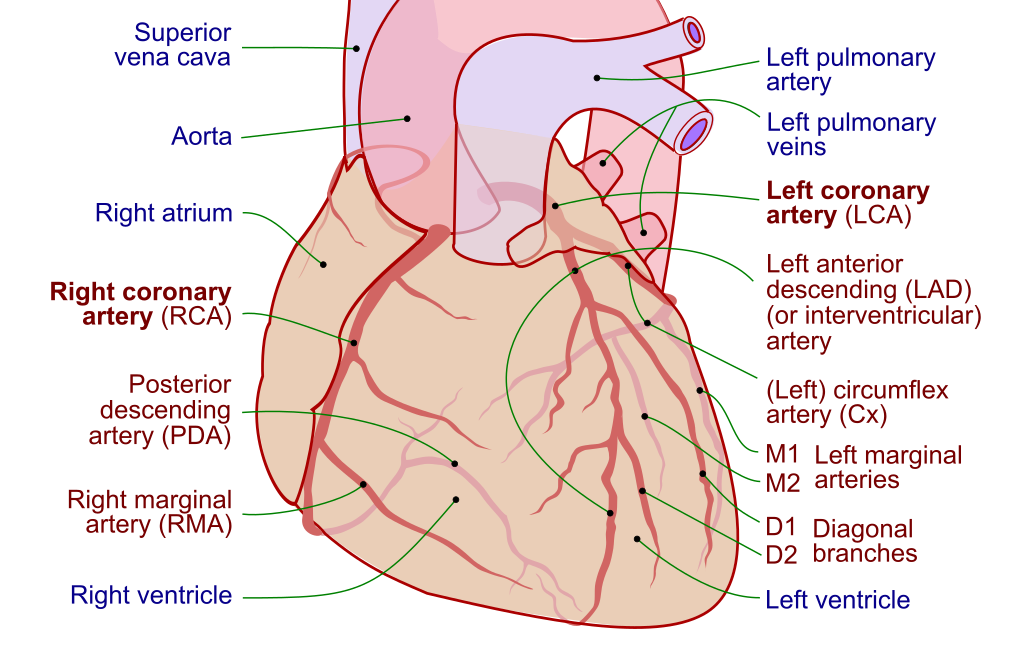
L. and R. Coronary arteries
- From aortic sinuses
- RCA
- In right atrioventricular groove (coronary sulcus)
- Branches to R.marginal and Posterior interventricular
- LCA
- Branches to Anterior interventricular, L.marginal, Circumflex
Describe the branches that arise from the arch of the aorta
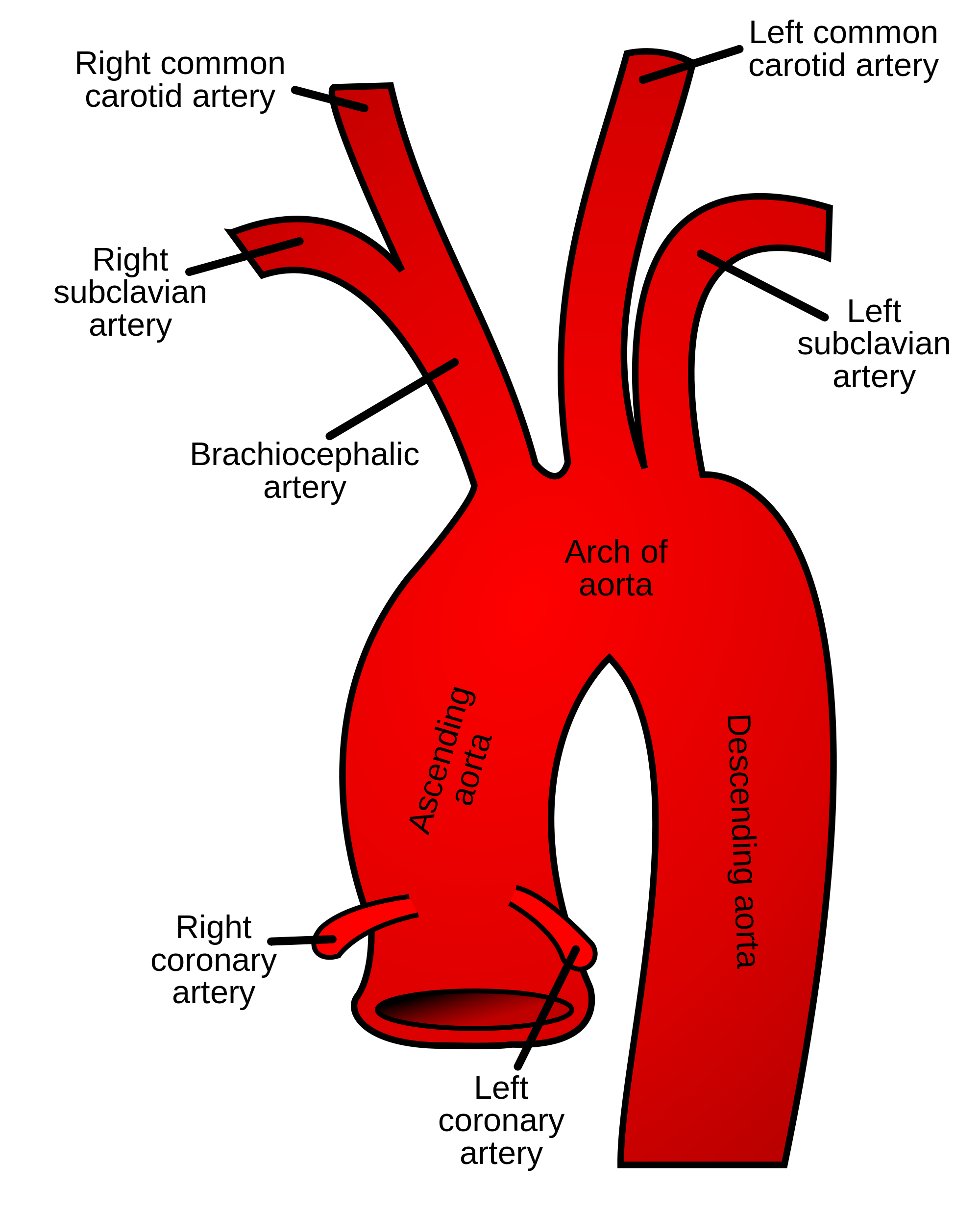
Right side of aortic arch
- Brachiocephalic trunk which gives rise to R.Subclavian and R.Common Carotid
Left side of aortic arch
- L.Common Carotid and L.Subclavian
Describe the features of the thoracic (descending) aorta

Anterior to vertebral column and azygous vein
Oesophagus initially on the right then moves to the left inferiorly
Lateral branches
- Posterior intercostal arteries (Vein, artery, Nerve from superior to inferior within the costal groove of the ribs)
Anterior branches
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Oesophagus
- Mediastinum
- Pericardium
- Superior phrenic
- Subcostal
Descends into the diaphragm at T12
Describe the features of the abdominal aorta
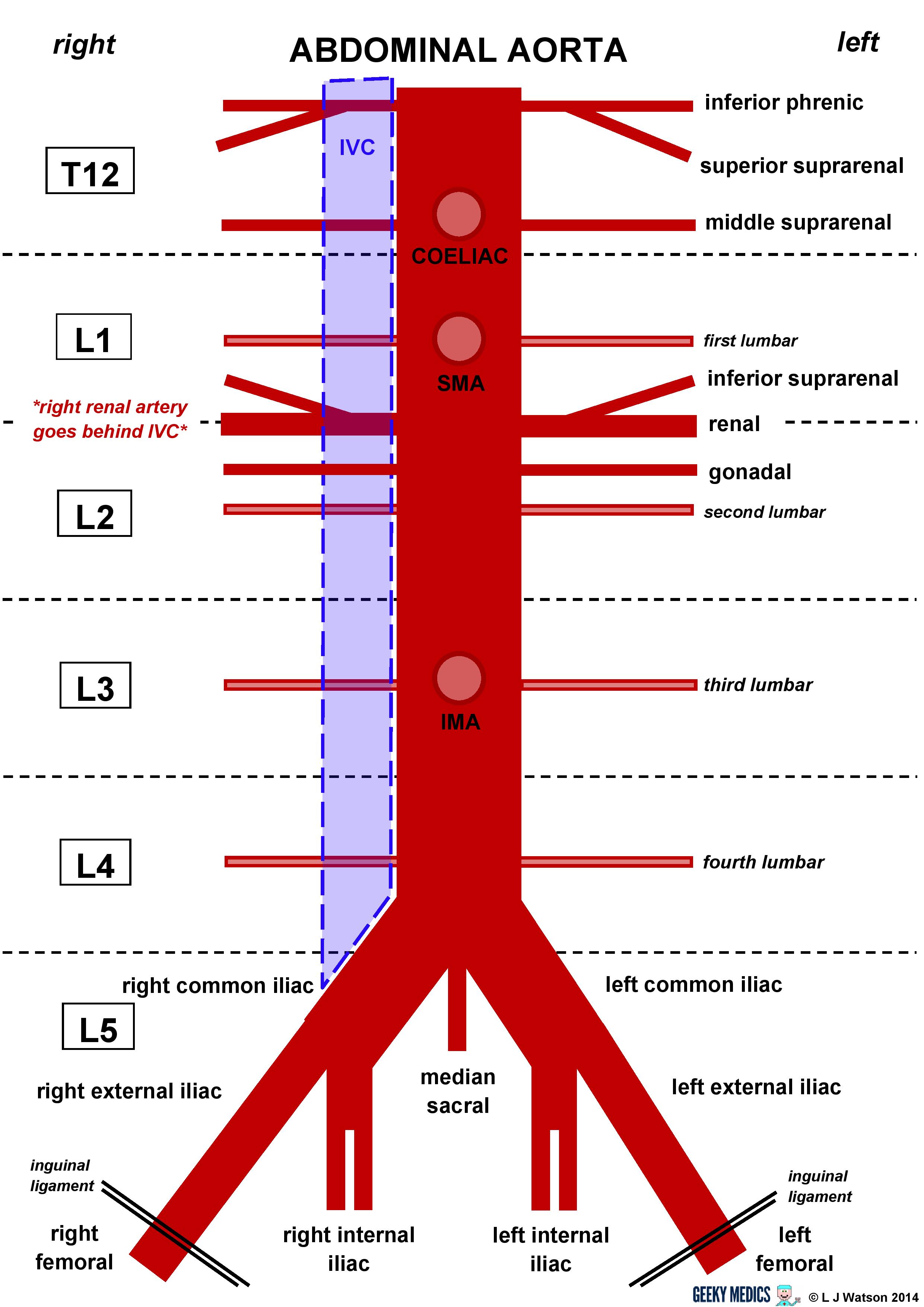
Inferior Phrenic
- Paired
- Originates just below the diaphragm, supplies it from below
- At T12 posteriorly
- Parietal
