Transcription and Translation
transcription
the process of copying a DNA gene into mRNA
takes place in the nucleus
product: mRNA
translation
the process of decoding the mRNA codons to build a protein
takes place in at the ribosome in the cytoplasm
mRNA
messenger RNA
carries the directions to build a protein
tRNA
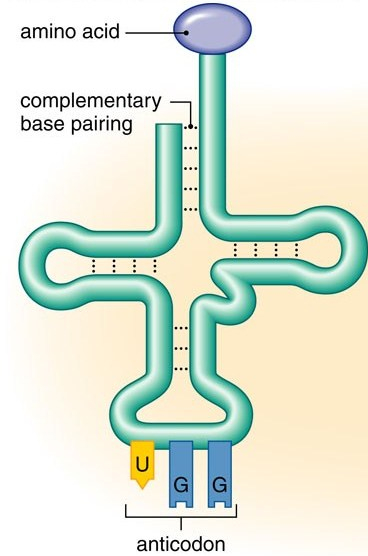
transfer RNA
carries the amino acid to the right spot on the mRNA during translation
top: amino acid
bottom: anticodon
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
makes up the ribosome
Differences between RNA And DNA
DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose
DNA contains A,G,T,C, RNA contains A, U,G, C
DNA : double helix, RNA comes in mRNA ,tRNA , rRNA
DNA double stranded, RNA single stranded
codon
sequence of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that codes for one amino acid
anticodon
section on tRNA that pairs with an mRNA codon
mRNA processing
the pre-mRNA has the introns cut out, the exons spliced together and a 5'methyl cap added at one end and a 3' poly A tail at the other
RNA polymerase
the enzyme that copies DNA into mRNA
mutation
change to the DNA
point mutation
when one nucleotide in the sequence is changed, many times it is a substitution
frameshift mutation
more dangerous mutation
usually an addition or deletion in the DNA sequence, changes the way the mRNA codons are read.
3 Steps to Translation
Initiation: mRNA binds to ribosome
Elongation: amino acids are added to grow the polypeptide chain
Termination: when the ribosome reaches the stop signal
genetic overlap
the idea that more than one codon codes for the same amino acid.
peptide bond
bond formed between two amino acids