Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Renal Disorders
front 1 Roles of the Kidney | back 1
|
front 2 Fluid Disctribution | back 2
|
front 3 Fluid & Electrolytes HYPERNATREMIA Serum level? Causes? Sodium Function
| back 3
|
front 4 Acid/Base Imbalance Ions involved? | back 4
|
front 5 Acid Base Balance: Normal pH Lungs and Kidney Role? Acidosis what pH, what is increased? Alkalosis what pH, what is decreased? | back 5
|
front 6 Respiratory Acidosis pH? Causes? | back 6
|
front 7 Respiratory Acidosis S/S Respiratory Acidosis Treatment | back 7
*Neurologic symptoms are caused by a decrease in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid and vasodilation because CO2 readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
|
front 8 Respiratory Alkalosis Causes? | back 8 *Deep and rapid respirations (tachypnea) are primary symptoms of the disorders that cause respiratory alkalosis BLOW OFF CO2
|
front 9 Respiratory Alkalosis pH? S/S? Treatment? | back 9
*Respiratory alkalosis is irritating to the central and peripheral nervous systems.
|
front 10 Metabolic Acidosis pH? Causes? Compensation? | back 10
|
front 11 Metabolic Acidosis S/S? Treatment? | back 11
|
front 12 Metabolic Alkalosis What is elevated? Causes? | back 12
|
front 13 Metabolic Acidosis S/S? **think of dec. Ca** Tx? | back 13
Because alkalosis increases binding of Ca++ to plasma proteins (albumin), ionized calcium concentration decreases, causing excitable cells to become hypopolarized, which initiates an action potential more easily.
|
front 14 Acute Renal Injury Pre renal? Intra renal? Post renal? | back 14 
|
front 15 Pre renal Injury Causes | back 15 Causes
|
front 16 Intrarenal Glomerulonephritis Patho? | back 16
Patho *(1) deposition of circulating antigen-antibody immune complexes into the glomerulus (type III hypersensitivity) *(2) reaction of antibodies in situ against planted antigens
within the glomerulus (type II hypersensitivity,
cytotoxic); *(4) cell-mediated immune injury (type IV hypersensitivity)
*Nonimmune glomerular injury is related to ischemia,
metabolic |
front 17 Glumerolonephritis S/S | back 17
|
front 18 Glomerulonephritis Treatment | back 18
Antibiotic therapy is essential for the management of underlying infections Corticosteroids decrease antibody synthesis and suppress inflammatory responses. Suppress the immune response in corticosteroid-resistant cases. |
front 19 Post Renal Renal Calculi What is it? Who is at risk? | back 19
Pathogenesis of Kidney stones: |
front 20  Compositions of Renal Calculi | back 20 
|
front 21 Post Renal Calculi S/S? Treatment? | back 21
|
front 22 UTI What is it? Classifications of UTI | back 22
|
front 23 UTI Patho | back 23 
|
front 24 Cystitis What is it? S/S? Diagnostic Test? Treatment? | back 24 
*The inflammatory edema in the bladder wall stimulates discharge of stretch receptors, initiating symptoms of bladder fullness with small volumes of urine and producing the urgency and frequency of urination associated with cystitis. ** Hematuria, cloudy and foul-smelling urine, and flank pain are more serious symptoms
*Urine dipstick that is positive for leukocyte esterase or nitrite reductase can be used for the diagnosis of uncomplicated UTI.
|
front 25 Intersitial Cystitis | back 25
unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort) perceived to
be
|
front 26  Pyelonephritis What is it? S/S? Diagnostic Test? | back 26 
Patho: Microorganisms usually associated with acute pyelonephritis include E. coli, Proteus, and Pseudomonas. T he inflammatory process is usually focal and irregular, primarily affecting the pelvis, calyces, and medulla. The infection causes medullary infiltration of neutrophils with tubulointerstitial inflammation, renal edema, and purulent urine.
