Cardiovascular Part 2
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
- Vascular disorder that narrows or occludes the coronary arteries
- Imbalance between coronary supply of blood and myocardial demand for oxygen and nutrients
Most COMMON CAUSE of CAD?
MOST COMMON CAUSE: Atherosclerosis
What are Non Modifiable and Modifiable risk factors for CAD, Myocardial Ischemia, and Acute Coronary Syndromes?
- Nonmodifiable risk factors
- Advanced age
- Family history
- Male gender
- Women after menopause
- Modifiable risk factors (disease,
disease injury, and bad habits)
- Dyslipidemia
- Hypertension
- Diabetes and Insulin resistance
- Metabolic Syndrome: Obesity, Dyslipidemia, and Hypertension
- Endothelial injury, increase in myocardial demand
- Vasoconstriction and Increase in LDL, Decrease in high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
- Endothelial damage, thickening of the vessel wall
- Cigarette smoking
- Obesity and/or Sedentary lifestyle
- Atherogenic diet
What is Transient MI?
- Transient myocardial ischemia
- Develops if the supply of coronary blood cannot meet the demand of the myocardium for oxygen and nutrients
Different Types of Angina?
- Stable angina
- Unstable Angina
- Prinzmetal angina (variant)
What is stable angina?
Factors that cause ?
- Stable angina: causes predictable chest pain
-
Stable Angina: Chronic chest pain or pressure
sensation that is paroxysmal (intermittent) and associated with
transient myocardial ischemia
-
Precipitated by either:
- Physical exertion
- Emotional stress
- Exposure to the cold
-
Relieved by either:
- Rest
- Nitroglycerin
What is Prinzemntal Angina?
- Prinzmetal angina (variant): causes unpredictable chest pain, caused by coronary artery spasm
What is Prinzemntal (Variant) Angina?
Patho? H.E.A.D.
Timing?
What is seen on the EKG?
VAriant Angina- VAsospasms
- Variant Angina (aka vasospastic angina or Prinzmetal angina): Angina that is caused by coronary artery spasm
- Pathogenesis: not completely understood H.E.A.D
- Hyperactive sympathetic nervous system responses
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Altered nitric oxide production * may all contribute
- Defective handling of calcium by vascular smooth muscle
-
Timing:
- Usually occurs at rest and at night (between midnight-8am)
- EKG changes: are transient and may include:
- ST elevation or depression
- T wave peaks
- U wave inversions
-
Arrhythmias: may occur
- Individuals who develop arrhythmias during spontaneous episodes of pain are at high risk of sudden death
Prinzemntal (Variant) Angina- Transient MI Treatment ?
Treatment
- Nitrates, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, statins, antithrombotics, antiarrhythmics
- Percutaneous coronary intervention- procedure is used to place coronary stents/wire-meshed tube to open narrowed coronary arteries
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
- Minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass (MIDCAB)
What is Unstable Angina?
What features does it have?
- Does it occur at rest?
- Onset
- How is the pain?
What does the EKG show?
- Is reversible myocardial ischemia and foreshadows an impending infarction
- Transient episodes of thrombotic vessel occlusion and vasoconstriction occur at the site of plaque damage with a return of perfusion before significant myocardial necrosis occurs
- Chest pain associated with unstable angina is persistent and severe
AND
- Has at least 1 feature below:
- occurs at rest
- severe and is of new onset
- more severe, prolonged, or frequent than previously experienced
*EKG in these patients is typically normal
Unstable angina Treatment
-
Treatment
- Immediate hospitalization with the administration of nitrates, antithrombotics, and anticoagulants
- Beta blockers and ACE inhibitors
- Emergent PCI (Percutaneous coronary intervention)
Two types of MI?

Two major types:
- Subendocardial infarction (smaller infarctions, do not extend thru ventricular wall) occurring beneath the endocardium
- Not associated with ST segment elevations (non-STEMI).
- Often have ST depressions
- Suggest that additional myocardium is still at risk for recurrent ischemia and infarction
- Transmural infarction (involve whole thickness of myocardium) occurring across the entire wall of an organ or blood vessel
- Individuals at high risk for complications
- ST segment elevations (STEMI) on the ECG require immediate intervention
What are structual and functional changes that occur?
- Structural and functional changes
- Myocardial stunning: is the temporary loss of contractile function that persists for hours to days after perfusion has been restored CONTRACTION STUNTED
- Hibernating myocardium: tissue that is persistently ischemic undergoes metabolic adaptation to prolong myocyte survival- heart muscle tissue doesn’t receive adequate blood flow. It receives enough nutrients to stay alive, but it can’t support the heart’s pumping
- Myocardial remodeling: process that occurs in the myocardium after an MI (up to 24 months, ventricular fxn)
- Repair
What is Myocardial Infarction?
- Prolonged ischemia
- Causes irreversible damage to the heart muscle (myocyte necrosis)
- Cellular injury leading to cellular death
Clinical Manifestations of MI?
What labs do you look at?
