Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
College bio midterm review
front 1 Charles Darwin proposed a mechanism for descent with modification
that stated that organisms of a particular species are adapted to
their environment when they possess | back 1 C) heritable traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in the local environment |
front 2 When an electron moves from the 4th principal energy level to the 3rd
principal energy level, energy is: | back 2 A) released |
front 3 The entire "library" of genetic instructions that an
organism inherits is called its | back 3 C)genome |
front 4 Water molecules are attracted to one another by... | back 4 D)hydrogen bond |
front 5 A covalent bond is one in which... | back 5 C)outer shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals |
front 6 Which of the following effects can occur because of the high surface
tension of water? | back 6 B)a raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond |
front 7 Bonds between two atoms that are equally electronegative
are | back 7 D)nonpolar covalent bonds |
front 8 In what type of chemical bond are electrons transferred from metal to
non metal? | back 8 B)ionic |
front 9 To understand the chemical basis of inheritance, we must understand
the molecular structure of DNA. This is an example of the application
of which concept to the study of
biology? | back 9 C)reductionism |
front 10 Water has many exceptional and useful properties. Which is the rarest property among compounds? A)water is a solvent B)water has a high heat capacity C)solid water is less dense than liquid warer D)water has surface tension | back 10 C)solid water is less dense than liquid water |
front 11 In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a
single oxygen atom by | back 11 D)polar covalent bond |
front 12 When are atoms most stable? | back 12 C)when all the electron orbitals in the valence shell are filled |
front 13 Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains.
What are the domains? | back 13 B)bacteria and archea |
front 14 What property of water allows for transport of water against gravity in plants? A)kinetic energy B)cohesion C)surface tension D)specific heat | back 14 B)cohesion |
front 15 Which two particles have approximately the same mass? A)electron and neutron B)neutron and neutrino C)proton and neutron D)proton and electron | back 15 C)proton and neutron |
front 16 Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following? A)the number of protons plus neutrons in the element B)the number of electrons in the element C)the number of protons plus electrons in the elemenr D)the hunger of protons in the element | back 16 A)the number of protonsvolus neutrons in the element |
front 17 A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is called a _______. A)family B)community C)ecosystem D)population | back 17 D)population |
front 18 Which component of a solution is responsible for dissolving? A)unsaturated B)solute C)solvent D)saturated | back 18 C)solvent |
front 19 Which of the following correctly describes a reaction that has reached chemical equilibrium? A)all of the reactants have been converted to the products of the reaction B)the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. C)all of the products have been converted to the reactants of the reaction, D)both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped, with no net effect on the concentration of the reactants and the products. | back 19 B)the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. |
front 20 In comparison to eukaryotes, prokaryotes ______. A)do no have membranes B)are smaller C)are larger D)are more structurally complex | back 20 B)are smaller |
front 21 Which of the following are compounds? A)H2O and O2 B)H2O and CH4, but not O2 C)H2O, O2, and CH4 D)O2 and CH4 | back 21 B)H2O and CH4, but not O2 |
front 22  Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely ______. A)positively charged B)nonpolar C)negatively charged D)without charge | back 22 A)positively charged |
front 23 When a person gets dehydrated while exercising on a hot day, their pituitary gland releases ADH, a hormone that signals the kidneys to retain more water. This is an example of... A)positive feedback regulation B)Emergent properties C)negative feedback regulation D)Chemical cycling | back 23 C)negative feedback regulation |
front 24 You need to write down information about a molecule, but need to indicate only the type and number of atoms it contains. Which representation would work best? A)structural formula B)ball-and-stick model C)space-filling model D)molecular formula | back 24 D) molecular formula |
front 25 Which of the following is property of liquid water? Liquid water _____. A)is non polar B)has a heat of vaporization that is higher than that for mos tother substances C)has a specific heat that is lower than that for most other substances D)is less dense than ice | back 25 B)has a heat of vaporization that is higher than that for most other substances |
front 26 What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atons? A)an ionic bond B)a nonpolar covalent bond C)a polar covalent bond D)a hydrophobic interaction | back 26 C)a polar covalent bond |
front 27 Which of the following solution would require the addition of the greatest amount of base to bring the solution to neutral pH? A)gastric juice at pH 2 B)vinegar at pH 3 C)household bleach at pH 12 D) black coffee at pH 5 | back 27 A) gastric joice at pH 2 |
front 28 From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the phosphorus atom has ____. A)5 neutrons, 5 protons, and 5 electrons B)15 neutrons and 15 protons C)8 electrons in its outermost electron shell D)15 protons and 15 electrons | back 28 D)15 protons and 15 electrons |
front 29 About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A)oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen B)carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen C)carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen D)carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen | back 29 D)carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen |
front 30 A solution with a pH of 5 has how many more protons in it than a solution with a pH of 7? A)5 times B)1000 times C)100 times D)10 times | back 30 C)100 times |
front 31 Hydrophobic substance such as vegetable oil are ____. A)nonpolar substances that repel water molecules B)non polar substances that have an attraction for water molecules C)polar substances that repel water molecules D)polar substances that have an affinity for water | back 31 A)nonpolar substance sthat repel water molecules |
front 32 What type of elements are required by an organism in minute quanitites? B)dietary C)essential | back 32 A)trace |
front 33 The addition of what compound to the water supply is most responsible for ocean solidification? A)O2 B)NaOH C)HCl D)CO2 | back 33 D)CO2 |
front 34 How many electrons are involved in a single covalent bond? A)one B)iodine C)two D)three E)four | back 34 C)two |
front 35 Which of these provide evidence of a common ancestry of all
life? B)structure of chloroplasts C)structure of the nucleus D)structure of cilia | back 35 A)near universality of the genetic code |
front 36 Which of the following statements is true about buffer solutions? A)they fluctuate in pH when either acids or bases are added to them B)they maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but not when acids are added to them. C)they maintain a constant pH when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them D)they maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them | back 36 D)they maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them |
front 37 Isotopes of a given element have the same number of what? A)protons B)orbitals C)electrons D)neutrons | back 37 A)protons |
front 38 In the organism Culex pipiens - Culex refers to the organism's A)kingdom B)species C)family D)genus | back 38 D)genus |
front 39 A substance that contains more hydroxide ions than hydronium ions is termed? A)acidic B)neutral C)saturated D)basic | back 39 D)basic |
front 40 Which of the following types of cells utilize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as their genetic material but do not have their DNA encased within a nuclear envelope? A)plant B)animal C)fungi D)archaean | back 40 D)archaean |
front 41 For an ecosystem to be self-sustaining it requires a constant flow of energy into the system and A)interactions with the environment B)consumers C)feedback regulation D)cycling of nutrients | back 41 D)cycling of nutrients |
front 42 Water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with ____. A)chloride ions B)oxygen gas O2 molecules C)compounds that have polar covalent bonds D)oils | back 42 C)compounds that have polar covalent bonds |
front 43 Acids release which type of ion in solution A)hydration B)hydroxide C)water D)hydrogen | back 43 D)hydrogen |
front 44 Cell are _____. A)only found in pairs because single cells cannot exist independently B)characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms C)characteristics of eukaryotic but not prokaryotic organisms D)limited in size to 200 and 50 micrometers in diameter | back 44 B)characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms |
front 45 Which subatomic particle is responsible for the activity of the aotm? A)neutron B)electron C)proton D)alpha particle | back 45 B)electron |
front 46 Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reaction and hydrolysis? A)Dehydration reactions and hydrolysis reactions assemble polymers from monomers. B)Dehydration reactions assemble polymers; hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart. C).Dehydration reactions eliminate water from membranes; hydrolosis reactions add water to membranes D)Hydrolysis reactions create polymers and dehydration reactions create monomers. | back 46 B)Dehydration reactions assemble polymers;hydrolosis reactions break polymers apart. |
front 47 Which of these classes of biological molecules does NOT include polymers? A)proteins B)nucleic acids C)carbohydrates D)lipids | back 47 D)lipids |
front 48 Which polysaccharide is an important component in the structure of many animals and fungi? A)cellulose B)amylopectin C)chitin D)anylose | back 48 C)chitin |
front 49 A molecule with the chemical formula C6H12O6 is probably a ____. A)polysaccharide B)nucleic acid C)monosaccharide D)fatty acid | back 49 C)monosaccharide |
front 50 What is the major structural difference between starch and glycogen? A)whether glucose is in the α or β form B)The amount of branching that occurs in the molecule C)the types of monosaccharide subunits in the molecule D)they type of glycosidic linkages in the molecule | back 50 B)the amount of branching that occurs in the molecule |
front 51 How do phospholipids interact with water molecules? A)phospholipids do not interact with water because water is polar and lipids are nonpolar. B)Phospholipids dissolve in water C)The polar head interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not D)the polar heads avoid water; the nonpolar tails attract water (Because water is polar and opposites attract) | back 51 C)the polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not |
front 52 Lipids ______. A)are made by dehydration reactions B)are insoluble in water C)are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and nitrogen D)contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates | back 52 B)are insoluble in water |
front 53  The molecule shown the accompanying figure is a ____. A)protein B)steroid C)phospholipid D)fatty acid | back 53 B)steroid |
front 54 Saturated fatty acids ______. A)are usually produced by plants B)have double bonds between carbon atoms of the fatty acids C)are usually liquid at room temperature D)are the principal molecules in lard and butter | back 54 D)are the principle molecules in lard and butter |
front 55 Which one of the following is NOT a component of each monomer used to
make proteins? B)a side chain, R C)a carboxyl group, COOH D)an amino functional group, NH2 | back 55 A)phosphorus atom P |