|
front 27 Chronic Kidney Disease | back 27
|
front 28 CKD Treatment | back 28
|
front 29 Nephrotic Syndrome What is it? S/S? Treatment? | back 29 Nephrotic syndrome is:
**Nephrotic syndrome occurs due to damage to the glomerular basement membrane and podocytes which causes increased permeability of the glomerulus and loss of plasma proteins in the urine
|
front 30 PEDIATRIC RENAL DISORDERS:
| back 30 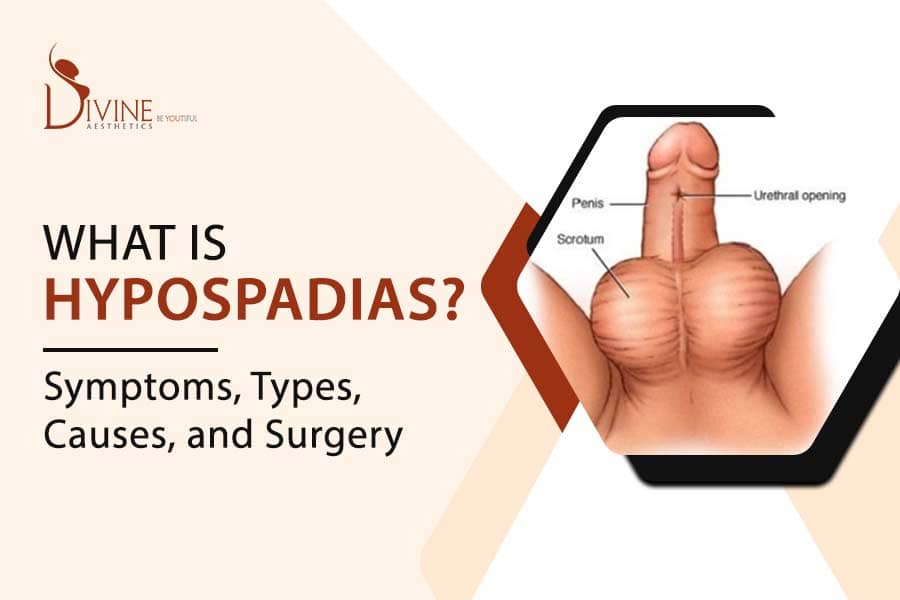
|
front 31 PEDIATRIC RENAL DISORDERS:
| back 31 
|
front 32
What is it? Where is the bladder located? Ideally when should the defect get fixed? | back 32 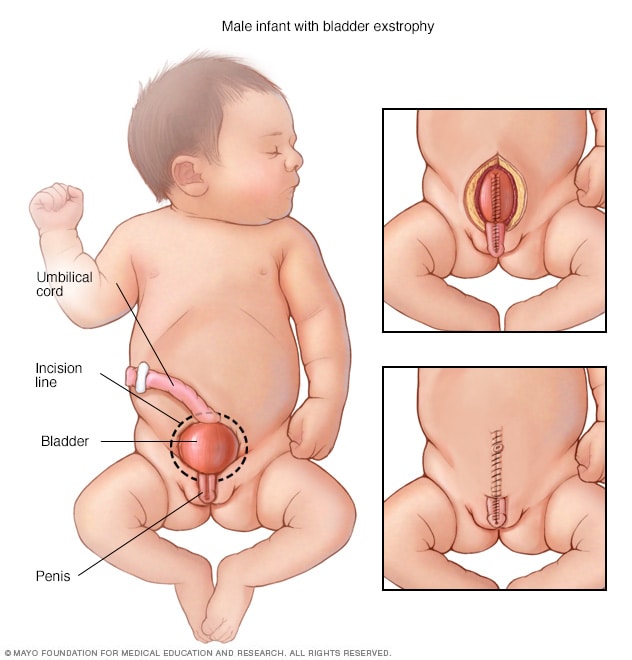
|
front 33 NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN | back 33
**Hypoalbuminemia leads to a deficiency in the carrier protein for the transport of fatty acids, and they remain elevated in the serum. |
front 34 NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN | back 34
|
front 35 NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN | back 35
|
front 36 WILMS TUMOR | back 36
|
front 37 WILMS TUMOR | back 37
|
front 38 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN | back 38
|
front 39 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN | back 39
|
front 40 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN | back 40
|