Celiac
- Large anterior branch
- Upper L1
- Visceral
- Divides into L.Gastric, Hepatic and Splenic
Superior mesenteric
- Large anterior just below celiac trunk
- Lower L1
- Visceral
Middle suprarenal
- Paired posterior
- To adrenal gland
- L1
- Visceral
Renal
- Paired
- Large from side of aorta
- Supplies kidney
- Arises in transpyloric plane
- L1-2
- Visceral
Gonadal
- Ovarian artery in females, testicular artery in makes
- Lateral and paired
- Directed Inferiorly
- Visceral
- L2
Lumbar
- 4 on either side to supply abdominal wall and SC
- Posterior and paired
- L1-4
- Parietal
Inferior mesenteric
- Large anterior branch
- L3
- Visceral
Median sacral
- Arising from middle of the aorta at its lowest part
- L4
- Parietal
Commom iliac
- Bifurcates the supply lower limbs and pelvis
- The ending of the abdominal aorta
- Terminal
- Paired
- L4
- Internal
- Supplies mostly inside of pelvis
- External
- Passes through femoral canal to form Femoral artery
- Inferior epigastric and deep circumflex iliac arteries branch
off before femoral canal
- Inferior Epigastric anastomoses with Superior Epigastric
What is the thoracic wall
It is the boundary of the thoracic cavity
Describe the functioning of the Internal Thoracic Artery (Internal Mammary Artery)