Myocardial Infarction (cont)
- Clinical manifestations
- Sudden severe chest pain
- Cool, clammy skin
- Labs
- ECG changes
-
Troponin I: most specific elevates in 2–4 hours
- proteins are released when the heart muscle has been damaged
-
Creatine phosphokinase–MB (CPK-MB)
- enzyme found primarily in heart muscle cells
-
LDH
- lactic acid dehydrogenase, screens for tissue damage
MI Treatment and Complications
Treatment
- Hospitalization
- Immediate oxygen and aspirin
- Morphine sulfate
- Bed rest
-
Cardiac medications
- thrombolytic
- antithrombotic
- vasodilators
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Surgery
What is Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Examples of ACS?
Complications of ACS?
- Sudden coronary obstruction because of thrombosis formation over a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque
-
Examples
- Unstable angina
- MI
-
Most Common Complications
- Dysrhythmias
- Congestive heart failure, and sudden death
** What are the 4 heart valves?

What is Valvular Stenosis and Valvular Regurgitation?
Valvular disorders are disorders of of the endocardium (the
innermost lining of the heart wall)
damage the heart valves,
which are made up of endocardial tissue.
Valvular stenosis
- Valve orifice is constricted and narrowed
-
valvular stenosis the valve orifice is constricted and
narrowed,
impeding the forward flow of blood and increasing the workload of
the cardiac chamber proximal (closest) to the diseased valve
-
valvular stenosis the valve orifice is constricted and
narrowed,
Valvular Regurgitation
- Valve fails to shut completely
- Also called
insufficiency or incompetence
- valve leaflets, or
cusps, fail to shut completely,
permitting blood flow to continue even when the valve is supposed to
be closed - Valvular
regurgitation increases the volume
of blood, the heart must pump and increases the workload of the
affected heart chamber = causing chamber dilation and hypertrophy
- valve leaflets, or
cusps, fail to shut completely,
What is Aortic Stenosis?
What valve is affected?
What are S/S?
What is treatment?
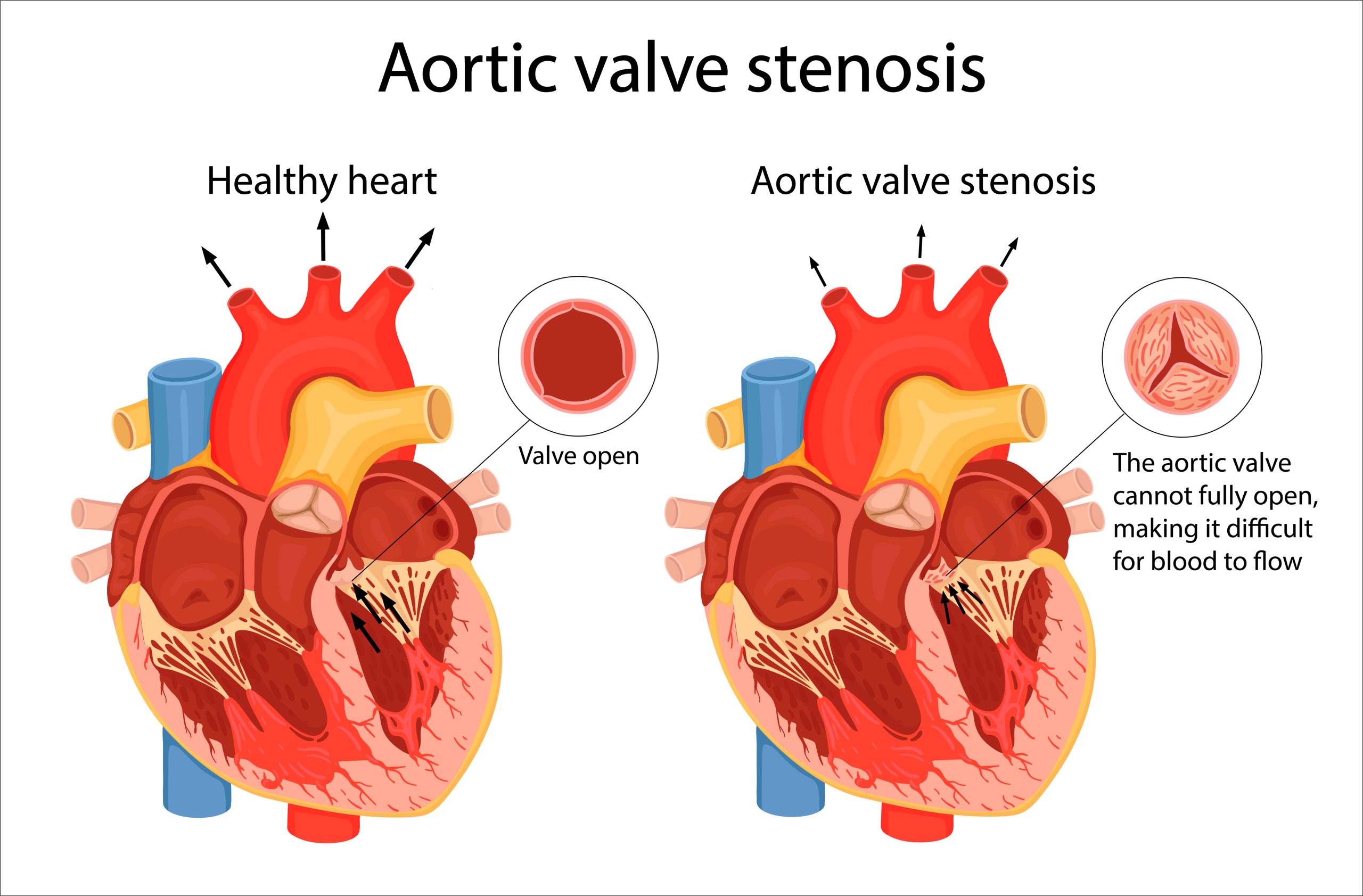
Orifice of the aortic semilunar valve narrows, causing diminished blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta
-
PATHO: gene
abnormalities polymorphisms of genes that code for LDL
- Lipoprotein deposition in the valve tissue with chronic inflammation and leaflet calcification.
