Renal Disorders
Roles of the Kidney
- Blood filtration
- Remove wastes, maintain electrolyte and acid/base balance
- Regulation of blood volume and blood pressure
- Activation of vitamin D
- Production of erythropoietin
Fluid Disctribution
-
Intracellular fluid
compartment
- the fluid contained within the cells
- makes up 2/3 of the total body water in adults
-
Extracellular fluid
compartment
- the fluid contained in the interstitial (tissue) spaces and plasma (vascular) compartment
- makes up 1/3 of the total body water in adults
Fluid & Electrolytes
HYPERNATREMIA
Serum level?
Causes?
Sodium Function
- Normal level is 135 to 145 mEq/L.
- Regulates extracellular fluid volume and osmolarity
- Serum sodium >145 mEq/L
- Related to sodium gain or water loss
- Causes:
-
Hypovolemic
Natremia
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- inadequate intake
- diuretics
- renal disease
- diarrhea
- burns
- diabetes insipidus nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
(lack of ADH or inadequate
renal response to ADH).
-
loss of body sodium accompanied by a relatively greater loss of
body water.
Causes include use of loop diuretics, osmotic diuresis - loss of free water with a near normal body sodium concentration. Causes include inadequate water intake; excessive sweating (sweat is hypotonic); fever with hyperventilation and increased water loss from lungs; burns; vomiting; diarrhea; and central or nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- Water movement from the ICF to the ECF
- Intracellular dehydration
Acid/Base Imbalance
Ions involved?
- Acid-base balance is mainly concerned with two ions
- Hydrogen (H+)
- Bicarbonate (HCO3−)
- Alterations of hydrogen and bicarbonate concentrations in body fluids are common in disease processes
Acid Base Balance: Normal pH
Lungs and Kidney Role?
Acidosis what pH, what is increased?
Alkalosis what pH, what is decreased?
- Normal arterial blood pH
- 7.35–7.45
- Obtained by arterial blood gas (ABG)
- Lungs: eliminate CO2 or retain CO2
- Kidneys: eliminate H+, reabsorb/generate HCO3
- Acidosis
- pH is less than 7.35.
- Systemic increase in H+ concentration
- Alkalosis
- pH is greater than 7.45
- Systemic decrease in H+ concentration or excess of base
Respiratory Acidosis
pH?
Causes?
- pH is below 7.35
-
CO2 elevates from
hypercapnia-Carbon dioxide excess in the
blood
-
Hypoventilation-
retention of CO2
- Depression of respiratory center (Trauma, Sedatives), Disorders of chest wall (Kyphosis, Flail chest), Disease of neuromuscular (MG, Guillen Burre)
- Edema, pulmonary edema
- Pneumonitis
- Respiratory center of brain damage (stroke, trauma), Respiratory Muscle Paralysis (MG)
- E mphysema overinflated alveoli
- Spasm of bronchial tubules (asthma)
- Sac of elasticity damaged (COPD)
Respiratory Acidosis S/S
Respiratory Acidosis Treatment
-
Manifestations:
- Headache
- Restlessness
- Blurred vision
- Apprehension
- Lethargy
- Muscle twitching
- Tremors, convulsions, coma
*Neurologic symptoms are caused by a decrease in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid and vasodilation because CO2 readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
-
Treatment
- Restore adequate ventilation; may need mechanical ventilation
Respiratory Alkalosis
Causes?
*Deep and rapid respirations (tachypnea) are primary symptoms of the disorders that cause respiratory alkalosis BLOW OFF CO2
- Causes
- High altitudes (bc breathing faster to catch breath)
- Hypermetabolic
states
- fever, anemia, and thyrotoxicosis (high levels of circulating thyroid hormones)
- Early salicylate intoxication
- Anxiety or panic disorder
Respiratory Alkalosis
pH?
S/S?
Treatment?
- Occurs with hyperventilation and decreased plasma CO2 (hypocapnia)
- pH above 7.45
- CO2 is decreased less than 38 mmH
-
Manifestations
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Tingling of extremities (paresthesias)
- Convulsions, and coma with signs of hypocalcemia
*Respiratory alkalosis is irritating to the central and peripheral nervous systems.
