Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Transcription and Translation
front 1 transcription | back 1 the process of copying a DNA gene into mRNA takes place in the nucleus product: mRNA |
front 2 translation | back 2 the process of decoding the mRNA codons to build a protein takes place in at the ribosome in the cytoplasm |
front 3 mRNA | back 3 messenger RNA carries the directions to build a protein |
front 4 tRNA | back 4 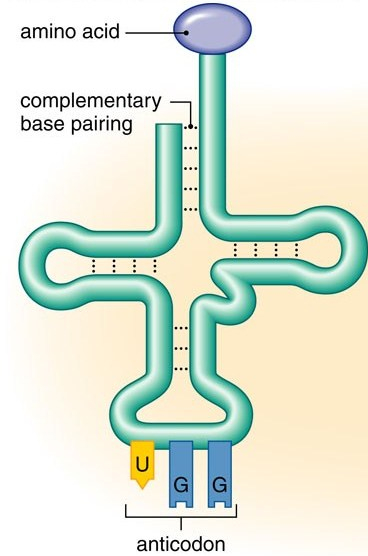 transfer RNA carries the amino acid to the right spot on the mRNA during translation top: amino acid bottom: anticodon |
front 5 rRNA | back 5 ribosomal RNA makes up the ribosome |
front 6 Differences between RNA And DNA | back 6 DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose DNA contains A,G,T,C, RNA contains A, U,G, C DNA : double helix, RNA comes in mRNA ,tRNA , rRNA DNA double stranded, RNA single stranded |
front 7 codon | back 7 sequence of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that codes for one amino acid |
front 8 anticodon | back 8 section on tRNA that pairs with an mRNA codon |
front 9 mRNA processing | back 9 the pre-mRNA has the introns cut out, the exons spliced together and a 5'methyl cap added at one end and a 3' poly A tail at the other |
front 10 RNA polymerase | back 10 the enzyme that copies DNA into mRNA |
front 11 mutation | back 11 change to the DNA |
front 12 point mutation | back 12 when one nucleotide in the sequence is changed, many times it is a substitution |
front 13 frameshift mutation | back 13 more dangerous mutation usually an addition or deletion in the DNA sequence, changes the way the mRNA codons are read. |
front 14 3 Steps to Translation | back 14 Initiation: mRNA binds to ribosome Elongation: amino acids are added to grow the polypeptide chain Termination: when the ribosome reaches the stop signal |
front 15 genetic overlap | back 15 the idea that more than one codon codes for the same amino acid. |
front 16 peptide bond | back 16 bond formed between two amino acids |