Physiology(lab)
What are the factors that increase the rist of diabetes
- Above 45
- Fat and not exercise
- High blood pressure
- High triglycerides
- Low HDL(High density lipoprotein)
- Being insulin resistant
- If diabetes runs in the family
What does hypoglycemia result in?
Seizures or coma
What does Hyperglycemia result in?
Ketoacidosis, neurophathy(nerve damage), heart, kidney and eye disease
Whats ketoacidosis
A condition most common amongst Diabetic I, its when your body starts using only fat for fuel
List blood sugar tests
- Glucometer
- FBS(Fasting blood sugar)
- Hemoglobin A1C test(tracks levels of glucose for 90 days)
- CGM(continues glucose monitors)(sticks beneath the skin, not so good bc its not sampling from the blood)
What are the ranges of blood sugar while using glucometer
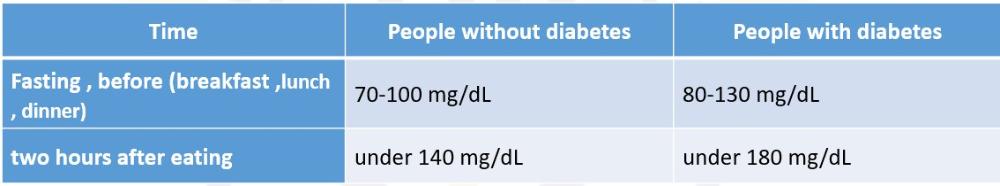
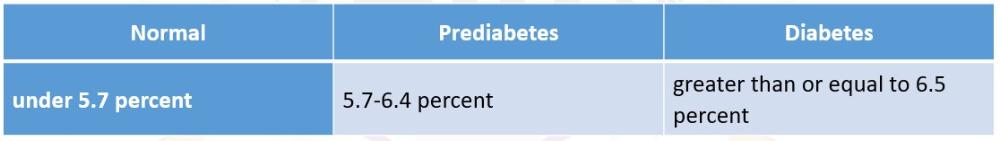
What are the ranges of blood sugar while using Hemoglobin A1C test
List requirements for injection
- Syringe & Needle
- The medication
- Gloves
- Band-Aid
- Alcohol for cleaning
What to do before injection
- Clean the table where u put the syringe
- Check if you have the right medication, dosage and expiration date
- Remove the air bubles in the barell of the syringe before injection
What are the types of injections
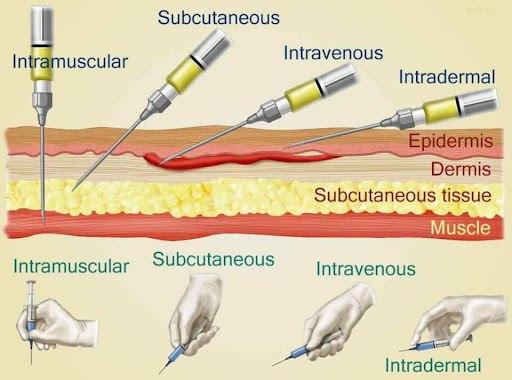
Common(the pic besides intradermal)
Uncommon:
- Intradermal
- Intra-artucular(joints)
- Intraspinal
- Intrapleural
For what we use subcutaneous injection
Morphine, insulin and vaccines
For what we use Intramuscular injection
and Sex Hormones(Testosterone, estradiol(made in the ovaries), Vitamin B12 and inactive or dead influenza virus
For what we use Intravenous injection
- Fluids to hydrate the body when the patient can't drink it
- electrolyte(like Ma, Na and ions) to balance the body when it has too much of one
- blood especially after a lot of blood loss
- Medication
For what we use Intradermal injection
to see if the person has tuberculosis, and other allergy diagnoses medication because you can see the reaction of the patient to the drug and for local anesthesia
Which route is the slowest in term of absorption?
intradermal
Where to apply subcutaneous injection
the anterior part of the thigh, arms and in the scapula part of the back and abdomen
Where to apply intramuscular injection
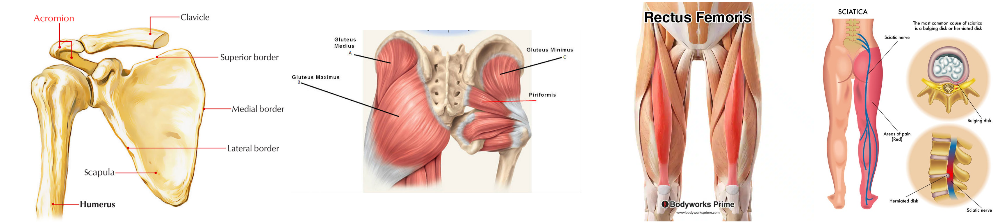
2 fingers below the acromion process, gluteus Medius just avoid the sciatic nerve and the rectus femoris
Where to apply intravenous injection
any prominent vein is possible