- Clinical manifestations: A.S.H. bc heart and brain not being fed (perfused)
- Angina
- Syncope
- Heart failure
-
Treatment
- Most require valve repair or replacement with a prosthetic valve, followed by long-term anticoagulation therapy
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
What is Mitral Stenosis?
Most common cause?
What are S/S?
What is treatment?
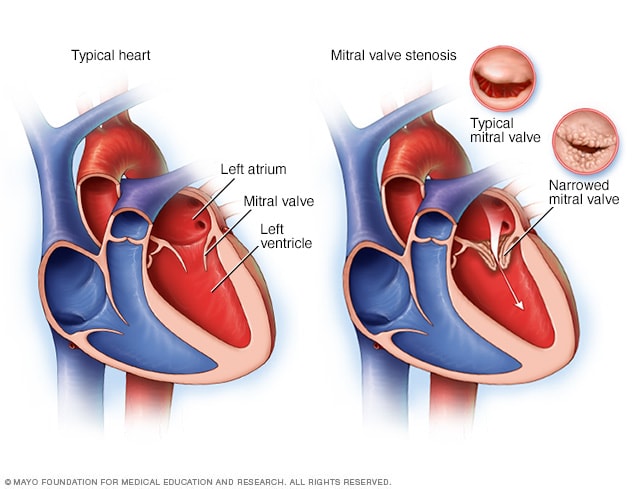
Mitral stenosis
- Impairment of blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle
-
Most
common cause: acute rheumatic fever
- Autoimmune activation of lymphocytes and macrophages leads to inflammatory damage and subsequent scarring of the valve leaflets
- Clinical manifestation * R sides HF S/S because blood is staying back to the lungs
- Dyspnea
- PND (Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea )
- Can lead to pulmonary congestion and right heart failure
-
Opening snap can sometimes be heard at apex
- If the mitral valve is forced open during diastole, it may make a sharp noise called an opening snap. The first heart sound (S1) is often accentuated and somewhat delayed because of increased left atrial pressure.
-
Treatment
- Surgical repair: percutaneous balloon commissurotomy
- May require valve replacement
What is Aortic Regurgitation?
Causes?
S/S?

- Inability of the aortic valve leaflets to close properly during diastole
- Causes "CCREaMM"
- Congenital: bicuspid valve disease
- Chronic HTN
- Rheumatic fever
- Endocarditis (bacterial)
- Atherosclerosis
- Marfan’s
- Meds: appetite suppressing medications
- Syphilis
-
Clinical
manifestations:
- Widened pulse pressure as a result of increased stroke volume and diastolic backflow
- Carotid pulsations
- Bounding peripheral pulses
- Symptoms of left heart failure when severe
- diastolic decrescendo murmur heard best in the second, third, or fourth intercostal spaces
What are Complications of Aortic Regurgitation?
What is treatment of Aortic Regurgitation?
Complications:
- Heart failure
- A-fib
- Stroke
- Pulmonary HTN
- Dysrhythmias and endocarditis are common complications of aortic regurgitation
Treatment:
- Valve replacement may be delayed for many years with the
use of vasodilators and inotropic agents
- surgical or transcatheter valve replacement
Mitral Valve Regurgitation
Causes?
- Permits backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left
atrium
- primary because of mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic heart disease, infective endocarditis, MI, connective tissue diseases (Marfan syndrome), and dilated cardiomyopathy, ischemic/nonischemic myocardial disease that damages the chordae tendineae or the mitral annulus
Most common causes
- mitral valve prolapse
- rheumatic heart disease
- infective endocarditis
- MI
- connective tissue disease
- dilated cardiomyopathy
Clinical Manifestations:
- varying levels of severity of symptoms HF S/S
- holosystolic murmur best heard at apex and radiates to axilla- backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium during ventricular systole
Treatment
- ACEI/ARBs
- Diuretics
- surgical repair or valve replacement- urgent replacement if caused by MI
- What is Mitral valve prolapse syndrome?