front 56 The tertiary structure of a protein is the ____. A)unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide B)overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits C)order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain D)organization of a polypeptide chain into a α-helix or β-pleated sheet | back 56 A)unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide |
front 57 Which level of protein structure do the α-helix or β-pleated sheet represent? A)primary B)secondary C)tertiary D)quaternary | back 57 B)secondary |
front 58 Which of the following is the strongest evidence that protein structure and function are correlated? A)proteins function best at certain temperatures B)denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally C)proteins have four distinct levels of structure and many functions D)enzymes tend to be globular in shape | back 58 B)denature (unfolded) proteins do not function normally |
front 59 What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins? A)renaturing protein B)tertiary protein C)denaturing protein D)chaperonin | back 59 D)chapteronin |
front 60  The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure _____. A)joins 2 fatty acids together B)is a hydrolysis reaction C)links 2 polymers to form a monomer D)results in a peptide bond | back 60 D)results in a peptide bond |
front 61 Which of the following includes all of the pyrimidines found in RNA
and DNA? B)cytosine and uracil C)cytosine, uracil, and thymine D)cytosine, uracil, and guanine | back 61 C)cytosine, uracil, and thymine |
front 62 Nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers? A)nucleotides B)amino acids C)sugars D)nitrogenous bases | back 62 A)nucleotides |
front 63 Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules
known as nucleotides? B)nitrogenous base and a phosphate group C)a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine D)a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar | back 63 D)a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar |
front 64 One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to _______. A)function in the synthesis of proteins B)make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity C)the bases in DNA contain sugars, whereas the bases in RNA do not contain sugars D)DNA encodes herediary information whereas RNA does not | back 64 A)function in the synthesis of proteins |
front 65 Which of the following statements best summarize the differences between DNA and RNA? A)DNA contains the base uracil, whereas RNA contains the base thymine B)DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides C)The bases in DNA contain sugars, whereas the bases in RNA do not contain sugar D)DNA encodes heredity information, where as RNA does not | back 65 B)DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides |
front 66 Cell size is limited by _____. A)the number of proteins within the plasma membrane B)surface to volume ratios C)the size of the endomembrane system D)the surface area of mitochondria in the cytoplasm | back 66 B)surface to volume ratios |
front 67 All of the following are parts of a prokaryotic cell EXCEPT A)ribosomes B)an endoplasmic reticulum C)a plasma membrane D)a cell well | back 67 B)an endoplasmic reticulum |
front 68 Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. hat
are the domains? B)archaea and protista C)bacteria and protista D)bacteria and eukarya | back 68 A)bacteria and archaea |
front 69 Which structure is common to plants and animal cells? B)mitochondrion C)centriole D)central vacuole | back 69 B)mitochondrion |
front 70 What is the function of the nuclear pore complex found in
eukaryotes? C)It assembles ribosomes from raw materials that are synthesized in the nucleus D)It synthesizes the proteins required to copy DNA and make mRNA | back 70 B)It regulates the movement of proteins and RNAs into and out of the nucleus |
front 71 Which of the following micromolecules leaves the nucleus of a
eukaryotic cell through pores in the nuclear
membrane? C)phospholipids D)mRNA | back 71 D)mRNA |
front 72 Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in
producing which of the following molecules? B)nucleic acids C)proteins D)lipids | back 72 C)proteins |
front 73 Which organelle often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell? B)Golgi apparatus C)vacuole D)peroxisome | back 73 C)vacuole |
front 74 Which structure is NOT part of the endomembrane system? B)nuclear envelope C)golgi apparatus D)cholorplast | back 74 D)cholorplast |
front 75 A cell with an extensive area of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is specialized to _______. A)synthesize large quantities of lipids B)import and export protein molecules C0play a role in storage D)actively exports protein molecules | back 75 A)synthesize large quantities of lipids |
front 76 Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating andbecome clogged with very large, complex, undigested lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition? A)mitochondrion B)the lysosome C)Golgi apparatus D)the endoplasmic reticulus | back 76 B)the lysosome |
front 77 Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell? A)Golgi vesicles B)roughER C)free cytoplasmic ribosomes D)plasmodesmata | back 77 B)rough ER |
front 78 What is the most likely pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein
that will be secreted by a cell? B)Golgi -> ER ->lysosome C)ER -> Golgi -> nucleus D)ER -> Golgi -> vesiscles that fuse with plasma membranes | back 78 D)ER -> Golgi -> vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane |
front 79 Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells? A)peroxisome B)mitochondrion C)Golgi apparatus D)lysosome | back 79 B)mitochondrion |
front 80 Cyanide binds with at least one molecule involved in producing ATTP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the ____. A)endoplasmic reticulum B)peroxisomes C)mitochondria D)lysosomes | back 80 C)mitochondria |
front 81 In a plant cell, DNA may be found _______. A)in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts B)only in the nucleus C)only in the nucleus and chloroplasts D)in the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes | back 81 A)in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts |
front 82 Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules,
consisting of 9 doublets of microtubules surrounding a pair of single
microtubles? B)motile cilia and primary (nonmotile) cilia C)centrioles and basal bodies D)flagella and motile cilia | back 82 D)flagella and motile cilia |
front 83 Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through _____. A)gap junctions B)desmosomes C)plasmodesmata D)tight junctions | back 83 A)gap junctions |
front 84 Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is
true? B)chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would have little effect on a cell's response to external stimuli C)movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other D)the cytoskeleton of eukaryotes is a static structure most resembling scaffolding used at construction sites | back 84 C)movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other |
front 85 Where would you expect to find tight junctions? B)in the epithelium of an animal's stomach C)between the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and the rough endoplasmic reticulum D)in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes | back 85 B)in the epithelium of an animal's stomach |
front 86 Which of the following membrane activities requires energy from
ATP? B)movement of carbon dioxide of a paramecium C)facilitated diffusion of chloride ions across the membrane through a chlorine channel D)movement of NA+ ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid | back 86 D)movement of NA+ ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid |
front 87 Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking
down large molecules into smaller oes? B)anabolism (anabolic pathways) C)metabolism D)dehydration | back 87 A)catabolism (catabolic pathways) |
front 88 White blood cells engulf bacteria using _______. A)receptor mediated endocytosis B)pinocytosis C)osmosis D)phagocytosis | back 88 D)phagocytosis |
front 89 Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase. The zinc most likely functions as _____. A)an allosteric activator of the enzyme B)a noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme C)a coenzyme derived from a vitamin D)a cofactor necessary for enzyme activity | back 89 D)a cofactor necessary for enzyme activity |
front 90 Which of the following allows water to move much faster across cell membranes? B)ATP C)peripheral proteins D)the sodium potassium pump | back 90 A)aquaporins |
front 91 The active site of an enzyme is the region that _______. A)binds noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzyme B)is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor C)is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme D)binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme | back 91 C)is involved in the catalystic reaction of the enzyme |
front 92 Which of the following statements is representative of he second law
of thermodynamics? B)cells require a constant input of energy to maintain their high level of organization C)conversion of energy from one form to another is always accompanied by some gain of free energy. D)every energy transformation by a cell decreases the entropy of the universe. | back 92 B)cells require a constant input of energy to maintain their high level of organization |
front 93 Which of the following most accurately describes selective permeability? A)Lipid-soluble molecules pass through a membrane B)there must be a concentration gradient for molecules to pass through a membrane C)only certain molecules can cross a membrane D)an input of energy is required for transport | back 93 C)only certain molecules can cross a cell membrane |
front 94 According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis _____. A)the binding of the substrate depends on the shape of the active site B)the active site creates a microenvironment ideal for the reaction C)some enzymes change their structure when activators bind to the enzyme D)The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site. | back 94 D)The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site. |
front 95 A sodium-potassium pump ______. A)moves three potassium ions out of a cell and two sodium ions into a cell while consuming 2 ATP in each cycle B)move three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell and generate an ATP in each cycle C)move 3 sodium ions out of a cell and 2 potassium ions into a cell hile consuming ATP for each cycle D)moves 3 potassium ions out a cell and 2 sodium ions into a cell while producing an ATP for each cycle | back 95 C)move 3 sodium ions out of a cell and 2 potassium ions into a cell hile consuming ATP for each cycle |
front 96 Diffusion ______. A)is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration B)requires integral proteins in the cell membrane C)requires an expenditure of energy by the cell D)is very rapid over long distances | back 96 A)is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration |
front 97 The voltage across a membrane is called the ____. A)electrochemical gradient B)chemical gradient C)membrane potential D)osmotic potential | back 97 C)membrane potential |
front 98 Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of
a plasma membrane most rapidly? B)an amino acid C)glucose D)K+ | back 98 A) CO2 |
front 99 Which of the following is true of osmosis? B)in osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration C)osmosis only takes place in red blood cells. D)in osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration. | back 99 D)in osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration. |
front 100 A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best described as _____. A)spontaneous B)enthalpic C)endergonic D)exergonic | back 100 C)endergonic |
front 101 You have isolated a previously unstudied protein, identified its
complete structure in detail, and determined that it catalyzes the
breakdown of a large substrate. You notice it has two binding sites.
