usmle prep
Drug used in tumor lysis syndrome to break down uric acid
Rasburicase (convert uric acid to allantoin)
Drug that reduces uric acid formation
Allopurinol
Febuxostat
MAOB metabolizes dopamine, the enzyme can be inhibited by_____
Selegiline
MAOi (prevent tyramine metabolism) interact with ____________ to cause hypertension
cheese(tyramine)
Phenytoin anticonvulsant works by___________
Blocking Na influx/channels
What are the side effects of phenytoin?
Gingival hyperplasia
Hirsutism
Osteomalacia (interferes with vitD met)
Anemia (folic acid decr)
What is the mechanism of action of Valproic acid?
decrease GABA transaminases
block T type Ca2+ channels
block Na channels
What are the side effects of VALPROIC ACID?
''vALPRoATe''
Anemia
Liver toxicity
Pancreatitis
Allopecia
Teratogenic, tremors
Drugs that cause steven johnsons syndrome are_________

What is the drug used to tx Malgnant hyperthermia and its MOA?
Dantrolene
It blocks ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Mechanism of action of opioids ___________
At presynaptic: decrease ca2+ influx.
At post synaptic: increase k+ efflux
Organisms not covered by cephalosporins are_________
'' LAME''
Listeria monocytogens
Atypicals (chlamydia, mycoplasma)
MRSA
Enterococi
___________ is a drug always given with Imepenem to prevent renal toxicity from its metabolites.
Cilastatin
_______ is the drug of choice for treatment of lyme disease and rickettsia (both caused by ticks)
tetracycline
'' tets for ticks''
Which medication has the same intracellular target as trimethoprim (in bact cell) in its mechanism of action?
Methotraxate (In human cells)
Pyrimethamine (in protozoa)
_______is an Antifungal medication that inhibits cytochrome p450 enzymes.
Azoles
Empiric treatment of Entamoeba hystolytica requires a 2-phase approach:
Tissue agent (eg, metronidazole) is administered first to kill trophozoites.
Intraluminal agent (eg, paromomycin) is given to eliminate intraintestinal cysts to prevent reinfection.
Penicillin is given together with clavulanic acid to_______
decrease hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring of penicillin (prevent cleavage of penicilin by bact cells)
Examples of beta lactamase inhibitors include___________
Clavulanic acid
Tazobactam
Sulbactam
What is the mechanism of resistance of aminoglycosides?
Antibiotic-modifying enzymes. These enzymes add chemical groups (eg, acetyl, adenyl, phosphate) to the antibiotic, which diminishes its ability to bind to the 16S ribosomal RNA within the 30s ribosomal subunit.
______________is a common adverse effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole due to the trimethoprim-induced blockade of the sodium channels in the collecting duct, which prevents sodium-potassium exchange and reduces renal excretion of potassium (similar to the action of amiloride).
Hyperkalemia
___________________is the most common benign liver tumor.

Cavernous hemangioma
Damage to the anterior and posterior vagal trunks (of vagus) during fundoplication procedure causes _________
Delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis) and gastric hypochlorhydria
_________ is derived from a zymogen produced by pancreatic acinar cells and activated by trypsin in the duodenum; levels correlate with pancreatic exocrine activity. ie low levels = pancreatic insufficiency.
Elastase (fecal elastase)
A drug that is non absorbabble antibiotic that is used to lower ammonia by modulating the bact that produces it in the GI tract
Rifaximin
Acute hemolysis following exposure to oxidative insults ie infection,oxidizing foods and meds (eg flouroquinolones) occurs in ________
Glucose 6 phosphste dehydrogenase deficiency
Patient without spleen have what kind of impairment?
Systemic bacteria clearance
Autosomal recessive disorder involving lack of homogentisic acid dioxygenase(metabolise tyrosine) leading to accumulation of homogentisic acid is called_______
Alkaptonuria
Clinical features of alkaptonuria are __________
Black urine when exposed to air
Blue black pigmentation on the face
Orchinosis (hyperpigmentaton in ear or eye sclera)
Arthritis in joint
What is the role of hCG therapy in a pt with PCOS receiving ovulation induction therapy with gonadotropins?
hCG mimic LH and act as ovulation trigger.