-
Treatment:
- Paper bag: rebreathing from a paper bag, increases the concentration carbon dioxide and reverses the respiratory alkalosis
- treat hypoxemia and hypermetabolic states
Metabolic Acidosis
pH?
Causes?
Compensation?
- Noncarbonic acids increase or bicarbonate (base) is lost from ECF or cannot be regenerated by the kidney
- pH drops below 7.35
- HCO3− drops: less than 24 mEq/L
- Causes:
- DKA- (excess production of keto acids from lack of insulin)
- Lactic acidosis
- Diarrhea
- Kidney injury- (failure to excrete acid)
-
Compensation:
- Hyperventilation and renal excretion of excess acid
Metabolic Acidosis
S/S?
Treatment?
- Manifestations:
- Headache
- Lethargy
- Kussmaul respirations
- Treatment:
- Treat the underlying cause(s)
- Base administration (sodium bicarb)
- Insulin in DKA
Metabolic Alkalosis
What is elevated?
Causes?
- Bicarbonate concentration is increased, usually from excessive
loss of metabolic acids (Cl −)
- pH is elevated
- HCO3− is elevated
- Causes
- Excessive bicarbonate intake
-
hydrogen and chloride depletion
- Prolonged vomiting
- Gastric suctioning
- Hyperaldosteronism with hypokalemia
- Diuretic therapy
Metabolic Acidosis
S/S? **think of dec. Ca**
Tx?
-
Manifestations:
- Weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Hyperactive reflexes with signs of hypocalcemia
Because alkalosis increases binding of Ca++ to plasma proteins (albumin), ionized calcium concentration decreases, causing excitable cells to become hypopolarized, which initiates an action potential more easily.
-
Treatment
- Sodium chloride
- Potassium
- Chloride IV (chloride replaces HCO3−)
Acute Renal Injury
Pre renal?
Intra renal?
Post renal?

- Prerenal Failure
- Any cause of marked decrease in renal blood flow
- Intrarenal Failure
- Damage to the structures of the kidneys
- Postrenal Failure
- Obstruction of urine outflow from kidney
Pre renal Injury Causes
Causes
- Hypovolemia
- dehydration
- loss of GI tract fluids via vomiting/diarrhea
- hemorrhage
- loss of fluid via burn injury
- dehydration
- Decreased vascular filling
- septic shock
- anaphylactic shock
- Heart failure and cardiogenic shock
- Decreased renal perfusion
- sepsis
- drugs
- diagnostic agents/contrast
- vasoactive mediators
Intrarenal
Glomerulonephritis
Patho?
- Pathophysiology
- Inflammation of glomerulus
- Antibodies produced against the organism that cross-react with the glomerular endothelial cells
- Recruitment and activation of immune cells and mediators
- Can be part of lupus
- Can be caused by infections (strep throat, HIV, Hep C, endocarditis)
- Most often due to Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcus organism
Patho
*(1) deposition of circulating antigen-antibody immune complexes into the glomerulus (type III hypersensitivity)
*(2) reaction of antibodies in situ against planted antigens
within the glomerulus (type II hypersensitivity,
cytotoxic);
*(3) action of antibodies directed against the
glomerular capillary wall
(antiglomerular basement membrane
antibodies), least common and most severe form of immune injury (type
II hypersensitivity)
*(4) cell-mediated immune injury (type IV hypersensitivity)
*Nonimmune glomerular injury is related to ischemia,
metabolic
disorders
Glumerolonephritis S/S
- Clinical manifestations
- Hematuria with red blood cell casts
- Smoky, brown-tinged urine
- Proteinuria exceeding 3–5 g/day with albumin
- Low serum albumin
- Edema
- Severe or
progressive glomerular disease: Eventual oliguria
- Oliguria: Urine output <30 mL/hour
Glomerulonephritis Treatment
- Treatment
- Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressants
- Diuretics
Antibiotic therapy is essential for the management of underlying infections
Corticosteroids decrease antibody synthesis and suppress inflammatory responses.
Suppress the immune response in corticosteroid-resistant cases.
Post Renal
Renal Calculi
What is it?
Who is at risk?
- Masses of crystals, protein, or mineral salts form in the urinary tract
- Obstruct the urinary tract
- Risk factors
- Male
- Most develop before 50 years of age
- Inadequate fluid intake: Most prevalent bc increase osmolality
Pathogenesis of Kidney stones:
1.