- What are S/S?
- What is treatment?
- Anterior and posterior cusps of the mitral valve billow upward
(prolapse) into the atrium during systole
- mitral
valve prolapse is myxomatous degeneration of the
leaflets in which the cusps are redundant, thickened, and scalloped
because of changes in tissue proteoglycans, increased proteinases, and
infiltration by myofibroblasts - mitral valve complex, which includes the annulus, leaflets, chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, and the left ventricular wall; dysfunction of any of these elements can lead to prolapse of the valve.
- mitral
valve prolapse is myxomatous degeneration of the
-
Clinical
manifestations:
- usually asymptomatic but can cause palpitations
- Atypical chest pain
- Lightheadedness
- Syncope
- Fatigue - in the morning
- Dyspnea
- Midsystolic click may be heard on auscultation
-
Treatment:
- none needed
- Beta blockers- needed to alleviate
syncope, severe chest pain, or
palpitations - surgical repair if necessary
Rheumatic Fever
What is it?
S/S?
Treatment
- Is a diffuse, inflammatory disease caused by a delayed immune
response to infection by the
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci
-
Antibodies against streptococci bacterial antigens display
cross
reactivity against laminin, a protein present in extracellular tissues
around heart cells and in the valves. - RHD begins as carditis, or inflammation of the heart layers= endocardium, myocardium, pericardium. Endocardium are where valves are, causes swelling of the valve leaflets, with secondary erosion along the lines of leaflet
-
Antibodies against streptococci bacterial antigens display
cross
- If left untreated, rheumatic fever causes rheumatic heart disease (It may have a genetic component)
- Clinical Manifestations "Feel a little F.l.a.n.e."
- Fever
- Lymphadenopathy- swollen lymph nodes
- Arthralgia- joint pain
- Nausea, vomiting,
- Epistaxis
-
Treatment:
- 10-day regimen of antibiotics, may need antibiotics for 5 years if it is recurrent
- NSAIDs
- Surgical repair of damaged valves may be necessary in cases of chronic recurrent rheumatic fever or carditis
Infective Endocarditis
What is it?
Patho

- Inflammation of the endocardium from infectious agents
- Most common: bacteria (especially streptococci, staphylococci, and enterococci)
- most common cause of IE with Staphylococcus aureus
- Pathogenesis
- Endocardial damage
-
Endocardial damage exposes the endothelial
basement membrane, which contains a type of collagen that
attracts platelets and thereby stimulates sterile thrombus
formation on the membrane. This causes an inflammatory
reaction -nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
-
Endocardial damage exposes the endothelial
- Bloodborne microorganism adherence
- Bacteria enters the bloodstream and adhere to the damaged endocardium using adhesins. (IV drug use, gingivitis, foley )
- Formation of infective endocardial
vegetations
- Bacteria infiltrate the sterile thrombi and
accelerate fibrin
formation by activating the clotting cascade.
- Bacteria infiltrate the sterile thrombi and
accelerate fibrin
Infective Endocarditis Risk Factors
P.E.L.V.I.I.C.
- Prosthetic heart valves
- Previous infective endocarditis
- Long-term indwelling IV catheterization (e.g., for pressure monitoring, feeding, hemodialysis)
- Valvular heart disease (Valves that are already scarred or damaged by RHD are more likely to have IE than undamaged valve)
- IV drug use
- Implantable cardiac pacemakers
- Congenital lesions associated with highly turbulent flow (e.g ventricular septal defect)
Infective Endocarditis S/S

F.W.C. P.A.T.H.O.J.E.N.
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Conjunctiva
- Petechial lesions on the skin
- Aye back pain
- The new or changed cardiac murmur
- HF
- Osler lesions(painful erythematous nodules on the pads of the fingers and toes)/Oral mucosa
- Jane lesions nonpainful hemorrhagic lesions on the palms and soles
- Emboli
- Night sweats
Infective Endocarditis Treatment
Treatment
- Antibiotics, usually for several weeks
Cardiac Terminology
Stroke Volume?
Cardiac Output?
Afterload?
Preload?
-
Stroke volume
- the amount of blood that is ejected with each heart beat
-
Stroke volume is influenced by three major factors:
contractility,
preload, and afterload
-
Cardiac output
- the product of the heart rate and stroke volume
(cardiac output = heart rate X stroke volume)
-
Preload (aka end-diastolic volume)
- the volume of blood that stretches the ventricle at the end of diastole (just before systole starts)
- It is determined by the venous return to the heart
-
Afterload
- the force that the contracting heart muscle must generate to eject blood from the ventricles
- The main components that determine afterload are the systemic vascular resistance and ventricular wall tension
What is Heart Failure ?
What are risk factors of heart failure?