___________ is a fungalorganism that replicates within macrophages and spreads from lungs to the reticuloendothelial system through pulmonary lymphatics.
Histoplasma capsulatam
__________ IS A/W URIC ACID FORMATION IN POST KIDNEY TRANS??
Cyclosporin
What causes aplastic anemia?
autoimmune destruction of multipotent hematologic stem cells due to alterations in their surface antigen leading to cytotoxic Tcell responce and release of interferon gamma hence apoptosis.
Whats the commonest cause of type1 DM?
Autoimmune insulitis (islet leukocytic infiltration) with progressive beta cell loss.
Didanosine (ART used in HIV) causes_______________
Pancreatisis (''pancreaDIDis'')
Eg of encapsulated organism
Salmonella
H.influenza
E.coli
Strep. pneumoniae
C1 esterase inhibitor def
Angioedema, laryngospasm
Pseudocholinesterase def
Failure to breathe after fast acting anaesthesia eg succinylcholine or mivacurian are administered
Disruption of heme synthesis via inhibition of aminolevulinate dehydratase is caused by
Lead toxicity
Lead toxicity findings
Lead lines on gingivae
Encephalopathy, erythrocyte basophilic stippling
Abdominal colic , sideroblastic anemia
Drops- wrist and foot
Renal artery stenosis is commonly due to ________
Atherosclerosis
Fibromascular dysplasia
prolonged exposure to noise
damage to organ of corti
test to do before starting eternacept (tnf alpha inh)
tb
finasteride acts on what part of the prostate?
on epithlial cells and smooth muscle
Ethambutol (arabinosyl transfarase inhibition) causes__________
optic neuritis
What is the mechanism of action of Bisacodyl?
Activates enteric nerves in colonic myoplexus to stimulate peristalsis.
cause of gestational diabetes is due to
human placental lactogen
Examples of common immunosuppressants and mechanisms........

During anaphylactic reaction what is likely to be elevated in the serum?
Histamine
Tryptase (specific marker of histamine)
NB:both result from mast cell and basophil degranulation
The immunoglobulin most abundant in the blood is ____________
IgG
Immunoglobulin found in tears, saliva and breast milk is__________
IgA
Which immunoglobulin is responsible of immediate response to antigen?
IgM
NB: IgG is a/w chronic response
Interferons α and β are produced by most human cells in response to viral infections. Their function is___________
Stop protein synthesis in infected cells
Promote apoptosis
What is the mechanism of vancomycin infusion reaction ?
Direct mast cell activation by the drug due to rapid infusion.
ie: Red man syndrome (not allergic rxn)
Hereditary angioedema is caused by deficiency of what enzyme?
C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency (leading to over activation of the complement system.)
What is serum sickness?
Immune complex–mediated type III hypersensitivity reaction that typically forms 5-14 days after exposure to foreign proteins in an antitoxin, antivenom, monoclonal antibody, or vaccine.
Patients typically develop fever, urticarial rash, and arthralgia that resolve spontaneously over days as the immune complexes are cleared by the mononuclear phagocyte system
The specific surface marker for monocyte-macrophage lineage cells is________
CD14
Whats the mechanism of action of glucocorticoids?
Reduces inflammation by binding to a cytosolic receptor, translocating into the nucleus, and inhibiting proinflammatory transcription factors eg nuclear factor-kappa-B (NF-κB).
Drug of choice in treatment of anaphylactic shock is _________________
Epinephrine
Disorders of innate immunity are____________

What is mechanism of action of rituximab?

