Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Physiology(lab)
front 1 What are the factors that increase the rist of diabetes | back 1
|
front 2 What does hypoglycemia result in? | back 2 Seizures or coma |
front 3 What does Hyperglycemia result in? | back 3 Ketoacidosis, neurophathy(nerve damage), heart, kidney and eye disease |
front 4 Whats ketoacidosis | back 4 A condition most common amongst Diabetic I, its when your body starts using only fat for fuel |
front 5 List blood sugar tests | back 5
|
front 6 What are the ranges of blood sugar while using glucometer | back 6 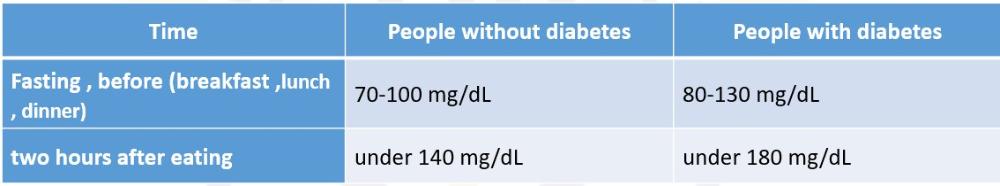 |
front 7 What are the ranges of blood sugar while using Hemoglobin A1C test | back 7 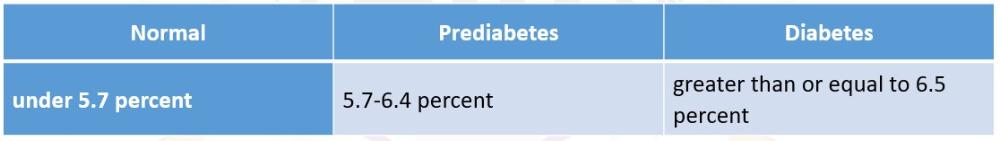 |
front 8 List requirements for injection | back 8
|
front 9 What to do before injection | back 9
|
front 10 What are the types of injections | back 10 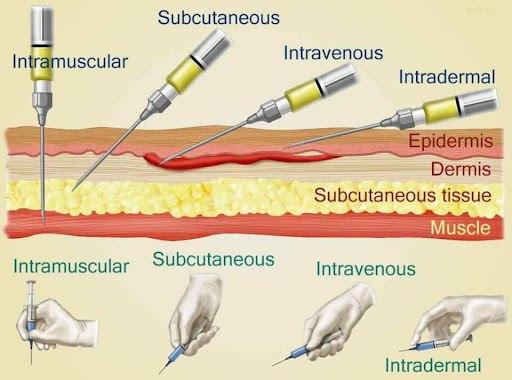 Common(the pic besides intradermal) Uncommon:
|
front 11 For what we use subcutaneous injection | back 11 Morphine, insulin and vaccines |
front 12 For what we use Intramuscular injection | back 12  and Sex Hormones(Testosterone, estradiol(made in the ovaries), Vitamin B12 and inactive or dead influenza virus |
front 13 For what we use Intravenous injection | back 13
|
front 14 For what we use Intradermal injection | back 14 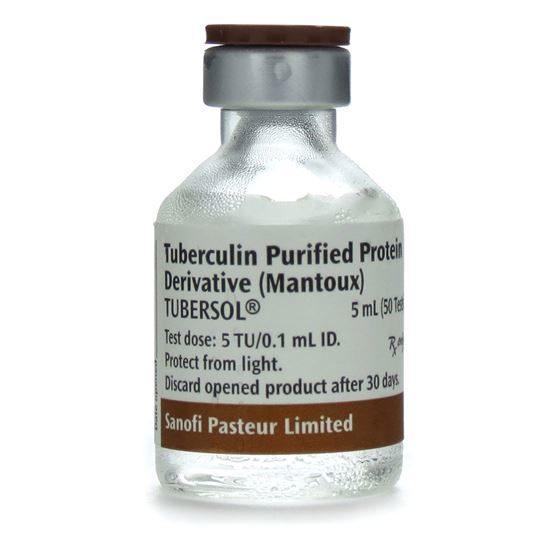 to see if the person has tuberculosis, and other allergy diagnoses medication because you can see the reaction of the patient to the drug and for local anesthesia |
front 15 Which route is the slowest in term of absorption? | back 15 intradermal |
front 16 Where to apply subcutaneous injection | back 16 the anterior part of the thigh, arms and in the scapula part of the back and abdomen |
front 17 Where to apply intramuscular injection | back 17 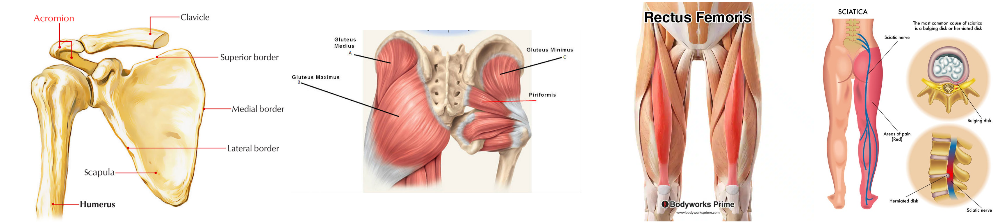 2 fingers below the acromion process, gluteus Medius just avoid the sciatic nerve and the rectus femoris |
front 18 Where to apply intravenous injection | back 18 any prominent vein is possible |