Exam 1 questions
How many moles of NaOH are required to titrate 0.1 mol of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) to its equivalence point?
0.1 mol of NaOH
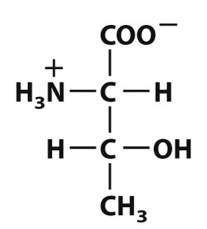
Which of the following defines the polar functional groups present in this amino-acid structure?
Amino group, carboxyl group, and hydroxyl group
Which of the following is a pyrimidine nucleotide component of RNA?
Uridine monophosphate
Two reactions are coupled, both in the forward direction.
One has ΔG°' = -25 kJ mol-1 and the other has ΔG°' = 15 kJ mol-1.
What is the net ΔG°' for the coupled process?
-10 kJ mol-1
Which statement best describes how water can participate in a buffer system?
Water can support both a weak acid and its conjugate base, due to its ability to dissociate into H⁺ and OH⁻.
All of the following statements regarding DNA sequencing are correct, EXCEPT:
A) DNA sequencing by dideoxy chain termination exploits the chemistry of DNA replication in living cells.
B)The products with an incorporated ddNTP are detected by fluorescence.
C) DNA polymerase will not catalyze nucleotide addition in the absence of an annealed primer.
D) The sequence of a DNA sample is deduced from the different fluorescent colors of the 5' phosphate on each primer strand.
E) Chain termination operates as a random process: not every polymerization step incorporates a ddNTP.
D) The sequence of a DNA sample is deduced from the different fluorescent colors of the 5' phosphate on each primer strand.
What causes the hydrophobic effect in aqueous solutions?
Water molecules forced to order in a structured "cage" around nonpolar molecules.
Why do ice and liquid water have different densities?
The arrangement of water molecules in ice forms an open lattice structure, making ice less dense.
Which element is central to organic molecules due to its ability to form four covalent bonds?
Carbon
The second law of thermodynamics states:
The entropy of the universe is constantly increasing.
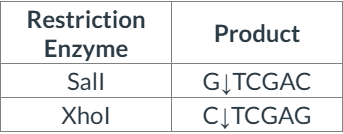
Consider the pair of restriction enzymes below and their products of restriction digestion.
Which of the following statements is correct?
The enzymes produce identical sticky ends, with 5' overhangs.
What is the equilibrium constant (Keq) for a reaction with the following parameters?
ΔG°' = -5.7 kJ mol-1
T = 25°C
10
For a biochemical reaction at 37°C, if the equilibrium constant (Keq) is 50, what is the ΔG°' for the reaction?
-10.1 kJ mol-1
All of the following are physical properties of water, EXCEPT:
A) Excellent solvent properties
B) High heat capacity
C) Less dense as a liquid
D) High boiling point
E) Cohesion and adhesion
C) Less dense as a liquid
What is the ΔG (Gibbs free energy) for a reaction with the following parameters?
ΔH = -40 kJ mol-1
ΔS = -0.1 kJ mol-1 K-1
T = 298 K
-10 kJ mol-1
What type of bond is formed between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the sugar in another nucleotide?
Phosphoester bond
Which nucleotide is the primary source of energy transfer reactions in cells?
ATP
Which of the following statements describes DNA synthesis?
The pyrophosphate product is hydrolyzed for energy, to drive the reaction forward.
Which type of bond is most commonly involved in maintaining the three-dimensional structure of nucleic acids?
Hydrogen bonds
Which of the following describes an amide bond?
Formed between a carboxyl group and an amino group
Which of the following best describes an endergonic reaction?
A) It releases free energy
B) It occurs spontaneously
C) It has a ΔG < 0
D) It involves the transfer of electrons
E) It requires an input of energy to proceed
It requires an input of energy to proceed
A newly sequenced genome consists of 31% thymine. Using Chargaff's rules for base pairing, what must be the GC content for this genome?
38%
Which functional group is present in alcohols and is responsible for their hydrophilic properties?
Hydroxyl group (-OH)
Given the following parameters, what is the pH of the buffer solution?
0.2 M acetic acid
0.2 M acetate.
pKa of acetic acid is 4.76
4.76
Which of the following scientists below recognized the helical structure of DNA based on X-ray diffraction images?
Francis Crick
Which buffer would be most effective at maintaining a pH of 7.4 if you have access to acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and phosphoric acid (pKa = 7.2)?