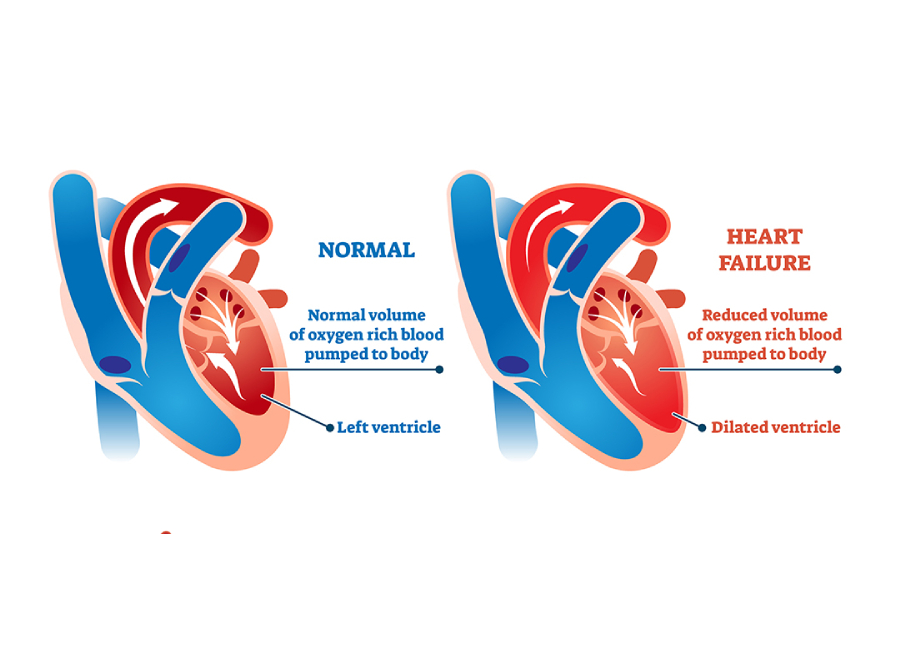
- Heart can not generate adequate cardiac output, resulting in
inadequate perfusion of
tissues or an
increased diastolic filling pressure of the left ventricle,
or both
- causes of heart failure result in dysfunction of the left ventricle (systolic and diastolic heart failure). The right ventricle also may be dysfunctional, especially in pulmonary disease (right ventricular failure)
-
Risk
factors
- Include ischemic heart disease bc part of heart dead so can not contract properly
- Hypertension
Other risk factors include age, smoking, obesity, diabetes, renal failure, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, congenital heart disease, and excessive alcohol use.
What is left sided HF?
What can it lead to? think of lungs

-
Left ventricular heart failure: Left ventricular failure is
characterized by:
- decreased cardiac output with decreased peripheral blood flow
- accumulation of blood in the pulmonary circulation
- This leads to:
- Pulmonary edema (blood backs up into the pulmonary circulation instead of being moved from the left ventricle to the systemic circulation)
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (shortness of breath episodes at night)
Systolic HF
- Inability of the heart to generate adequate cardiac output to perfuse tissues and ejection fraction ≤40%
- Complex constellation of neurohumoral, inflammatory, and metabolic processes
- BNP INC to increase salt and water excretion
- Angiotensin II and aldosterone = remodeling and fibrosis
- ADH = vasoconstriction, fluid retention, hyponatremia
- Catecholamines released by SNS = myocardial remodeling
- Inflammatory cytokines= myocardial damage and weight loss
These diseases contribute to inflammatory, immune, and neurohumoral changes (activation of the SNS and RAAS) that mediate a process called ventricular remodeling. Ventricular remodeling results in disruption of the normal myocardial extracellular structure with resultant dilation of the myocardium and causes progressive myocyte contractile dysfunction over time
Systolic heart failure S/S
Systolic HF Treat
- Clinical manifestations
- Dyspnea
- Orthopnea
- Cough of frothy sputum
- Fatigue
- Decreased urine output and edema
-
Treatment
- Apply oxygen
- Administer nitrates, morphine, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, aldosterone blockers, and/or beta-blockers
- Increase contractility
- Reduce preload and afterload
Oxygen, nitrates, and morphine administration improve myocardial
oxygenation and help relieve coronary spasm while lowering preload
through systemic
venodilation
What is Diastolic heart failure
S/S?
Treatment?
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Decreased compliance of the left ventricle and abnormal diastolic relaxation (lusitropy)
- Clinical manifestations:
- dyspnea on exertion and fatigue
-
Treatment
- Physical training (aerobic and weight training)= improves endurance and quality of life
- Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and aldosterone blockers
What is Right Sided HF?
What can it cause?
- Right ventricular heart failure: Right ventricular failure is characterized by the inability of the right ventricle to move blood from the systemic venous circulation into the pulmonary circulation
- Right ventricular heart failure causes:
- Left ventricular heart failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Intrinsic lung diseases
Right HF S/S?
Clinical Features: ***(because blood backs up into the systemic venous circulation instead of moving from the right ventricle to the pulmonary circulation)***
E. D.A.S.H.
- Edema of the lower extremities
- Distension of the jugular neck veins
- Ascites
- Splenomegaly
- Hepatomegaly
What are consequences of Heart Failure ?