Supersaturation (i.e. too much) of stone components in the
urine (e.g. calcium salts, magnesium ammonium,
phosphate, uric acid, or cysteine) And
2. A nidus (i.e. center area) that facilitates crystal
aggregation

Compositions of Renal Calculi

- Composition of mineral salts
- Calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate: 70% to 80%
- Struvite (magnesium, ammonium, phosphate): 1% to 5%
- Uric acid: 5% to 10%
- Staghorn calculi
- Are large kidney stone
- Fills the minor and major renal calyces
-
Non-Staghorn
calculi
- Variable size
- Located in calyces, renal pelvis, different sites of ureter
Post Renal
Calculi S/S?
Treatment?
- Clinical manifestation
- Renal colic (pain)
- Treatment
- Managing pain
- Reducing the concentration of stone-forming substances- increasing urine flow rate with high fluid intake
- Adjusting pH of urine - make it more alkaline with potassium citrate administration
- Decreasing amount of stone-forming substances
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (procedure used to remove kidney stones from the body when they can't pass on their own)
- Ureteroscopy or ultrasonic or laser lithotripsy to fragment stones for excretion
UTI
What is it?
Classifications of UTI
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Inflammation of the urinary epithelium caused by bacteria from gut flora
- Retrograde movement of bacteria into the urethra, bladder, ureter, kidney
- Classification: Location or complicating factors
- Complicated UTI vs. Uncomplicated UTI
- Uncomplicated UTIs are generally mild and without complications
- complicated(febrile) UTI develops when there is an abnormality in the urinary system or a health problem that compromises host defenses
- Recurrent UTI (>2 in 6 months, >3 in 12 months)
- Cystitis: Bladder inflammation
UTI Patho

-
Most
common pathogens
-
Escherichia coli
-
Staphylococcus
saprophyticus
-
Escherichia coli
- Women have UTI more commonly than men because the urethra is shorter in women
- Contamination of the urine occurs by way of retrograde movement of the microorganism into the urethra (causing urethritis) → ascends to the bladder (causing cystitis) → ascends to the ureter(s) → ascends to the kidney(s) (causing pyelonephritis)
Cystitis
What is it?
S/S?
Diagnostic Test?
Treatment?

- Cystitis
- inflammation of the bladder and the most common site of UTI
- Acute or chronic
-
Clinical
manifestations
- Asymptomatic OR
- Frequency, Dysuria, Urgency, Suprapubic pain
- Older adults with cystitis may be asymptomatic or demonstrate confusion or vague abdominal discomfort.
- Older adults with recurrent UTI and other concurrent illness have a higher risk of morbidity and mortality
*The inflammatory edema in the bladder wall stimulates discharge of stretch receptors, initiating symptoms of bladder fullness with small volumes of urine and producing the urgency and frequency of urination associated with cystitis.
** Hematuria, cloudy and foul-smelling urine, and flank pain are more serious symptoms
-
Diagnostic
Test
- Urine dipstick in office or microscopic urinalysis in lab
- Urine culture is + with specific microorganisms with counts of 10,000/mL or more
*Urine dipstick that is positive for leukocyte esterase or nitrite reductase can be used for the diagnosis of uncomplicated UTI.
-
Treatment
- Antimicrobial therapy
Intersitial Cystitis
unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort) perceived to
be
related to the urinary bladder associated with
lower urinary tract
symptoms of more than 6 weeks'
duration in the absence of infection
or other
identifiable causes.
- Autoimmune reaction causes inflammatory response
- Symptoms of cystitis for longer than 6 weeks’ duration but with negative urine cultures and no other known cause
- Treatment: FOR SYMPTOM RELIEF
- Oral and Intravesical therapies
- Sacral nerve stimulation
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox)
- Surgery

Pyelonephritis
What is it?
S/S?
Diagnostic Test?

- Acute pyelonephritis
- Acute infection of the ureter, renal pelvis, and/or kidney interstitium
Patho: Microorganisms usually associated with acute pyelonephritis include E. coli, Proteus, and Pseudomonas. T he inflammatory process is usually focal and irregular, primarily affecting the pelvis, calyces, and medulla. The infection causes medullary infiltration of neutrophils with tubulointerstitial inflammation, renal edema, and purulent urine.