Phosphoric acid
What differentiates a nucleoside from a nucleotide?
The addition of one or more phosphate groups
Which of the following statements describes the structure of DNA?
A) Nature chose to replace the 2' OH with H for stability, but it could have been the 3' hydroxyl replaced with H, instead.
B) A 2' hydride and a methylated version of adenine's base-pair partner allow for greater stability of this storage form of nucleic acids.
C) The nucleotides from one strand are linked to the nucleotides of the other strand through phosphodiester bonds.
D) The hydrogen bonds in GC are shorter than in AT.
E) The enol tautomer and anti-conformation predominate in the double helix at pH 7.
B) A 2' hydride and a methylated version of adenine's base-pair partner allow for greater stability of this storage form of nucleic acids.
Which of the following makes “palindromic,” double-stranded DNA?
A) GATATC
B) TAGGTA
C) CATGTG
D) TTGGAA
E) GACCTC
A) GATATC
Which functional group serves as a hydrogen bond donor from adenine, when it is part of a base pair?
Amino (-NH2)
Which nucleotide contains a ribose sugar and adenine base?
ATP
Which of the following statements about entropy is true?
A) ΔS = 0 at 0 °C
B) Biological polymers have more entropy than their inorganic precursors.
C) Ice has a more positive entropy than liquid water.
D) A reaction with a negative entropy is endergonic.
E) Dialysis is driven by entropy.
Dialysis is driven by entropy.
All of the following are common nitrogenous base found in nucleotides, EXCEPT:
A) Cytosine
B) Adenine
C) Thymine
D) Uracil
E) Guanosine
Guanosine
Water molecules participate in hydrogen bonding with the following functional groups, EXCEPT:
A) amino groups
B) methylene groups
C) carboxyl groups
D) hydroxyl groups
E) All of these form hydrogen bonds with water
B) methylene groups
The standard free energy change (ΔG°') for the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi is -30.5 kJ/mol.
If 1 mole of ATP is hydrolyzed, what is the overall change in free energy?
-30.5 kJ
Using the convention for writing nucleic acid sequences, what is the sequence of DNA complementary to the sequence, below?
AGATCGGTATCAGGT
ACCTGATACCGATCT
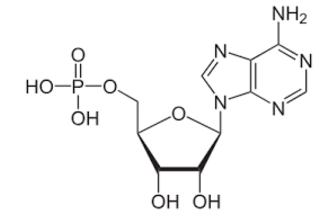
What is the correct name for the structure below?
Adenosine monophosphate
Thymine contains which functional group that participates as a hydrogen bond acceptor in DNA?
Carbonyl (C=O)
Given the parameters for the reaction below, solve for Q.
2E + F --> G
T = 37oC
ΔG°’ = 4.3 kJ mol-1
ΔG' = 23 kJ mol-1
1.4 x 103
Which of the following is true regarding the ionization of water?
Water has a very low degree of ionization, forming equal concentrations of H⁺ and OH⁻ ions at 10⁻⁷ M each.
All of the following are considered one of the four major classes of biomolecules, EXCEPT:
A) lipids
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) amino acids
E) proteins
D) amino acids
After chain termination, the sequencing products are separated by gel electrophoresis based on_____,
via migration from the______electrode to the______electrode.
length, negative, positive
Given a reaction with ΔG' = 15 kJ mol-1, what can be said about the reaction?
Non-spontaneous
In an exergonic reaction, the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) is
Negative
A buffer contains 0.1 M lactic acid (pKa = 3.86) and 0.05 M sodium lactate. What is the pH of the buffer?
3.56
What is the primary function of a restriction enzyme in DNA analysis?
To cleave double-stranded DNA at specific sequences
Identify the functional group(s), in the following chemical structures, that contribute to buffering capacity:
R-COOH
R-COO−
Both carboxyl group (−COOH) and carboxylate group (−COO−)
What type of ends do some restriction enzymes generate after cutting DNA?
Sticky ends
Which property of water allows it to dissolve a wide variety of solutes?
Its polar nature and ability to form hydrogen bonds
Due to 2, consecutive hydroxyls on the carbon backbone (vicinal diol), ______ is vulnerable to hydrolysis,
compared to its counterpart in DNA, ______, which has one of the vicinal hydroxyls removed.
The synthetically-designed ______ has both vicinal hydroxyls removed, resulting in chain termination, during DNA polymerization.
ribose, deoxyribose, dideoxyribose