Depletion of B cells (binds CD20 of B cells inducing cytotoxicity and phagocytosis)
The mediator released from macrophages and one of the most important during systemic inflammation in sepsis is___________
TNF alpha
others: IL1, IL6
Fluticasone MOA is__________
Promote apoptosis of eosinophils
NB: Glucocorticoids inhibit transcription of proinflammatory mediators and promote apoptosis of eosinophils, T cells, and monocytes.
venous congestion causes expansion of which part iof the spleen?
red pulp
__________ is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in purine metabolism, to prevent accumulation of toxic metabolites(lymphocytotoxic).
__________inhibitors lead to destruction of the cell due to accumulation of metabolites.
Adenosine deaminase (ADA)
ADA inhbitors eg ( Medications that block ADA are used to treat lymphocyte-derived cancers )
Hyperacute rejection during transplant is due to recipient's preformed antibodies which are____________
Anti ABO blood group
Anti HLA antibodies
Hereditary angioedema is characterized by recurrent episodes of cutaneous and/or mucosal swelling due to__________ deficiency. C4 levels are low due to uninhibited cleavage of C4 by excess activated C1.
C1 inhibitor deficiency
What is the difference between pneumococcal conjugate and polysaccharide vaccine?
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines are strongly immunogenic in infancy due to both B and T cell recruitment. They provide higher, longer-lasting antibody titers
The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is poorly immunogenic in infants due to their relatively immature humoral antibody response. recommended for ages >65 and btn 2-65 with certain med condition eg DM
________________destroy parasite via antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity with enzymes from their cytoplasmic granules. Another function is regulation of type I hypersensitivity reactions.
Eosinophils
_____________is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis as it decreases further mast cell release of inflammatory mediators and counteracts existing systemic inflammatory effects (eg, shock, bronchoconstriction).
Epinephrine
MECONIUM ILEUS IS ALMOST ALWAYS A/W _______
CF
DEEP INGUINAL RING AND SUPERFICIAL INGUINAL RING CAN BE DIFFERENTIATED BY ____________
INFERIOTR EPIGASTRIC VEIN
INCREASE P
OXANDROLONE
Many types of cancers evade immunodetection by increasing expression of _____________on their surface. Monoclonal antibodies against PD-1 upregulate the T-cell response and promote tumor cell apoptosis
PD-L1
_____________stimulates neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation. Other important chemotactic agents include 5-HETE (leukotriene precursor), C5a, and IL-8.
Leukotriene B4
Topical corticosteroids are the first-line therapy for atopic dermatitis. Their mechanism of action is __________
Decreasing tissue production of proinflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes through the inhibition of phospholipase A2
TESTESTERONE HAS EFFECT ON HB
INCREASES ERYTHROPOIETIC CAISING POLYCYTHEMIA
PERMETRIN
TO TX SCABIES
The only antibody that can cross the placenta______________
IgG
Chronic lung transplant rejection is due primarily to progressive scarring of the____________, leading to bronchiolitis obliterans. (months or years after transplantation and include obstructive lung disease (eg, reduced FEV1) with dyspnea and dry cough)
Small airways
The most important opsonins (coating proteins that enhance phagocytosis) are___________
IgG
C3b
metabolic syndr
olanzapine and second gen antipsychotics
Drug of choice foe panic attacks
SSRI
benzos foe immediate relief
long standing RA can lead to
vertebral sublaxation
nerve likely to be injured during cardiac catheter ablations
phrenic nerve
commoon infe in burn pt
pseudomonas aureginosa
Key Th2 cytokines that trigger acute inflammation in atopic dermatitis are _____
IL-4 and IL-13
____________is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction caused by drugs (eg, anticonvulsants, antibiotics) or their metabolites that typically occurs 5-21 days following drug initiation

Pt with auto immune thyroiditis are at risk of developing which thyroid ca?
Thyroid lymphoma
There is decreased responsiveness to __________ in old age making it hard to cope with critical illness eg sev burns
Adrenergic response
Mechanismof action of botulinum toxin
Blocks presynaptic exocytosis of Ach
Benzodiazepine withdrawal
Anxiety
Tremors
Insomnia
Sympathetic hyperactivity eg diaphoresis
Psychotic features eg hallucinations
Mitochondria DNA
In eukaryotic cells is in mitochondria
Sugar that is metabolized fast than others ?
