Chapter 6
What is an orderly and permanent increase in the mass of protoplasm of an organism or population?
Growth
What is "orderly" growth?
A proportionate increase in all constituents
What is microbial growth?
An increase in the number of cells, not cell size
What is an increase in the number of individuals and can be independent of growth?
Reproduction: cells may grow without reproducing or may reproduce without growth
The lowest temperature where growth occurs?
Minimum temperature
The best temperature where growth occurs?
Optimum temperature
The highest temperature where growth occurs?
Maximum temperature
Which organisms are "cold-loving" with a growth temperature of 0 to 20 degrees Celsius and an optimum growth at 15 degrees Celsius?
Psychrophiles
What are mesophiles?
Organisms that are "middle-loving" and grow at 20 to 45 degrees Celsius and have optimum growth at 20 to 37 degrees Celsius.
Which organisms are "heat-loving" and grow at 37 to 65 degrees Celsius?
Thermophiles
Most bacteria grow in what range of pH?
6.5 to 7.5 (same as human levels)
What is the optimum pH for acidophiles?
0 to 5.5
What is the optimum pH for basophiles?
8.5 to 11.5
What can cause organisms to change the culture media to toxic due to pH change?
Their own waste products (generally acidic)
Which environment increases salt or sugar, cause plasmolysis?
Hypertonic
Which type of halophiles REQUIRE high osmotic pressure?
Extreme or obligate halophiles
Which type of halophiles TOLERATE high osmotic pressure?
Facultative
What are the environmental factors impacting growth?
Temperature, pH, osmotic pressure and chemicals
True or False: Obligate aerobes can live without oxygen.
False
Facultative anaerobes can grow...
with or without oxygen
Obligate anaerobes...
cannot live with oxygen
Aerotolerant anaerobes...
tolerate oxygen
Microaerophiles
need less oxygen and more carbon dioxide
When oxygen becomes toxic an enzyme is needed to convert the very toxic, free radical to get rid of hydrogen peroxide. Explain which enzyme is used to remove peroxide
superoxide dismutase removes H2O2 to make H20 AND O2
catalase removes H2O2 to make 2 H20 AND O2
peroxidase removes H202 to make 2 H2O
*PEROXISOME makes and gets rid of H2O2
What are the chemical requirements for growth?
Carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus
Cells are what percentage water?
80 to 90%
What are trace elements and name them?
Inorganic elements required in small amounts and usually enzyme cofactors - Iron, manganese, magnesium and vitamins
What is an example of an autotroph? Why?
Plants - they use CO2 but they can make it for themselves
What is a chemoheterotroph?
Organisms that use organic carbon sources; such as humans and fungi.
Which chemicals can be limiting factors in growth?
Nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus (NSP to remember)
Most organisms can produce more energy when growing in oxygen but what are the risks?
Toxic byproducts of oxygen can be fatal to cells
What must aerobes, faculative anaerobes and aerotolerant have in order to deal with toxic byproducts?
superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase
Obligate aerobes...
cannot live WITHOUT oxygen (O2)
Faculative anaerobes...
Can live WITH orWITHOUT oxygen
Obligate anaerobes...
cannot live WITH oxygen
Aerotolerant anaerobes...
TOLERATE oxygen
Microaerophiles...
Require oxygen but can only grow at low oxygen tension - they need less oxygen and more CO2
What are toxic forms of oxygen?
Singlet oxygen: O2 boosted to a higher-energy state, extremely reactive
Superoxide free radicals: O2- (VERY TOXIC)
Peroxide anion (O2)2-
Which enzyme gets rid of superoxide free radicals?
superoxide dismutase
Which enzyme(s) gets rid of peroxide anion?
catalase and peroxidase
What is inoculum?
The introduction of microbes into a medium
What is a culture?
Microbes growing in/on culture medium.
What is a culture medium?
Nutrients prepared for microbial growth.
What does sterile mean?
No living microbes
What is a pure culture?
A culture coming from an isolated colony on a plate containing only one colony type
In what type of culture are most microorganisms found?
mixed culture
What is a synthetic or defined medium?
A medium made of known amounts of chemicals
What is a complex medium?
A medium made of some ingredients are of unknown composition or amount (extracts of plants, yeast or meat). Examples would be: nutrient broth or tryptic soy broth
What is agar?
A solidifying agent for culture media in Petri plates, slants and deeps. A complex polysaccharide made from red algae. It is generally not metabolized by microbes (microbes cannot degrade it so it remains solid). However, it liquefies at 100C and solidifies at -40C.
What percentage of agar is used for a solid media?
1.5%
What percentage of agar is used for a semi-solid media and why are semi-solid media used?
0.5% and it is used for motility studies
What percentage of agar is used for liquid media?
0 (no agar)
What is blood agar?
a differential medium containing red blood cells
What is MacConkey agar?
a specialized bacterial growth medium that is selective for Gram-negative bacteria and can differentiate those Gram- bacteria that are able to ferment lactose.
What is a selective medium?
A medium that encourages the growth of certain organisms while discouraging the growth of others
What is a differential medium?
A medium that distinguishes between different groups of bacteria
What is generation time?
The time required for cells to divide (and thus double the population), can be as short as 20 minutes or longer than a day.
If a single bacterium reproduced every 30 minutes, how many would there be in 2 hours?
16
1_2_4_8_16
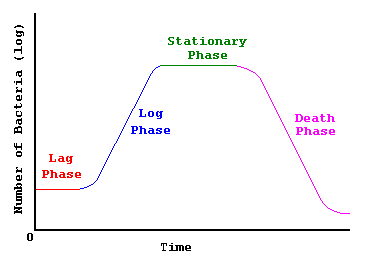
What are the phases of the growth curve?
1. Lag
2. Log
3. Stationary
4. Death
Describe the lag phase.
The period of little or no cell division but the cells are not dormant. There is intense metabolic activity involving synthesis of enzymes and various molecules.
What is the log phase?
Or the exponential growth phase, cellular reproduction is most active and the generation time reaches a constant minimum
Describe the stationary phase.
Eventually, the growth rate slows, the number of microbial deaths balances the number of new cells and the population stabilizes - a period of equilibrium.
What is the death phase?
When the number of deaths exceeds the number of new cells formed and continues until the population is diminished to a tiny fraction of the number of cells in the previous phase or until the population dies out entirely.
What are direct methods of measuring growth?
Plate counts (serial dilution; filtration, MPN (most probable number; statistical method); direct microscopic count
What are indirect methods of measuring growth?
Increase in turbidity with time
metabolic products
dry weight
What is the main difference between direct and indirect measurements of growth?
In direct we only measure live bacteria