-
Manifestations F.F.U.C
- Flank/Groin pain
- Fever/Chills
- UTI symptoms
- Costovertebral tenderness/Chills
- Older adults may have nonspecific symptoms, such as low-grade fever and malaise
- Diagnostic Test
- White blood cell casts indicate pyelonephritis
-
Treatment
- Antibiotic administration
Chronic Kidney Disease
- Progressive loss of renal function associated with systemic diseases
- Guidelines for staging CKD using GFR and albuminuria estimates
- Clinical manifestations: Do not occur until renal function declines to less than 25% of normal
CKD Treatment
- Treatment
- Management of protein intake
- Supplemental Vitamin D
- Maintenance of sodium and fluid
- Restriction of potassium
- Maintenance of adequate caloric intake
- Monitor for anemia
Nephrotic Syndrome
What is it?
S/S?
Treatment?
Nephrotic syndrome is:
- the excretion of 3.5 g or more of protein in the urine per day, is characteristic of glomerular injury &
- occurs when filtration of proteins exceeds tubular reabsorption
**Nephrotic syndrome occurs due to damage to the glomerular basement membrane and podocytes which causes increased permeability of the glomerulus and loss of plasma proteins in the urine
- Clinical manifestations
- Heavy proteinuria (>3.5 grams/day)
- Hypoalbuminemia (<3 grams/dL)
- Severe edema
- Hyperlipidemia
- Fatty casts in urine
- Treatment
- Normal-protein (1 g/kg body weight/day)
- Low-fat diet
- Salt restriction
- Diuretics, glucocorticoids, anticoagulants
- Immunosuppressive drugs and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors used when steroid-resistant
- ARBs
PEDIATRIC RENAL DISORDERS:
- Hypospadias
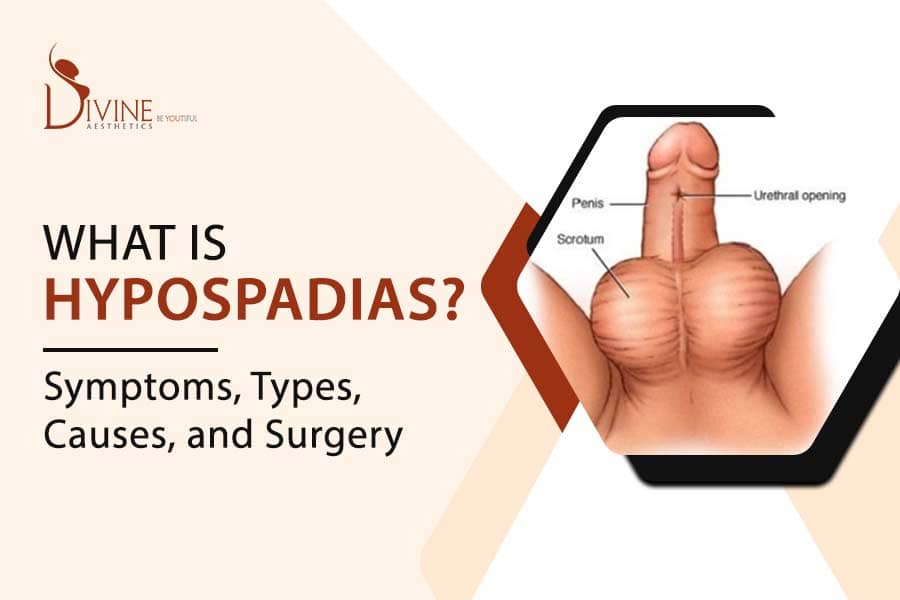
- Hypospadias
- Urethral meatus is located on the ventral side or undersurface of the penis
-
Treatment:
- Surgery
PEDIATRIC RENAL DISORDERS:
- Epispadias

- Epispadias
- Males: Urethral opening is on the dorsal surface of the penis.
- Females: Cleft along the ventral urethra usually extends to the bladder neck
- Twice as many boys are affected as girls
- Surgery may be needed
- Exstrophy of the bladder
What is it?