Fructose 1 phosphate
The most common outcome of hep c infection without tx is_______
Life long infection
Methadone is an opioid agonist that prevents opioid withdrawal by its _______
Long half life
Damage to the pterion cause damage to which vessel?
Middle meningeal artery branch of maxillary artery
Spinal stenosis
Ligamentum flavin hypertrophy
Role of hcg(secreted by placental syncytiotrophoblast)in preg
Maintenance of corpus luteum(maintain pregnancy)
Drug of choice of listeria
Ampicillin
Posterior cerebral artery stroke
Contralateral hemianopia??
Peripheral acting mu opioid receptor antagonist for treating constipation (doesn't induce withdrawal symptoms; doesn't cross BBB)
Methylnaltrexone
Discolouration of skin due to station dermatitis (chronic venous insufficiency)
Hemosiderin deposit
Halogenated inhaled anesthesia can cause
Hepatocellular liver injury
(Have incr ast and prolonged PT)
Tx of priapism may involve penile injection with which medication?
Alpha adrenergic agonist (eg phenylephrin)
Breakdown of dipeptide and tripeptide to free amino acids takes place where in the GI
Intestinal mucosa
Needle shaped Crystal in gout are due to
Urate.
Diuretic drug that improve survival rate in heart failure with reduced EF_____
Spironolactone
Lithium interact with _______ to cause toxicity symptoms
NSAIDS
ACE inhibitors
Thiazides diuretics
Renal cell carcinoma classic sings include______
Hematuria
And mass
Flank pain
Weight loss
Patients with cleft palate are at increased risk of ear infection due to dysfunction of
Ani palatini muscles
Best intial treatment of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy due to uncontrolled DM is
Amitriptyline
Function of golgi tendon is to _______
Maintains muscle tone
Opioid can generate pseudoallergic reaction by directly acting on ___________
Mast cells and cause degranulation
First line tx for trigeminal neuralgia is
Carbamazepine
Prolonged seizures,crush injuries can predispose to?
Rhabdomyolysis
Aldolase b deficiency
Sucrose or fructose should be avoided
Buzz words for PCP (Phencyclidine)
Agitation
Nystagmus
Ataxia
- Mechanismof ace inhibitors post MI
Prevent remodeling and reduce LV dysfunction/dilatation
Tramadol can interact with ssri to cause ___
Serotonin syndrome
After 12 months of amenorrhea _______ confirms menopause in 50+ yr old women
Increased FSH
Patient with hyperuricemia have def of _______
Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribotransferase
Treatment of malaria with primaquine is for _______
Treating exoerythrocytic parasite
NB chloroquine treats parasite circulating in blood but will not treat liver hypnozoites
Severe self limited watery diarrhea in immunocompromised pt is due to
Cryptosporidiosis
Atrophy of mammillary bodies is classically seen in ______
Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome
How does Phenytoin and antiepileptic drug cause decrease in VIT d ?
Inducing cyp24 which convert vit d to inactive form
Subacute thyroiditis usually follows viral infection and patient may show __________ on investigation
Low radioactive iodine uptake
Mesothelioma histologically shows__________
NB: asbestos exposure is the primary risk factor
Spindle cells positive for cytokeratin
Before fertilization oocyte is arrested at what stage ?
Metaphase of meiosis ii
Tx of ADHD

Ovarian torsion usually involve
Ovarian torsion usually involves
Twisting if infundibulopelvic ligament
Hepatocellular carcinoma can be caused by viruses _______
Hep B and hep C
Mitochondrial damage leading to impaired fatty acid metabolism is seen in ________
Reye syndrome
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome

Diffuse atelectasis is seen on x-ray as ground glass opacities and air brinchogram
Epiglottis
Inspiratory stridor
Hypercalcemia In_________ is caused by PTH independent VIT d activation by macrophages
Sarcoidosis
Drugs that are given rectally avoid _______
First pass metabolism by going directly into the circulation
Agammaglobulinemia is characterized by _________
Low or absent circulating mature Bcell CD19,CD20
Vocal cord nodule in immunocompromised is usually a resiult of_______
HPV
Hypersplenism (as seen in liver cirrhosis or portal htn) is associated with __________
Pancytopenia
Formation of non caseating granuloma due to type IV hypersensitivity reaction to an unknown antigen is seen in_________
Sarcoidosis
NB: a/w uveitis, erythema nodosum
Malignant hyperthermia is caused by genetic defect in____________
Ryanodine receptor
nb symptoms occur when pt is exposed to inhaled anaesthetics
Neomycin mechanism of action?