- Atrial and ventricular arrhythmias can develop in patients who have heart failure
- The most common arrhythmia in heart failure patients is atrial fibrillation
- Patients with heart failure also have increased risk of sudden cardiac death (death within 1 hour of symptom onset)
- This sudden death is most commonly due to either ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation
Cardiomyopathy
What is it?
What are they different types?
- Cardiomyopathy: A disorder of the heart muscle which is associated with myocardial disorder of either:
- mechanical (heart failure) failure Or
- electrical (arrhythmia) failure
- Primary Cardiomyopathy: Cardiomyopathy due to genetic, acquired, or mixed (genetic and non-genetic) etiology
- Secondary Cardiomyopathy: Cardiomyopathy that develops in the presence of a multisystem disorder
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
What is it?
Who does it commonly affect?
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM):
-
- Left ventricular hypertrophy and thickening of the interventricular septum associated with impaired diastolic filling, arrhythmias, and sometimes left ventricular outflow obstruction
- Occurs in 1 in 500 people
- Most common cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes!
- Inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
S/S?
Treatment?

-
Clinical
manifestations: G.A.S.P.
- GENETICS (causes)- autosomal dominant disorder
- Angina
- Syncope
- Palpitations
- symptoms of MI, symptoms of left heart failure
Obstruction of left ventricular outflow can occur when heart rate is increased and intravascular volume is decreased
- Treatment
- Beta blockers or ACE inhibitors
- Surgical resection of the hypertrophied myocardium
- Septal ablation
- Prophylactic placement of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in high-risk individuals
Dilated cardiomyopathy
What is it?
What are causes?

- Dilated cardiomyopathy:
- Cardiac dilation and systolic dysfunction, usually with concurrent hypertrophy.
- All 4 chambers of the heart are dilated.
- Common cause for heart failure and most common indication for heart transplantation
- Causes "G.E. T.I.C." you have cardiomyopathy
- Genetics
- ETOH alcohol
- Toxins
- Idiopathic/Infections
- Chemotherapeutic agents
Dilated cardiomyopathy
S/S?
Treatment
- Clinical symptoms: bc blood backs up into the lungs from systolic HF
- Dyspnea
- Orthopnea
- Reduced exercise tolerance
-
Treatment:
- Reduce blood volume
- Increase contractility
- Reverse underlying disorder
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
What is it?
Causes?
-
Restrictive
cardiomyopathy:
- Ventricular filling is restricted because of excessive rigidity of the ventricular walls
myocardium becomes rigid and noncompliant, impeding
ventricular
filling and raising filling pressures
during diastole
- Causes: 2 D's
- Darn Genetics: deposits particles into the heart
- "H.A.S. particle deposits"
- Hemochromatosis- body can build up too much iron
- Amyloidosis- a protein called amyloid builds up in organs
- Sarcoidosis- immune system to overreact and make lumps or nodules called granulomas- can turn to fibrosis
- Damage to heart from radiation
- radiation fibrosis
- or idiopathic cause
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
S/S?
Treatment?
-
Clinical
manifestations:
- right heart failure occurs with systemic venous congestion
-
Treatment:
- correct the underlying cause
- placement of left ventricular assist devices
(LVADs) followed by heart
transplantation
Atrial Fibrillation
What is it?
Causes?
S/S?
Treatment?
- Abnormal heart rhythm caused by rapid and irregular beating of the atria
-
Causes:
- Hyperthyroidism
- CAD
- HTN
- MI
- Valvular dysfunction
- Increased risk of stroke to due to pooling of blood in the atria
- Clinical Manifestations
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
-
Treatment
- Ablation
- Cardioversion
-
Medications
"A.B.C.D."
- anti-arrhythmics, anticoagulants, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin
β-blockers usually act to modulate the activity of the SA and AV nodes
Infants: Congenital Heart Disease
- Leading cause of death (except for prematurity) in the first year of life
- Cause is known in only 10% of defects
- Prenatal, environmental, and genetic risk factors
- Maternal: rubella, lupus, insulin-dependent diabetes, alcoholism, illicit drug use, age (> 40 years) phenylketonuria (PKU), and hypercalcemia
- Chromosomal aberrations
Defects With Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
What is it?
S/S?
Treatment?