One of these is large, apparently the bonding site for the large
substrate; the other is small, possibly a binding site for a
regulatory molecule. What do these findings tell you about the
mechanism of this protein? B)it is probably an enzyme that works through allosteric regulation C)it is probably a cell membrane transport protein-like an ion channel D) it is probably a structural protein that is involved in cell-to-cell adhesion | back 101 B)it is probably an enzyme that works through allosteric regulation |
front 102 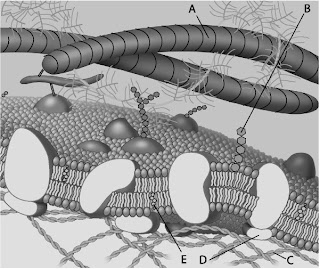 Which component is cholesterol? | back 102 D)E |
front 103  Which component is a peripheral protein? | back 103 D)D |
front 104  Which component is a glycolipid? | back 104 B)B |
front 105 For a protein to be an integral membrane protein, it would have to be ___. A)hydrophilic B)amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region C)exposed on only one surface of the membrane D)hydrophobic | back 105 B)amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region |
front 106 Which of these are NOT embedded in the hydrophobic portion of the
lipid bilayer at all? B)integral proteins C)peripheral proteins D)all of these are embedded in the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer | back 106 C)peripheral proteins |
front 107  Which curve(s) on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH
profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly
alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher? | back 107 A)curves 3 and 5 |
front 108  Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acid. A) curves 1 and 5 B) curves 1 and 4 C) curves 2 and 4 D) curves 3 and 4 | back 108 B)curves 1 and 4 |
front 109 A noncompetitive inhibitor decreases the rate of an enzyme reaction by __. A)changing the shape of the enzyme's active site B)acting as a coenzyme for the reaction C)binding at the active site for the enzyme D)changing the free energy change of the reaction. | back 109 A)changing the shape of the enzyme's active site |
front 110 HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. In the mid-1990s, researchers
discovered an enzyme in HIV called protease. Once the
enzyme's structure was known, researchers began looking for drugs that
would fit into the active site and block it. If this strategy for
stopping HIV infections were successful, it would be an example of
what phenomenon? B)vaccination C)competitive inhibition D)allosteric regulation | back 110 C)competitive inhibition |
front 111 What kind of molecules pass through a cell membrane most
easily? B)large and hydrophobic C)large polar D)ionic | back 111 A)small and hydrophobic |
front 112 The mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway is most precisely described as _____. A)allosteric inhibition B)feedback inhibition C)metabolic inhibition D)noncooperative inhibition | back 112 B)feedback inhibition |
front 113 You have discovered an enzyme that can catalyze two different
chemical reactions. Which of the following is most likely to be
correct? B)Two types of allosteric regulation occur: the binding of one molecule activates the enzyme, while the binding of a different molecule inhibits it. C)the enzyme contains alpha-helixes and beta-pleated sheets. D)Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the reactants involved in the two reactions are very similar in shape and size. | back 113 D)Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the reactants involved in the two reactions are very similar in shape and size. |
front 114 The lock and key model analogy for enzymes applies to the specificity of enzymes _____. A)interacting with ions B)binding to their substrate C)as they form their tertiary and quaternary structure D)interacting with water | back 114 B)binding to their substrate |
front 115 Which of the following is true of enzymes? A)enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by providing activation energy to the substrate. B)enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by providing activation energy to the substrate. C)enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering activation energy barriers D)enzyme function is increased if the 3D structure or conformation of an enzyme is altered. | back 115 C)enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering activation energy barriers |
front 116 Anabolic pathways ____. A)release energy as they degrade from polymers to monomers B)consume energy to decrease the entropy of the organism and its environment C)are usually highly spontaneous chemical reactions D)consume energy to build up polymers from monomers | back 116 D)consume energy to build up polymers and monomers |
front 117 Which of the following processes includes all the others? B)facilitated diffusion C)transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient D)passive transport | back 117 D)passive transport |
front 118 Which of the following is true for all exergonic reactions A)the reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy B)the reaction goes only in a forward direction: all reactants will be converted to products, but no products will be converted to reactants. C)a net input of energy from the surroundings is required for the reactions to proceed. D) the products have more total energy than the reactants. | back 118 A)the reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy |
front 119 A patient was involved in a serious accident and lost a large quantity of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water--equal to the volume of blood lost--is added to the blood directly via one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A)the patients red blood cells will burst because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells. B)the patients red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells C)the patients red blood cells will shrivel up because the boood has become hypotonic compared to the cells D)the patients red blood cells will swell and possibly burst because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells. | back 119 D)the patients red blood cells will swell and possibly burst because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells. |
front 120 The force driving simple diffusion is _____, while the energy source for active transport is _____. A)phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP B)transmembrane pumps; electron transport C)the concentration gradient; ATP D)the concentration gradient; ADP | back 120 C)the concentration gradient; ATP |