kills gut flora hence reducing ammonia production
How do you differentiate between kaposis sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis (Bartonella spp)?
Biopsy: Kaposi's sarcoma will show lymphocytic infiltrates in the sample while angiomatosis will show neutrophilic infiltrates.
Medulla of the adrenal gland is stimulated by
Acetylcholine
Drugs that don't require dose adjustment in hepatic or renal conditions
Monoclonal antibodies
Drug used for bulimia nervosa________
Fluoxetine(ssri)
Drug of choice for ADHD is___________
Methylphenidate (A drug that increase availability of norepinephrine and dopamine)
_________Is a polypeptide hormones that binds to transmembrane receptor along plasma membrane
Prolactin
NB:other hormones are intracellular
Proliferating spindle cells forming slit like spaces filled with blood is seen in ________
Kaposi sarcoma
Cytokine involved in class switching of immunoglobulin
Il4
Il13
Angiodysplasia of ascending colon is common disorder in old age and usually present with ________
Bleeding
First line treatment for claudication ?
Cilostazol
In hypersensitive type I mast cell secrete histamine in immediate phase and then secret ______ in late phase.
Prostaglandins
Circulation in lungs
Bronchial circulation
Pulmonary circulation
Rituximab moa
Lymphocytes mediated release of cytokines
Maple syrup disease is caused by ____________
Branched chain alpha keto acid dehydrogenase
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive disease caused by mutation of the gene that codes for____________________
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Earliest response to bleeding injury is caused by_________
Secretion of Endothelin
What hormone increase during pre prandial period and declines after a meal ?
Ghrelin
Impaired binding of testosterone to it's receptors can be caused by __________
Spironolactone (cause gynecomastia)
Role of dextrose in ORS is_________
To enhance sodium absorption
The IV drug that causes arterial vasodilation and improve renal perfusion __________
Fenoldepam
What cells can't use ketones as a form of energy
Erythrocytes
Liver cells
Increased TGF-β activity is responsible for ___________________
Hypertrophic/keloid scar
(Also fibrosis of the lung, liver, and kidney that occur with chronic inflammation)
Following ischemic to cardiac muscle after how long does contractility stop when ATP starts to decline?
Within 60 seconds after ATP starts to decline
Side effects of succinylcholine _____________?
Malignant hyperthermia
Severe hyperkalemia
Bradycardia
What's the mechanism of HUS due to shiga toxin?
Microthrombi in small blood vessels formation
Effect of UV light on the skin ?
Endonuclease nicking of the damaged DNA strand
Which component of cardiovascular system is more susceptible to nitrates
Large veins
H influenza protection/ vaccination MOA?
Antibodies against hemagglutinin
Lesions in syphilis
Primary - chancre
Secondary - condylomata lata
Tertiary - gummas
Mechanism of vit D in treatment of psoriasis
Inhibit T-cell and keratinocyte proliferation and stimulate keratinocyte differentiation
A topical drug that acts like a toll like receptor to increase antiviral cytokine production and upregulate NFkB is called ______________
Imiquimod
Neck /head of femur is supplied by
Medial circumflex arteries
Antilipid drug that impairs excretion of statins
Fibrates
External branch of superior laryngeal nerve can be injured in thyroidectomy. The nerve supplies which muscle?