Where is the bladder located?
Ideally when should the defect get fixed?
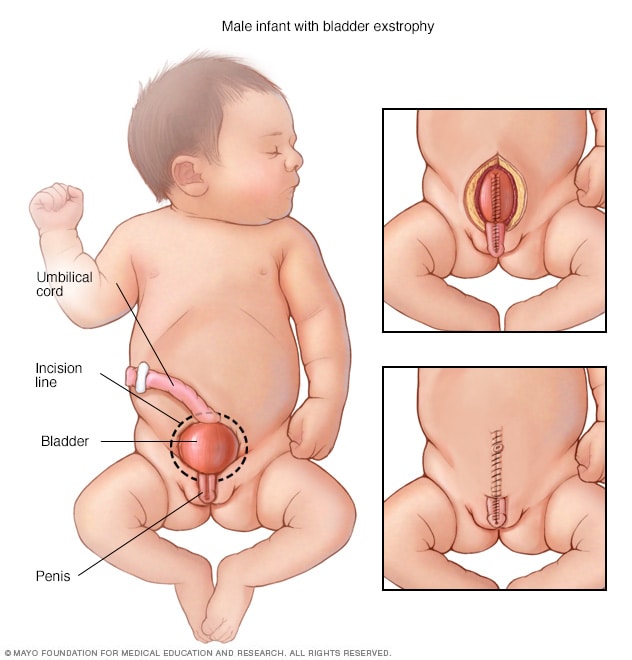
- Exstrophy of the bladder
- Herniation of the bladder through the abdominal wall occurs with a failure of the abdominal muscles, pelvic ring, and pelvic floor musculature to fuse in the midline
- Ideally, the bladder and pubic defect should be closed before the infant is 72 hours old
- Surgical reconstruction is usually performed within the first year
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN
- Group of symptoms characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, and edema
- Caused by an increased permeability of the glomerular capillary wall, which leads to massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia
- Primary (idiopathic) vs. secondary
- Secondary causes can include lupus, IgA vasculitis, malignancy (lymphoma and leukemia), and infections (hepatitis, HIV, and malaria)
**Hypoalbuminemia leads to a deficiency in the carrier protein for the transport of fatty acids, and they remain elevated in the serum.
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN
- Clinical manifestations
- Periorbital edema (first sign)
- Edema of intestinal mucosa (Edema of the intestinal mucosa may cause diarrhea, anorexia, and poor absorption)
- Signs and symptoms of malnourishment (Edema often masks the malnutrition) caused by malabsorption and protein loss)
- Irritability, fatigue, lethargy
- Increased susceptibility to infection
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN
- Treatment
- Prevent or treat infection
- Glucocorticosteroids (prednisone)
- Low-sodium, well-balanced diet
- Provide skin care
- If edema becomes problematic: Administer diuretic agents (furosemide, metolazone)
- ACE inhibitors
- Immunosuppressive agents
WILMS TUMOR
- Is an embryonal cancerous tumor of the kidney
- Most common between 1 and 5 years of age
- Is also called nephroblastoma
- Is the most common solid tumor of childhood
- Clinical Manifestations
- Enlarging asymptomatic abdominal mass, vague abdominal pain, hematuria, anemia, and fever
WILMS TUMOR
- Treatment
- Surgical
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy for higher stages of disease and metastasis
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN
- Involuntary passage of urine by a child who is beyond the age when voluntary bladder control should have been acquired
- 5 years old
- Enuresis: Bedwetting at night
- Functional incontinence
- Urinary incontinence in which no structural or neurologic abnormality can be identified
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN
- Enuresis theories
- Organic causes
- Maturational lag
- Genetic factors
- Sleep patterns
- Psychosocial theories
- Clinical manifestations
- Primary enuresis: Child has never been continent
- Secondary enuresis: Child was continent 6 months after toilet training but becomes incontinent again
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN
- Treatment
- Begins with education
- Treatment of Daytime incontinence includes:
- Behavioral therapy, including timed voiding; fluid management
- Treatment of constipation, UTIs, and other coexisting conditions, if present
- Medications (anticholinergic, α-blocker)
- Enuresis treatment also includes:
- Enuresis alarms
- Medication administration: Desmopressin