front 121 Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a carrier protein in a plasma membrane? A)it works against diffusion B)it requires the expenditure of cellular energy to function C)it exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule D)it has no hydrophobic regions | back 121 C)it exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule |
front 122  How do cells use the ATP cycle shown in the figure? A)cells use the cycle to recycle ADP, phosphate, and the energy by ATP hydrolysis. B)cells use the cycle to recycle energy released by ATP hydroylsis C)cells use the cycle to recycle ADP and phosphate D)cells use the cycle primarily to generate heat | back 122 C)cells use the cycle to recycle ADP and phosphate |
front 123 Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of the figure? A)ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work, B)Pi acts as a shuttle molecule to move energy from ATP to ADP C) Energy from catabolism can be used directly for performing cellular work. D)ATP + Pi are set of molecules that store energy for catabolism | back 123 A)ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work, |
front 124 Which of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics? A)energy cannot be transferred or transformed B)energy cannot be created or destroyed C)the entropy of the universe is decreasing D)the entropy of the universe is constant | back 124 B)energy cannot be created or destroyed |
front 125 The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that _____. A)pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity B)pinocytosis increases the surface area of the plasma membrane, where as receptor mediated endocytosis decreases the plasma membrane surface area C)pinocytosis brings only water molecules into the cell, but receptor mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well D)pinocytosis can concentrate substances from the extra cellular fluid, but receptor mediated endocytosis cannot | back 125 A)pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity. |
front 126 When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes _____. A)reduced B)hydrolyzed C)oxidized D)an oxidizing agent | back 126 C)oxidized |
front 127 When a molecule of NAD+ gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton) the molecule becomes _____. A)dehydrogenated B)reduced C)oxidized D)redoxed | back 127 B)reduced |
front 128 The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A)gycolosis B)accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain C)the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA D)the citric acid cycle | back 128 B)accepting electrons st the end of the electron transport chain |
front 129 Where does the process of glycolysis occur in the cell? A)cytoplasm B)mitochondria matrix C)inner mitochondrial membrane D)christae | back 129 A)cytoplasm |
front 130 Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy-containing products of glycolysis are _____. A)2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP B) 6CO2, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP C)2 FADH2, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP D)2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP | back 130 A)2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP |
front 131 In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate ______. A)two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced B)two molecules of ATP are used and six muldcules of ATP are produced C)two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced D)four molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced | back 131 A)two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced |
front 132 Pyruvate must be converted into what molecule for it to enter the citric acid cycle? A)oxaloacetate B)G3P C)acetyl co-A D)ferradoxin | back 132 C)acetyl co-A |
front 133 Which electron carriers function in the cytric acid cycle? A)NADH and FADH2 B)NAD+ only C)ADP and ATP D)the electron transport chain | back 133 A)NADH and FADH2 |
front 134 For each turn of the citric acid cycle, how many of each molecule are produced? A)1 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 B)0 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 C)2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 D)2 ATP, 1 NADH, 3 FADH2 | back 134 A)1 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 |
front 135 Where in the cell does the citric acid cycle take place? A)mitochondrial matrix B)cytopalsm C)inner mitochondrial membrane D)nucleus | back 135 A)mitochondrial matrix |
front 136 Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located? A)mitochondrial outer membrane B)mitochondrial intermembrane space C)mitochondrial matrix D)mitochondrial inner membrane | back 136 D)mitochondrial inner membrane |
front 137 Which of the following events takes place in the electron transport chain? A)the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules B)substrate-level phosphorlyation C)the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycld D)the breakdown of an acetyl group to carbon dioxide | back 137 C)the extraction of energy from high energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle |
front 138 During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence A)glucose -> ATP -> electron transport chain -> NADH B)glucose -> NADH -> electron transport chain -> oxygen C)food -> glycolysis ->citric acid cycle -> NADH -> ATP D)glucose -> pyruvate -> ATP -> oxygen | back 138 B)glucose -> NADH -> electron transport chain -> oxygen |
front 139 Approximately how many molecule of ATP are produced from the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose (C6H12O6) in aerobic cellular respiration? A)2 B)30-32 C)4 D)18-24 | back 139 B)30-32 |
front 140 Which of the following normally occurs of whether or not oxygen (O 2) is present? A)oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis) B)citric acid cycle C)fermentation D)glycolysis | back 140 D)glycolysis |
front 141 Which of the following occurs in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell? A)oxidation of pyruvate to acytol CoA B)citric acid cycle C)glycolysis and fermentation D)fermentation and chemiosmosis | back 141 C)glycolysis and fermentation |