Cricothyroid muscle
Conversion of norepinephrine to epinephrine is facilitated by the_________

PNMT
___________ is found in adipose tissue, where it functions to drive the breakdown of stored triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol. During times of starvation, this enzyme provides substrates for hepatic gluconeogenesis and ketone body formation.
Hormone-sensitive lipase
Patients with turners syndr can be treated with growth hormone that stimulates the __________
JAC-STAT pathway
(this induce prod of IGF-1)
Whats the function of cholecytokinin (CCK)?
Causes contraction of the gallbladder to release bile
Side effects of tamoxifen (that are not caused by Raloxifene)
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial carcinoma
Uterine sarcoma
1o hyperparathyroidism causes hypercalcemia which causes constipation by __________________
Inhibit nerve depolarization leading to reduced colonic motility and impaired smooth muscle contraction.
PT with crohn disease are prone to get kidney stones due to _______
Reduced intestinal calcium oxalate formation
Vitamin necessary fo RBC membrane integrity ______
Vit E
(Def causes acanthocytes and hemolysis)
A carrier protein that transport both T4 and vit A is called
Transthyretin
Coadministration of levothyroxine with other medications can impair its absorption, these include
Iron
Calcium
Antiacids
(Also foods like soy products)
Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder is
Ssri/snri (Citalopram )
An oral macrolide antibiotic that inhibits the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase is _______
Fidaxomicin
(TX of c defficile)
Fracture of the 12th rib is likely to cause injury to which structure?
Kidney
The precursor for serotonin synthesis is ________
Tryptophan
Non stimulant drugs for ADHD __________
Atomoxetine
Alpha 2 adrenergic agonists
___________should be monitored in tx with olanzapine and other 2nd gen antipsychotics
Fasting glucose and lipid panel
Common side effects of SSRI is _______
Sexual dysfunction
Drug induced parkinsonism is treated with
Benztropine
Generalized anxiety disorder treatment with no risk of dependence
Buspirone
Turner syndrome is associated with what cardiovascular abnormality?
Bicuspid aorta
The vessel with highest O2 saturation in a fetus is
Umbilical vein that drains directly into IVC
Cancer cells usually have increased __________ activity that prevent chromosomal shortening
Telomerase
For maximum tensile strength collagen requires hydroxylation of proline and lysine this occurs in ________
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
NB: vit C is used as a cofactor in the reaction
Enzyme that removes short RNA fragment(RNA primers) that are base paired to DNA template
DNA polymerase l
Crohn's dse affects commonly the terminal ileum impairing bile reabsorption causing _______
Gall stones
Duodenal atresia is due to ____________ while intestinal atresia of midgut (jejunum, ileum, prox colon) is due to _______________
Failure of lumen to recanalize
Vascular occlusion
P falciparum ability to be more infectious/achieve higher parasitemia is because ______
Can infect erythrocytes of all ages
Cells that increase in COPD
Neutrophils
Macrophages
- CD8 T lymphocytes
CD8 t lymphocytes present antigen to MHC I which comprises of ________
Heavy chain and B2 microglobulin
Slow abnormal rise of Bhcg is seen in _________
Ectopic pregnancy
__________ targets tumor cells and virally infected cells that lack MHC I expression.
Natural Killer cells
Severe nodulocystic acne is treated with_____________
Oral Isotretinoin
Chronic use of glucocorticoids (glucocorticoids induced osteoporosis) predisposes to fractures of ________
Vertebral
usually asymptomatic
Leukemic cells can have resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs via different mechanism, the commonest one is ___________
What represents apoptosis in the hepatocytes (seen in both acute and chronic hepatitis)?