Arises from the subclavian artery
Runs down the postero-lateral sides of the sternum, outside the parietal pleura and internally to the ribcage
- Between the transversus thoracus muscle posteriorly and the costal cartilages and innermost intercostal muscles anteriorly
Branches to adjacent thoracic structure
- Pericardiophrenic - runs with phrenic nerve to pericardium
- Thymic
- Sternal
- Mediastinal
- Pericardial
- 3-5 anastomose with posterior intercostal and bronchial artery
to form subpleural mediastinal plexus
- Supplies anterior 6 intercostal spaces with the VAN (vein, artery, nerve) within the costal groove
Internal thoracic terminates through its bifurcation to the musculophrenic artery and the superior epigastric artery
Collateral branch of the posterior intercostal artery (Anterior Intercostal Artery) goes upon the superior border of the inferior rib
Describe the superior epigastric artery

The superior epigastric arises from the bifurcation of the internal thoracic artery at the level of 6th-7th costal cartilage
Accompanied by the superior epigastric vein
Anterior to the transverse abdominis muscle and perforates the rectus abdominis muscle
- Supplies anterior abdominal wall and some the the diaphragm
Anastomoses with Inferior epigastric artery at the umbilicus
Describe the Inferior Epigastric Artery
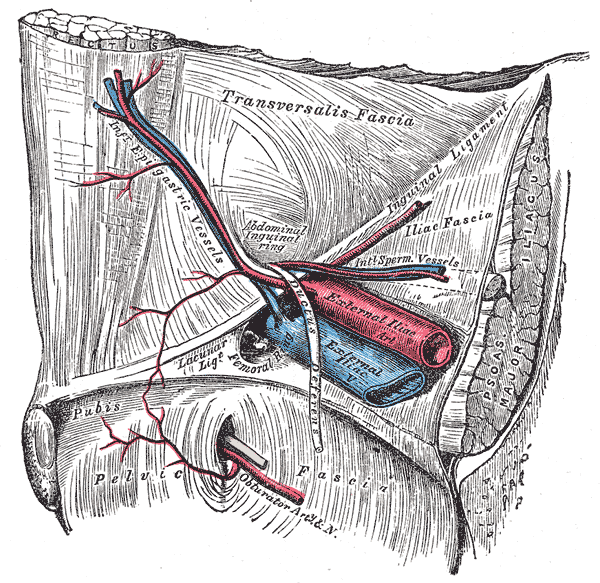
Arises from external iliac artery above the inguinal ligament
Anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery above the umbilicus and the lower intercostal arteries
Pierces transversalis fascia, pases infant of linea semicircularis, between rectus abdominus and the posterior lamina of its sheath
Describe the musculophrenic artery

Provides the lowest 5 paired anterior intercostal arteries
Provides fine branches to supply the superior anterior abdominal wall
Anastomoses with the posterior intercostal arteries and the superior epigastric
Describe surface anatomy points of the thoracic and abdominal walls

Sternal angle = underside of aortic arch
Centre point of manubrium = Brachiocephalic artery arises
Sternoclavicular joint = 2cm above for internal thoracic artery from subclavian arteries
1cm Lateral to sternal margin = Internal throracic artery
Transpyloric plane/L1 = Superior mesenteric artery, celiac trunk 1cm superiorly
L3 = Inferior mesenteric artery, 3-4cm above aortic bifurcation
L4 = Aortic bifurcation into common iliac arteries