Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ch 17
front 1 What type of immunity results from vaccination? -innate immunity -naturally acquired active immunity -naturally acquired passive immunity -artificially acquired active immunity -artificially acquired passive immunity | back 1 -artificially acquired active immunity |
front 2 What type of immunity results from transfer of antibodies from one individual to a susceptible individual by means of injection? -innate immunity -naturally acquired active immunity -naturally acquired passive immunity -artificially acquired active immunity -artificially acquired passive immunity | back 2 artificially acquired passive immunity |
front 3 What type of immunity results from recovery from mumps? -innate immunity -naturally acquired active immunity -naturally acquired passive immunity -artificially acquired active immunity -artificially acquired passive immunity | back 3 -naturally acquired active immunity |
front 4 Which of the following is the best definition of epitope? -specific regions on antigens that interact with perforins -specific regions on antigens that interact with haptens -specific regions on antigens that interact with MHC class molecules -specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies -specific regions on antigens that interact with T-cell receptors | back 4 -specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies |
front 5 Newborns' immunity due to the transfer of antibodies across the placenta is an example of -artificially acquired active immunity -innate immunity -naturally acquired active immunity -artificially acquired passive immunity -naturally acquired passive immunity | back 5 naturally acquired active immunity. |
front 6 Which of the following statements is NOT a possible outcome of antigen-antibody reaction? -agglutination -ADCC -activation of complement -clonal deletion -opsonization | back 6 clonal deletion |
front 7 Which of the following cells is NOT an APC? -natural killer cells -dendritic cells -mature B cells -macrophages -None of the answers is correct; all of these are APCs | back 7 -natural killer cells |
front 8 When an antibody binds to a toxin, the resulting action is referred to as -apoptosis -opsonization -ADCC -agglutination -neutralization | back 8 neutralization |
front 9 CD4+ T cells are activated by -cytokines released by B cells -interaction between TCRs and MHC II -interaction between CD4+ and MHC II -complement -cytokines released by dendritic cells | back 9 -interaction between CD4+ and MHC II |
front 10 Which of the following recognizes antigens displayed on host cells with MHC II? -natural killer cell -TC cell -B cell -TH cell -basophil | back 10 TH cell |
front 11 The specificity of an antibody is due to -the L chains -the H chains -the variable portions of the H and L chains -its valence -the constant portions of the H and L chains | back 11 the variable portions of the H and L chains |
front 12 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of B cells? -They originate in bone marrow. -They are responsible for antibody formation. -They are responsible for the memory response. -They have antibodies on their surfaces. -They recognize antigens associated with MHC I | back 12 They recognize antigens associated with MHC I. |
front 13 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cellular immunity? -The cells originate in bone marrow. -B cells make antibodies. -T cells interact with epitopes in MHC molecules. -Cells mature in the thymus gland. -Response to abnormal cells. | back 13 B cells make antibodies. |
front 14 Plasma cells are activated by a(n) -B cell -T cell -antigen -APC -memory cell | back 14 -antigen |
front 15 The antibodies found in mucus, saliva, and tears are -IgD -IgM -IgG -IgA -IgE | back 15 IgA |
front 16 The antibodies found almost entirely and only on the surface of B cells (not secreted from them), and which always exist as monomers, are -IgA -IgE -IgG -IgD -IgM | back 16 -IgD |
front 17 The antibodies that typically bind to large parasites are -IgA -IgE -IgD -IgG -IgM | back 17 igE |
front 18 In addition to IgG, the antibodies that can fix complement are -IgM -IgD -IgA -IgE -None of the answers is correct | back 18 IgM |
front 19 Large antibodies that agglutinate antigens are -IgG -IgE -IgM -IgA -IgD | back 19 IgM |
front 20 The most abundant class of antibodies in serum is -IgM -IgD -IgG -IgE -IgA | back 20 -IgG |
front 21 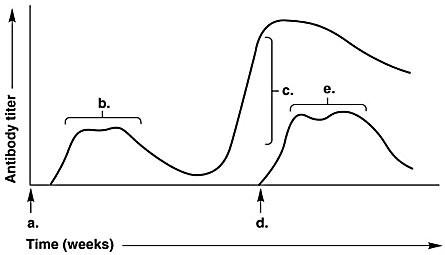 In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the patient's secondary response to a repeated exposure with the identical antigen? -a -b -c -d -e | back 21 -c |
front 22  In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the highest antibody titer during the patient's response to a second and distinct/different antigen? -a -b -c -d -e | back 22 e |
front 23  In Figure 17.1, the arrow at time (d) indicates -exposure to a new antigen -the secondary response -the time of exposure to the same antigen as at time (a) -the T-cell response -the primary response | back 23 exposure to a new antigen |
front 24 Which of the following statements is FALSE? -The Fc region may attach to a host cell. -The variable region of a heavy chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen. -The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies. -The variable region of a light chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen. -All of the answers are correct. | back 24 The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies. |
front 25 Which of the following is the best definition of antigen? -a pathogen -something foreign in the body -a chemical that combines with antibodies -a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies -a protein that combines with antibodies | back 25 a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies |
front 26 Which of the following are NOT lymphocytes? -helper T cells -B cells -cytotoxic T cells -M cells -NK cells | back 26 -M cells |
front 27 The following events elicit an antibody response. What is the third step? -B cell is activated. -TH cell produces cytokines. -TH cell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II -Antigen-digest goes to surface of APC. -APC phagocytizes antigen. | back 27 TH cell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II |
front 28 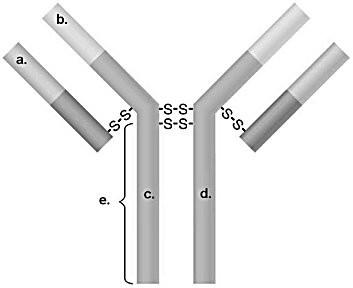 In Figure 17.2, which areas are similar for all IgG antibodies? -b and d -a and b -a and c -c and d -b and c | back 28 -c and d |
front 29  In Figure 17.2, which areas are different for all IgM antibodies? -a and b -b and c -a and c -c and d | back 29 a and b |
front 30  In Figure 17.2, which areas represent antigen-binding sites? -a and c -b and d -b and c -a and b -c and d | back 30 -a and b |
front 31  In Figure 17.2, what portion will typically attach to a host cell? -a and c -e -b -b and c -a and d | back 31 e |
front 32 Which of the following bacterial components would most likely result in B cell stimulation by T-independent antigens? -capsule -plasmid -flagellum -ribosome -pili | back 32 capsule |
front 33 The presence of which of the following indicates a current infection rather than a previous infection or vaccination? -IgA -IgE -IgM -IgG | back 33 -IgM |
front 34 Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells? -B cells -dendritic cells -CTL -TH -Treg | back 34 CTL |
front 35 The following events occur in cellular immunity, leading to a response from TH cells. What is the third step? -Antibodies are produced. -Dendritic cell takes up antigen. -Antigen enters M cell. -TH cells proliferate -TH cells produce cytokines | back 35 -TH cells proliferate |
front 36 Cytokines released by TH1 cells -convert TH1 cells to TH2 cells. -convert TH2 cells to TH1 cells. -directly kill parasites. -convert B cells to T cells. -activate CD8+ cells to CTLs | back 36 activate CD8+ cells to CTLs. |
front 37 Which one of the following causes transmembrane channels in target cells? -perforin -hapten -granzymes -IL-2 -IL-1 | back 37 perforin |
front 38 At a minimum, the human immune system is capable of recognizing approximately how many different antigens? -10^5 -10^25 -10^20 -10^15 | back 38 10^15 |
front 39 Thymic selection -activates B cells. -destroys B cells that make antibodies against self. -destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC -destroys CD4+ cells that attack self. -destroys MHC molecules. | back 39 destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC. |
front 40 Which of the following statements about natural killer cells is FALSE? -They destroy tumor cells. -They destroy cells lacking MHC I. -They destroy virus-infected cells. -They are stimulated by an antigen -None of the answers are correct; all of these statements are true | back 40 They are stimulated by an antigen |
front 41 An antibody's Fc region can be bound by -macrophages -B cells -antibodies -CTLs -T helper cells | back 41 macrophages |
front 42 A Treg cell deficiency could result in -transplant rejection. -increased number of viral infections. -increased number of bacterial infections. -increased severity of bacterial infections. -autoimmunity | back 42 autoimmunity. |
front 43 ADCC is a process that is most effective in destroying -eukaryotic pathogens -extracellular viruses -prions -bacterial pathogens -bacterial toxins | back 43 eukaryotic pathogens |
front 44 IL-2, produced by TH cells, -activates TC cells to CTLs -causes phagocytosis. -stimulates TH cell maturation. -activates macrophages. -activates antigen-presenting cells. | back 44 stimulates TH cell maturation. |
front 45 NK cells do all of the following EXCEPT -kill cells not expressing MHCI. -comprise 10-15% of circulating lymphocytes. -bind to Fc regions of bound antibodies. -become activated by TH-2 cells. -participate in antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity. | back 45 become activated by TH-2 cells. |
front 46 Which terms regarding components of adaptive immunity are mismatched? -TH-17 cells - recruit neutrophils. -Dendritic cells- Langerhans cell. -TH cells - MHCI interaction. -M cell - microfolds. -activated macrophage - membrane ruffling. | back 46 TH cells - MHCI interaction. |
front 47 Which of the following statements about cytokines is FALSE? -They are chemical communication between cells. -Some have multiple functions. -They are soluble proteins or glycoproteins. -They are produced by immune cells in response to a stimulus. -There are 10 types. | back 47 There are 10 types |
front 48 A cell undergoing apoptosis -will likely damage nearby cells. -bursts and releases intracellular contents. -was necessarily bound by antibodies. -is employed as an infection-fighting mechanism. -is a malfunction of the immune system | back 48 is employed as an infection-fighting mechanism |
front 49 The importance of M cells concerns -presentation of epitopes in MHCII molecules. -ability to migrate along the intestinal tract. -having microvilli to facilitate antigen capture. -facilitation of contact between antigens in the intestinal tract and the immune system. | back 49 facilitation of contact between antigens in the intestinal tract and the immune system. |
front 50 Which of the following terms regarding roles of chemical messengers is mismatched? - interleukins - communication between white blood cells -hematopoetic cytokine - development of blood cells -interferons - interruption of viral infection -tumor necrosis factor - stimulate tumor metastasis -chemokines - stimulate chemotaxis | back 50 tumor necrosis factor - stimulate tumor metastasis |