ch 17
What type of immunity results from vaccination?
-innate immunity
-naturally acquired active immunity
-naturally acquired passive immunity
-artificially acquired active immunity
-artificially acquired passive immunity
-artificially acquired active immunity
What type of immunity results from transfer of antibodies from one individual to a susceptible individual by means of injection?
-innate immunity
-naturally acquired active immunity
-naturally acquired passive immunity
-artificially acquired active immunity
-artificially acquired passive immunity
artificially acquired passive immunity
What type of immunity results from recovery from mumps?
-innate immunity
-naturally acquired active immunity
-naturally acquired passive immunity
-artificially acquired active immunity
-artificially acquired passive immunity
-naturally acquired active immunity
Which of the following is the best definition of epitope?
-specific regions on antigens that interact with perforins
-specific regions on antigens that interact with haptens
-specific regions on antigens that interact with MHC class molecules
-specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
-specific regions on antigens that interact with T-cell receptors
-specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
Newborns' immunity due to the transfer of antibodies across the placenta is an example of
-artificially acquired active immunity
-innate immunity
-naturally acquired active immunity
-artificially acquired passive immunity
-naturally acquired passive immunity
naturally acquired active immunity.
Which of the following statements is NOT a possible outcome of antigen-antibody reaction?
-agglutination
-ADCC
-activation of complement
-clonal deletion
-opsonization
clonal deletion
Which of the following cells is NOT an APC?
-natural killer cells
-dendritic cells
-mature B cells
-macrophages
-None of the answers is correct; all of these are APCs
-natural killer cells
When an antibody binds to a toxin, the resulting action is referred to as
-apoptosis
-opsonization
-ADCC
-agglutination
-neutralization
neutralization
CD4+ T cells are activated by
-cytokines released by B cells
-interaction between TCRs and MHC II
-interaction between CD4+ and MHC II
-complement
-cytokines released by dendritic cells
-interaction between CD4+ and MHC II
Which of the following recognizes antigens displayed on host cells with MHC II?
-natural killer cell
-TC cell
-B cell
-TH cell
-basophil
TH cell
The specificity of an antibody is due to
-the L chains
-the H chains
-the variable portions of the H and L chains
-its valence
-the constant portions of the H and L chains
the variable portions of the H and L chains
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of B cells?
-They originate in bone marrow.
-They are responsible for antibody formation.
-They are responsible for the memory response.
-They have antibodies on their surfaces.
-They recognize antigens associated with MHC I
They recognize antigens associated with MHC I.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cellular immunity?
-The cells originate in bone marrow.
-B cells make antibodies.
-T cells interact with epitopes in MHC molecules.
-Cells mature in the thymus gland.
-Response to abnormal cells.
B cells make antibodies.
Plasma cells are activated by a(n)
-B cell
-T cell
-antigen
-APC
-memory cell
-antigen
The antibodies found in mucus, saliva, and tears are
-IgD
-IgM
-IgG
-IgA
-IgE
IgA
The antibodies found almost entirely and only on the surface of B cells (not secreted from them), and which always exist as monomers, are
-IgA
-IgE
-IgG
-IgD
-IgM
-IgD
The antibodies that typically bind to large parasites are
-IgA
-IgE
-IgD
-IgG
-IgM
igE
In addition to IgG, the antibodies that can fix complement are
-IgM
-IgD
-IgA
-IgE
-None of the answers is correct
IgM
Large antibodies that agglutinate antigens are
-IgG
-IgE
-IgM
-IgA
-IgD
IgM
The most abundant class of antibodies in serum is
-IgM
-IgD
-IgG
-IgE
-IgA
-IgG
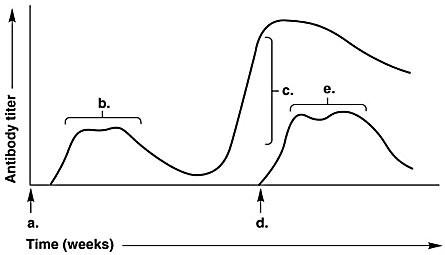
In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the patient's secondary response to a repeated exposure with the identical antigen?
-a
-b
-c
-d
-e
-c

In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the highest antibody titer during the patient's response to a second and distinct/different antigen?
-a
-b
-c
-d
-e
e

In Figure 17.1, the arrow at time (d) indicates
-exposure to a new antigen
-the secondary response
-the time of exposure to the same antigen as at time (a)
-the T-cell response
-the primary response
exposure to a new antigen
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
-The Fc region may attach to a host cell.
-The variable region of a heavy chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen.
-The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies.
-The variable region of a light chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen.
-All of the answers are correct.
The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies.
Which of the following is the best definition of antigen?
-a pathogen
-something foreign in the body
-a chemical that combines with antibodies
-a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
-a protein that combines with antibodies
a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
Which of the following are NOT lymphocytes?
-helper T cells
-B cells
-cytotoxic T cells
-M cells
-NK cells
-M cells
The following events elicit an antibody response. What is the third step?
-B cell is activated.
-TH cell produces cytokines.
-TH cell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II
-Antigen-digest goes to surface of APC.
-APC phagocytizes antigen.
TH cell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II
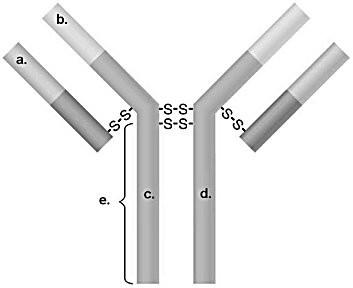
In Figure 17.2, which areas are similar for all IgG antibodies?
-b and d
-a and b
-a and c
-c and d
-b and c
-c and d