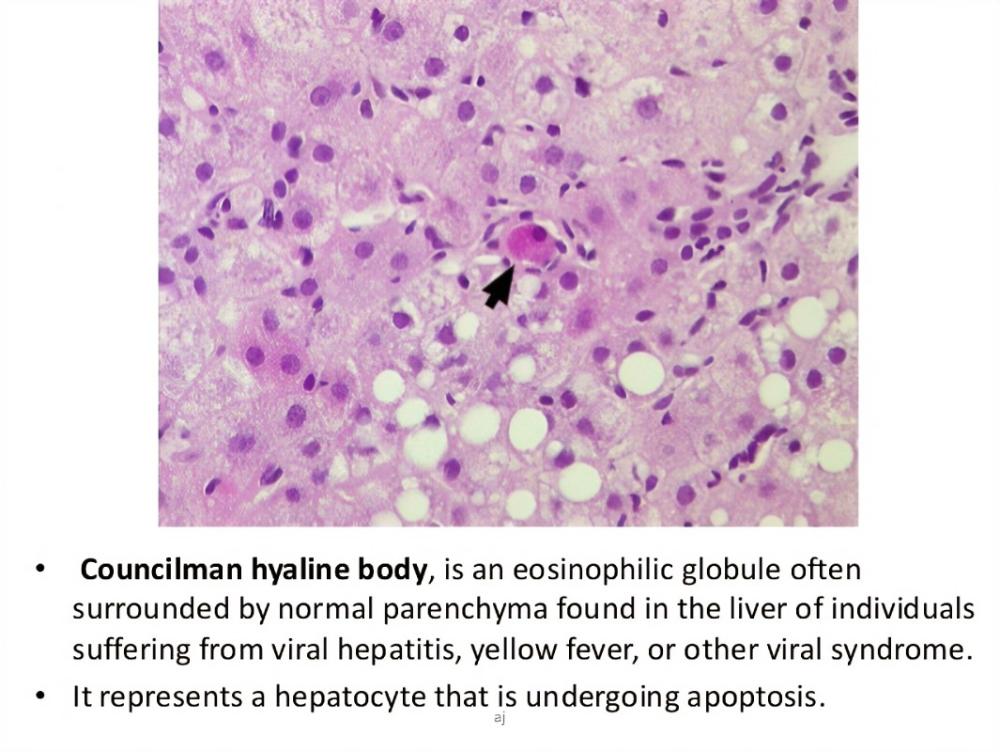
council man bodies
Function of proteosome inhibitors chemotherapy (eg. Bortezomib)is to______________
Induce apoptosis of neoplastic cells
Oocyte remain in __________ till ovulation. And after maturation they arrest in _________ till its fertilized.
Prophase of meiosis I
Metaphase II
Whats the mechanism of acetazolamide in pt with increased ICP?
Decrease CSF production by choroid plexus
Cisplatin chemotherapy causes damage to dorsal root ganglia which would cause____________
Peripheral sensory neuropathy
Hyporeflexia
Complications of neostigmine (in tx of myesthenia gravis) can cause ______
Desensitization of nicotinic receptors due to prolonged exposure to acetylcholine
Tx: Atropine
Mechanism of action of protease inhibitors.
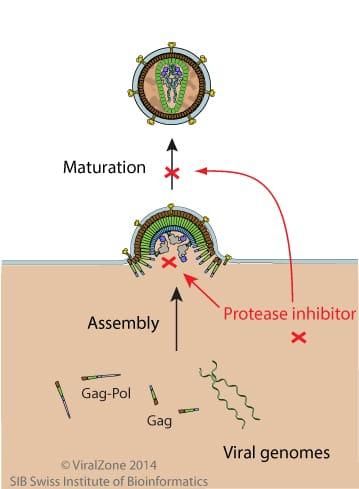
Prevents formation of mature viral core.
Damage to the lateral horn of spinal cord (intermediate horn) in c8-t2 level causes_______
Horner syndrome
Melanocytes are dendritic cells that are derived from _____________
Neural crest cells
Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus can be differentiated from adenocarcinoma of esophagus by?
Squamous cell carcinoma forms a foci of keratin.
Iron deficiency anemia presents with _________
Hypochromic microcytic RBCs
Locations of chambers on CT scans________

Multiple myeloma is what type of neoplasm?
B lymphocyte neoplasm
Bacteria infection that can mimic appendicitis is__________________
Yersinia Enterocolitica
Remodelling of a scar during wound healing is mediated by?
