MicroLab(2-Intro+nutrition)
What is a vegetative cell?
growing, and metabolically active form of a microorganism.
What is a spore?
An inactive, highly resistant form of a microorganism
What happens during sporulation?
A vegetative cell transforms into a spore, forming a thick protective coat around DNA.
What is The process where a spore transforms back into a vegetative cell
Germination
What is The process where a vegetative cell transforms into a spore
Sporulation
What is sterilization?
The complete removal of all microbes, including endospores
how hot is dry heat sterilization?
ovens at 150-180°C
how long is dry heat sterilization?
1-3 hours
how hot is Moist heat sterilization?
121°C
how long is Moist heat sterilization?
15-20 minutes.
How Wide is Filtration for for bacterial removal?
0.22 μm filters
How Wide is Filtration for mycoplasma removal.
0.1 μm
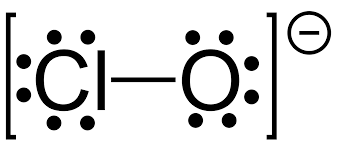
What is inorganic Hypochlorite(bleach)` used for
viruses and
bacteria.
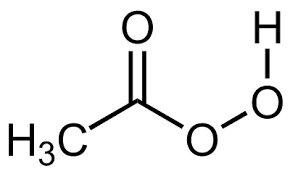
What is paracetic acid used for?
spores, bacteria, and viruses
What is Alcohol (70%) used for?
vegetative bacteria and viruses.
What are antiseptics?
Used on living tissue to inhibit or destroy microbes, usually not effective against spores
What is most effective for biofilms
anti-biofilms

What is agar extracted from?
Seaweed (more specifically agarophytes)
What temperature does agar liquefies
100C
How much agar does a semisolid medium contain
less than 1% agar
How much agar does a solid medium contain
1.5-1.8% agar
What temperature does agar Solidifies
40°C
What is the Cultivation temperature for agar
37.5C
What are environmental factors for optimal growth
1. pH
2. Temperature
3. Osmotic pressure
4. Gaseous requirements
What Does Test tubes contain
broth or agar (solid or Liquid medium)
What materials are wire loops and needles made from?

Inert metals like Nichrome or platinum.
How are wire loops and needles sterilized?
By incineration in the blue part of a Bunsen burner flame.
What materials are used for liquid transfers in microbiology?
Pipettes made of glass or plastic.
What is the purpose of micropipettes?
Transferring volumes of liquid less than 1 mL
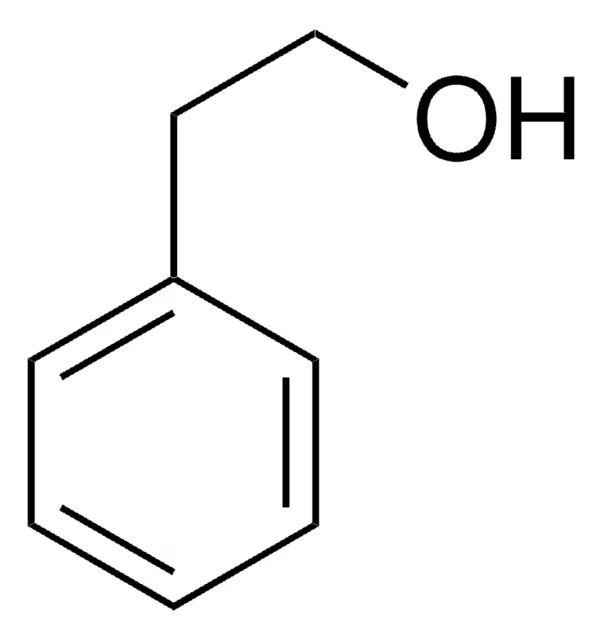
What is Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar used for?