front 142 In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of A)ATP, CO2, ethanol (ethyl alcohol) B)ATP, NADH, and pyruvate C)ATP, CO2, and lactate D)ATP, pyruvate, and acetyl CoA | back 142 A)ATP, CO2, ethanol (ethyl alcohol) |
front 143 Why is glycolysis considered to be one of the first metabolic pathways to have evolved? A)it does not involve organelles or specialized structured, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms B)it requires the presence of membrane- enclosed organelles are found only in eukaryotic celk C)it produces much less ATP than does oxidative phosphorylation D)it is found in prokaryotic cells but not in eukaryotic cells | back 143 A)it does not involve organelles or specialized structured, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms |
front 144 The process of photosynthesis probably originated ____. A)in plants B)three separate times duringe evolution C)in prokaryotes D)in fungi | back 144 C)in prokaryotes |
front 145 Plants in photosynthesize _____. A)and respire only in the light B)only in the light but respire in light and dark C)only in the dark but respire only in the light D)only in the light but respire only in the dark | back 145 B)only in the light but respire in light and dark |
front 146 Early investigators thought the oxygen produced by photosynthesis plants came from carbon ____. A)air B)glucose C)electrons from NADPH D)water | back 146 D) water |
front 147  The figure shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different? A)Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a. B)Green and yellow wavelengths inhibit the absorption of red and blue wavelengths. C)Oxygen given off during photosynthesis interfere with the absorption of light D)aerobic bacteria take up oxygen, which changes the measurement of the rate of photosynthesis | back 147 A)other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a |
front 148  What wavelength of light in the figure is most effective in driving photosynthesis? A)625mm B)420mm C)575mm D)730mm | back 148 B)420mm |
front 149 A spaceship is designed to support animals life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide since the spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an artificial light source will be needed. A)green light B)a mixture of blue and red light C)UV light D)full spectrum white light | back 149 B)a mixture of blue and red light |
front 150 Suppose a plant has a unique photosynthesis pigment and the leaves of this plant appear to be reddish yellow. What wavelengths of visible light are absorbed by this pigment? A)red and yellow B)green and yellow C)blue and violet D)blue, green, and yellow | back 150 C)blue and violet |
front 151 What event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll (or other pigment molecules of the antenna complex)? A)ATP is synthesized of energy absorbed B)A carboxylation reaction of the Calvin cycle occurs. C)an electron is excited. D)electrons are stripped from NADPH | back 151 C)an electron is excited. |
front 152 What are the products of linear electron flow? A)ATP and P700 B)heat and fluorescense C)ATP and NADPH D)ADP and NADPH | back 152 C)ATP and NADPH |
front 153 What are the products of cyclic electron flow? A)ATP and P700 B)ATP and NADPH C)ATP only D)ADP and NADP+ | back 153 C)ATP only |
front 154 In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located? A)inner mitochondrial membrane only B)thylakoid membrane and plasma membrane C)thylakoid membrane only D)thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane | back 154 D)thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane |
front 155 In mitochondria, chemiosmosis moves protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, whereas in chloroplasts, chemiosmosis moves protons from the _____. A)thylakoid space to the stroma B)matrix to the stroma C)intermembrane space in the matrix D)stroma to the thylakoid space | back 155 D)stroma to the thylakoid space |
front 156 Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration? A)photosynthesis occurs only in plants; respiration occurs only in animals B)photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases energy from complex organic molecukes C)photosynthesis in catabolic; respiration in anabolic D)respiration runs the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis in reverse | back 156 B)photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases from complex organic molecules |
front 157 In a plant, the reactions that produce molecular oxygen (O2) take place in ____. A)the light reactions alone B)neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle C)the light reactions and the Calvin cycle D)the Calvin cycle alone | back 157 A)the light reactions alone |
front 158 Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin cycle? A)ADP, Pi, and NADP+ B)ATP and NADPH C)CO2 and glucose D)H2O and O2 | back 158 B)ATP and NADPH |
front 159 Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A)interior of the thylakoid (thylakoid space) B)thylakoids membrsne C)stroma of the chloroplast D)outer membrane of the chloroplast | back 159 C)stroma of the chloroplast |
front 160 What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle? A)synthesize simple sugars from carbon dioxide B) split water and release oxygen C) transport RuBP out of the chloroplast D)use NADPH to release carbon dioxide | back 160 A)synthesize simple sugars from carbon dioxide |
front 161 The alternative pathways of photosynthesis using the C4 or CAM systems are said to be compromises. Why? A)CAM plants allow more water loss, while C4 plants allow less CO2 into the plant. B)C4 compromises on water loss and CAM compromises on photorespiration C)Each one minimizes both water loss and rate of photosynthesis D)Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation | back 161 D)Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation |
front 162 Photorespiration _____. A) consumes carbon dioxide and generate ATP, sugars, and oxygen B)generates carbon dioxide and consumes ATP and oxygen C)generates ATP and sugars and consumes oxygen and carbon dioxide D)generates oxygen and consumes ATP, carbon dioxide, and sugars | back 162 B)generates carbon dioxide and consumes ATP and oxygen |
front 163 Every ecosystem must have ____. A)producers and primary consumers B)photosynthesizers C) autotrophs D)autotrophs and heterotrophs | back 163 C)autotrophs |