Matrix Metalloproteinases (collagen breakdown)
Large AV fistulas increase__________ and decrease______________.
Preload
Afterload
nb: eventually leads to high output cardiac failure
Thiazolidinediones (glitazones) and fibrates have a similar receptors where they act. this is____________
PPAR-gamma (peroxisomes proliferator acticated receptor gamma)
Glitazones increase insulin sensitivity
In leukocyte function polymerization of actin filaments allows ____________
Phagocytosis
Renal age related changes include ________?
Decreased response to ADH
Side effects of beta2 receptor agonists (eg.albuterol) include?
Tremors
Hypokalemia
Hyperglycemia
Tachycardia
Htn
Headache
Topical antibiotic ointment given to neonates to prevent STIs _______________
Erythromycin
NB: inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 50s subunit of bact ribosome
Substance P is the cause of peripheral neuropathy in pts with diabetic neuropathy. Treatment is by______________.
Capsaicin cream ( stimulates substance P release till its depleted causing pain relief)
What happens to systole and diastole in sinus tachycardia?
Diastole is shortened more than systole
When SVC is obstructed the blood returns to the heart via __________
Internal mammary and intercoastal veins
Drug that antagonize NMDA ____________
Ketamine
Dextromethorphan
Function of paclitaxel in stents is _________________
To prevent smooth muscle formation over stent
Seizures from which lobe are usually partial?
Frontal lobe
One pound of body fat has how many calories?
3500 calories
Mechanism of action of albendazole and mebendazole
They bind to tubulin and prevent microtubule polymerization
Elevated alpha fetal protein and acetylcholinesterase in aminocentesis suggest
Neural tube defect
Trendelenburg sign/gait is seen in injury to which nerve?
Superior gluteal nerve
NB:weak gluteus medius or minimus
Hippocampal sclerosis is a common cause of _____________
Temporal lobe epilepsy
NB: astrocyte proliferation
Anti lipid that acts in the intestinal lumen to prevent cholesterol absorption
Ezetimibe
Women get quickly intoxicated with alcohol compared to men. Why?
Women have lower proportion of total body water hence decreased alcohol dehydrogenase activity
Silicosis is an interstitial lung disease that presents with silicosis nodule that are characterized by__________________
Central area of hyaline core consisting of collagen fibers
When accessing the left atrium care should be taken not to damage the AV node which is located at____________________
Posteroinferior region above the opening of the coronary sinus
Effect of cortisol in arteries........
Upregulates alpha receptors (increase effect of norepinephrine)
Lymphatic spread is a characteristic of______________
Carcinomas
The primary treatment for diphtheria is the urgent administration of _____________
Diphtheria antitoxin
NB: contains preformed, neutralizing antibodies that binds and inactivates circulating toxin
A drug that inhibits platelets aggregation and is also a direct arterial vasodilator
Cilostazol
what happens to systemic vascular resistance during exercise
It reduces due to vasodilation in the skeletal muscles
Common cause of progression from paroxysmal AF to persistent AF is__________
Atrial remodeling
The most important cells against invasive candida infection are __________
Neutrophils
Commonest site of diverticulosis is _________
Sigmoid colon
Use of _____________ can induce the formation of antidrug antibodies (ADAs)
Adalimumab
NB: ADAs preventing the drug from functioning and leading to more rapid drug clearance.
Medications that block Adenosine deaminase (ADA) (converts of adenosine to inosine) is used to treat __________
Lymphocyte derived cancers e.g. Hairy cell leukemia
nb: Adenosine deaminase (ADA) inhibition/absence is highly lymphocytotoxic
What is the difference in DI caused by damage to posterior pituitary vs caused by damage to hypothalamic nuclei?
DI due to posterior pituitary damage usually resolves
DI due to hypothalamic nuclei is permanent.
Bone marrow features of MM include:

The bone marrow aspirate in MM shows numerous plasma cells, which are identified by their abundant basophilic cytoplasm, perinuclear paleness (due to a large Golgi apparatus), and nuclei with "clock-face" chromatin.