Isolating most gram-positive organisms + Partially inhibits gram-Negative
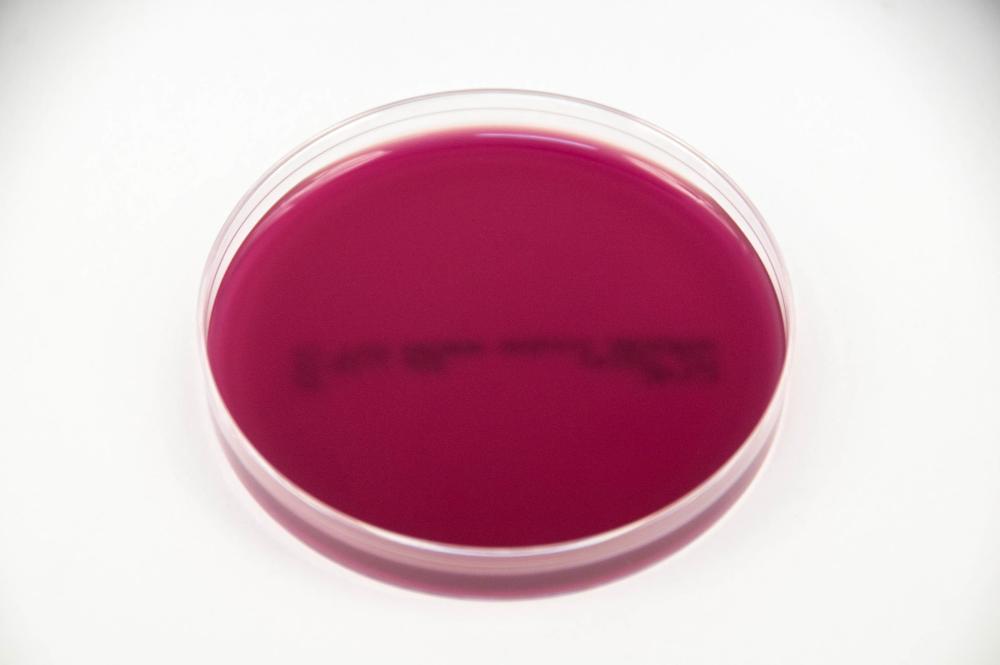
What type of microorganisms does Crystal Violet Agar select for?
Most gram-negative microorganisms + Inhibits Most gram-positive organisms
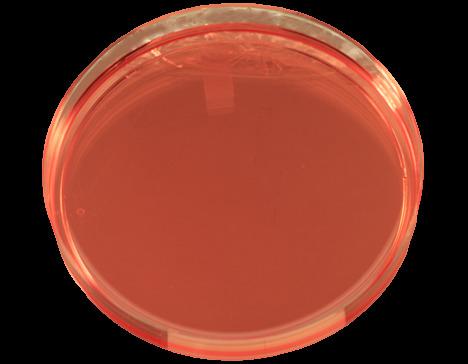
What type of organisms does 7.5% Sodium Chloride Agar inhibit?
Most organisms except halophilic(salt loving) microorganisms.
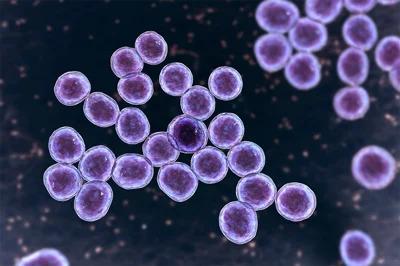
What Selective Media is best to detect Staphylococcus species
7.5% Sodium Chloride Agar
What does Mannitol salt agar contain?
7.5 sodium chloride agar+ mannitol(fermentable alcahol sugar)+ pH indicator(Phenol red)
Name a fastidious organism?
Streptococcus
On what bases does Blood agar differentiate microbes
Hemolysis(How red blood cells rapture and secrete their contents in the surroundings fluid)
What is the general range of temperature bacterias can grow at?
-5C to 80C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of psychrophiles?
-5 to 20C
What is generally the range of temperature for the growing of mesophiles
20-45C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of plant saprophytes
20-30C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of warm blooded hosts
35-40C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of Thermophiles
>35C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of facultative thermophiles
Can grow at 37C, they optimally grow within in the range of 45-60C
What is the range of temperature for the growing of obligate thermophiles
They can only grow>50C, with an optimal growth temperature of 60C