In Figure 17.2, which areas are different for all IgM antibodies?
-a and b
-b and c
-a and c
-c and d
a and b

In Figure 17.2, which areas represent antigen-binding sites?
-a and c
-b and d
-b and c
-a and b
-c and d
-a and b

In Figure 17.2, what portion will typically attach to a host cell?
-a and c
-e
-b
-b and c
-a and d
e
Which of the following bacterial components would most likely result in B cell stimulation by T-independent antigens?
-capsule
-plasmid
-flagellum
-ribosome
-pili
capsule
The presence of which of the following indicates a current infection rather than a previous infection or vaccination?
-IgA
-IgE
-IgM
-IgD
-IgG
-IgM
Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells?
-B cells
-dendritic cells
-CTL
-TH
-Treg
CTL
The following events occur in cellular immunity, leading to a response from TH cells. What is the third step?
-Antibodies are produced.
-Dendritic cell takes up antigen.
-Antigen enters M cell.
-TH cells proliferate
-TH cells produce cytokines
-TH cells proliferate
Cytokines released by TH1 cells
-convert TH1 cells to TH2 cells.
-convert TH2 cells to TH1 cells.
-directly kill parasites.
-convert B cells to T cells.
-activate CD8+ cells to CTLs
activate CD8+ cells to CTLs.
Which one of the following causes transmembrane channels in target cells?
-perforin
-hapten
-granzymes
-IL-2
-IL-1
perforin
At a minimum, the human immune system is capable of recognizing approximately how many different antigens?
-10^5
-10^25
-10^20
-10^15
10^15
Thymic selection
-activates B cells.
-destroys B cells that make antibodies against self.
-destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC
-destroys CD4+ cells that attack self.
-destroys MHC molecules.
destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC.
Which of the following statements about natural killer cells is FALSE?
-They destroy tumor cells.
-They destroy cells lacking MHC I.
-They destroy virus-infected cells.
-They are stimulated by an antigen
-None of the answers are correct; all of these statements are true
They are stimulated by an antigen
An antibody's Fc region can be bound by
-macrophages
-B cells
-antibodies
-CTLs
-T helper cells
macrophages
A Treg cell deficiency could result in
-transplant rejection.
-increased number of viral infections.
-increased number of bacterial infections.
-increased severity of bacterial infections.
-autoimmunity
autoimmunity.
ADCC is a process that is most effective in destroying
-eukaryotic pathogens
-extracellular viruses
-prions
-bacterial pathogens
-bacterial toxins
eukaryotic pathogens
IL-2, produced by TH cells,
-activates TC cells to CTLs
-causes phagocytosis.
-stimulates TH cell maturation.
-activates macrophages.
-activates antigen-presenting cells.
stimulates TH cell maturation.
NK cells do all of the following EXCEPT
-kill cells not expressing MHCI.
-comprise 10-15% of circulating lymphocytes.
-bind to Fc regions of bound antibodies.
-become activated by TH-2 cells.
-participate in antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity.
become activated by TH-2 cells.
Which terms regarding components of adaptive immunity are mismatched?
-TH-17 cells - recruit neutrophils.
-Dendritic cells- Langerhans cell.
-TH cells - MHCI interaction.
-M cell - microfolds.
-activated macrophage - membrane ruffling.
TH cells - MHCI interaction.
Which of the following statements about cytokines is FALSE?
-They are chemical communication between cells.
-Some have multiple functions.
-They are soluble proteins or glycoproteins.
-They are produced by immune cells in response to a stimulus.
-There are 10 types.
There are 10 types
A cell undergoing apoptosis
-will likely damage nearby cells.
-bursts and releases intracellular contents.
-was necessarily bound by antibodies.
-is employed as an infection-fighting mechanism.
-is a malfunction of the immune system
is employed as an infection-fighting mechanism
The importance of M cells concerns
-presentation of epitopes in MHCII molecules.
-ability to migrate along the intestinal tract.
-having microvilli to facilitate antigen capture.
-facilitation of contact between antigens in the intestinal tract and the immune system.
facilitation of contact between antigens in the intestinal tract and the immune system.
Which of the following terms regarding roles of chemical messengers is mismatched?
- interleukins - communication between white blood cells
-hematopoetic cytokine - development of blood cells
-interferons - interruption of viral infection
-tumor necrosis factor - stimulate tumor metastasis
-chemokines - stimulate chemotaxis
tumor necrosis factor - stimulate tumor metastasis