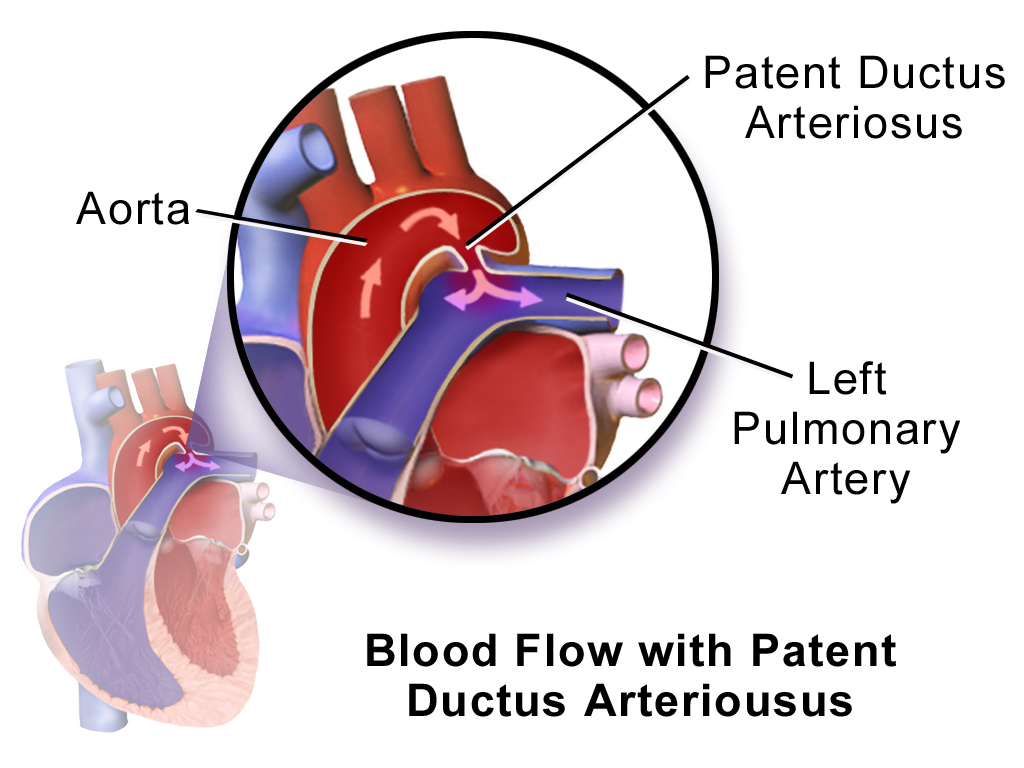
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Failure of the ductus arteriosus to close
- Normally closes within first few hours of birth
- During fetal circulation the PDA allows blood to shunt from the aorta to the pulmonary artery
- Clinical manifestations
-
Continuous, machinery-type murmur heard best at
the left upper
sternal border - Bounding pulses, active precordium, thrill upon palpation, and signs and symptoms of pulmonary overcirculation
- Treatment
- Surgical closure involving ligation by incision, catheter, or video-assisted thoracoscopy
Defects With Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow
- Atrial septal defect
What is it?
S/S?
Treatment?
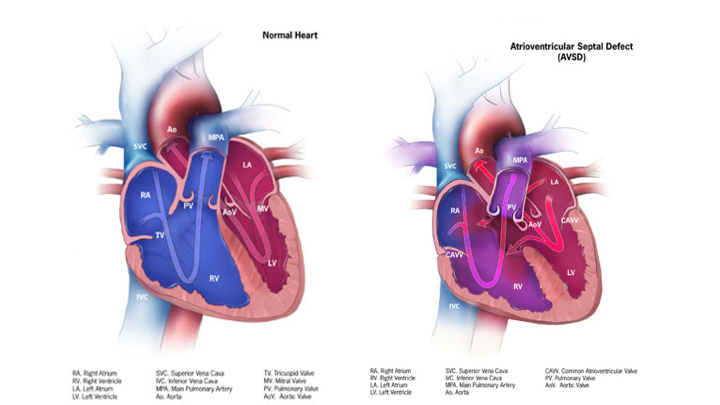
- Atrial septal defect
- Abnormal communication between the atria
- Allows blood to be shunted from left to right
- Clinical manifestations:
- Often asymptomatic; diagnosed by murmur
- Treatment
- Surgical closure before school age results in better health
Defects With Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
What is it?
S/S?
Treatment?
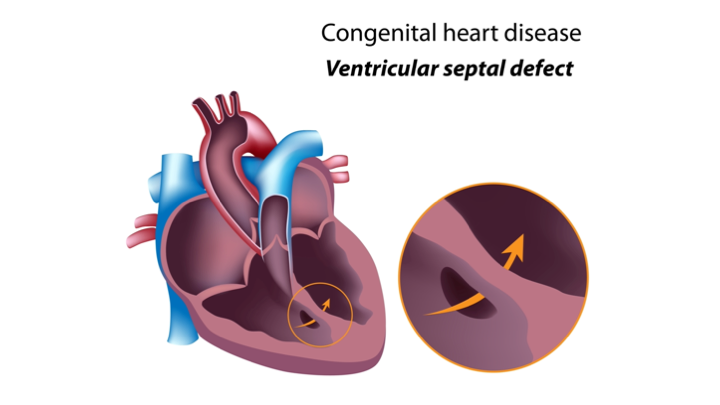
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Abnormal communication between ventricles
- Shunting from the high-pressure left side to the low-pressure right side
- Common congenital heart lesion (15% to 20%)
- Pulmonary over circulation accounts for symptoms associated with a large VSD
-
Clinical
manifestations
- Heart failure
- Poor weight gain
- Murmur and systolic thrill
- Treatment
- Patch closure
- Right ventriculotomy
Defects With Decreased Pulmonary Blood Flow: Tetralogy of Fallot
What is the defect?
S/S?
Treatment

- Tetralogy of Fallot- Have a right to left shunt
- Syndrome represented by four defects: R.A.P.S
- Right ventricle hypertrophy - (caused because resistance to pulmonary stenosis)
- Aorta displacement (Overriding aorta opening is at the Ventricular Septal Defect)
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Septal Defect- Large Ventricular Septal Defect
- Clinical Manifestations A.F.L.I.C.T.
- Annoyed/ Restlessness
- Feeding difficulty
- Lift knee to chest/S quatting (increases systemic pressure helps them breath better)
- Inability to breath: Dyspnea/Hypoxia
- Cyanosis/Clubbing
- Tet Spell: Hypercyanotic spell or a “tet spell” that generally occurs with crying and exertion
- Treatment
- Most cases corrected surgically in early infancy before 1 year of age
Obstructive Defects: Coarctation of the Aorta

- Coarctation of the aorta
- Narrowing of the lumen of the aorta that impedes blood flow (8% to 10% of defects)
- Is almost always found in the juxtaductal position, but it can occur anywhere between the origin of the aortic arch and the bifurcation of the aorta in the lower abdomen
- Clinical manifestations: Newborns usually exhibit HF
- Once the ductus closes, rapid deterioration occurs from hypotension, acidosis, and shock
Obstructive Defects: Coarctation of the Aorta
S/S?
Treatment?
-
Clinical
manifestations: Older children
- Hypertension in the upper extremities
- Decreased or absent pulses in the lower extremities
- Cool mottled skin
- Leg cramps during exercise
-
Treatment
- Prostaglandin administration
- Mechanical ventilation
- Inotropic support
- Maintain cardiac output
- Surgery
Obstructive Defects: Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
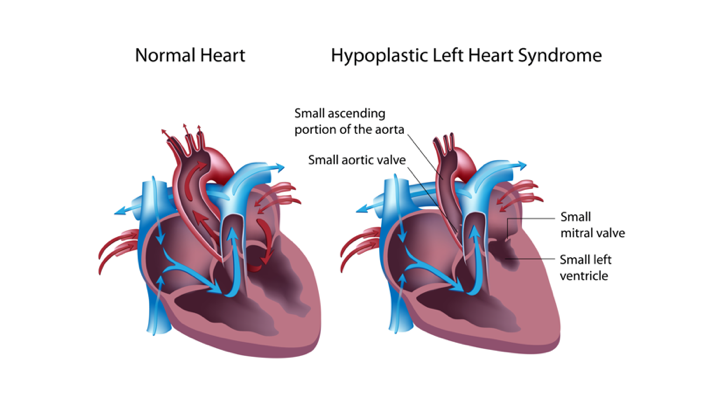
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Left-sided cardiac structures develop abnormally
- Obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricular outflow tract
- Left ventricle, aorta, and aortic arch are underdeveloped
- Mitral atresia (sbsent) or stenosis is observed
- As the ductus closes, systemic perfusion is decreased, resulting in hypoxemia, acidosis, and shock
-
Treatment
- Prostaglandin administration to keep PDA and ASD open
- Correction of acidosis
- Inotropic support for adequate cardiac output
- Ventilatory manipulation
- Surgical intervention includes a three-stage approach
- Cardiac transplantation
Mixing Defects: Transposition of the Great Arteries
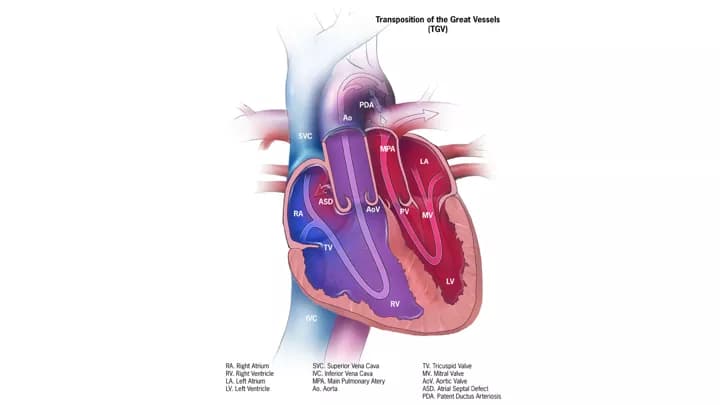
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle
- Results in
two separate, parallel circuits
- Unoxygenated blood continuously circulates through the systemic circulation
- Oxygenated blood continuously circulates through the pulmonary circulation
- Extrauterine survival requires communication between the two circuits
-
Clinical
manifestations:
- Cyanosis may be mild shortly after birth and worsen during the first day
-
Treatment:
- Surgery to switch the arteries