front 164 Which of the following does NOT occur during the Calvin cycle? A)regeneration of the CO2 acceptor B)consumption of ATP C)release of oxygen D)oxidation of NADPH | back 164 C)release of oxygen |
front 165 CAM plants keep stomata closed in the daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they ____. A)fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells B)fix CO2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells C)fix CO2 into organic acids during the night D)use photosystem I and photosystem II at night | back 165 C)fix CO2 into organic acids during the night |
front 166 In yeast signal transduction, a yeast cell released a mating factor which ______. A)passes through the membranes of neighboring cells, bind to DNA, and initiates transcription B)diffuses through the membranes of distant cells, causing them to produce factors that initiate long distance migrations C)acts back on the same cell that secreted the mating factor, changing its development D)binds to receptors on the membranes of other types of yeast cells | back 166 D)binds to receptors on the membranes of other types of yeast cells |
front 167 Which of the following is a type of a local signaling in which a cell secretes a signal molecule that affects neighboring cells? A)a synaptic signaling B)paraffins signaling C)autocrine sigjaling D)hormonal signaling | back 167 b)paracrine signaling |
front 168 Hormones are chemical substances produced in one organ that are released into the bloodstream and affect the function of a target organ. For the target organ to respond to a particular hormone, it must ____. A)have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule B)be from the same cell type as the organ that produces the hormone C)modify its plasma membrane to alter the hormone entering the cytoplasm D)experience an imbalance that disrupts its normal function | back 168 A)have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule |
front 169 A G-protein receptor with a GTP bound to it ____. A)Directly affects gene expression B)signals a protein to maintain its shape and conformation C)will use cGMP as a second messenger D)is in its active state | back 169 D)is in its active state |
front 170 One of the major categories of receptors in the plasma membrane reacts by forming diners, adding phosphate group, and then activating relay proteins. Which type does this? A)steroid receptors B)G protein-coupled receptors C)ligand-gated ion channels D)receptor tyrosine kinases | back 170 D)receptor tyrosine kinases |
front 171 Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane? A)ligand-gated ion channel B)receptor tyrosine kinase C)intracelluoar receptor D)g protein coupled receptor | back 171 A)ligand-gated ion channel |
front 172 If an animal cell suddenly lost the ability to produce GTP, what might happen to its signaling system? A)it would employ a transduction pathway directly from an external messenger B)it would use ATP instead of GTP to activate and inactivate the G protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane C)It would not be able to activate and inactivate G protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane D)it would be able to carry out reception and transduction but would not be able to respond t is signal. | back 172 C)It would not be able to activate and inactivate G protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane |
front 173 Which of the following would be inhibited by a drug that specifically blocks the addition of phosphate groups to proteins? A)G-protein coupled receptor bindinf B)adenylyl cyclase activity C)receptor tyrosine kinase activity D)ligand gated ion channel signaling | back 173 C)receptor tyrosine kinase activity |
front 174 What does it mean to say that a signal is transducer? A)the signal enters the cell directly and binds to a receptor inside B)the signal is amplified, such than ever a signal molecule evokes a large response C)the signal triggers a sequence of phosphorylation events inside the cell D)the physical form of the signal changes from one form to another | back 174 D)the physical form of the signal changes from one form to another |
front 175 In general, a signal transmitted via phosphorlyation of a series of proteins _____. A)results in a conformational change to each protein B)activates a transcription event C)requires binding of a hormone to a intracellular receptor D)generates ATP in the process of signal transduction | back 175 A)activates a transcription event |
front 176 Protein kinases is an enzyme that ____. A)activates or inactivated other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them B)functions as a second messenger molecules C)produces second messenger molecules D)generates ATP in the process of signal transduction | back 176 A)activates or inactivated other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them |
front 177 Protein kinase is an enzyme that ____. A)activates or inactivated other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them B)functions as a second messenger molecule C)produces second messenger molecules D)serves as a receptor for various signal molecules | back 177 A)activates or inactivated other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them |
front 178 In signal transduction, phosphatases ___. A)inactivated protein kinases and turn off the signal transduction B)prevent a protein kinase from being reused when there is another extracellular signal C)move the phosphate group of the transduction pathway D)amplify the second messengers such as cAMP | back 178 A)inactivate protein kinases and turn off the signal transduction |
front 179 Put the steps of the process of signal transduction in the order they occur: 1. A conformational change in the signal receptor complex activates an enzyme 2 protein kinases are activated 3. A signal molecule mines to a receptor 4. Target proteins are phosphorylated 5. Second messenger molecules are released A)3,1, 2, 4, 5 B)1, 2, 5, 3, 4 C)3, 1, 5, 2, 4 D)1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | back 179 C)3, 1, 5, 2, 4 |
front 180 Transcription factors _____. A)control gene expression B)regulate the synthesis of DNA in respeomde to a signal C)transcribe ATP into cAMP D)regulate the synthesis of lipids in the cytoplasm | back 180 A)control gene expression |
front 181 Scaffolding proteins are ____. A)microtubular proteins arrays that allow lipid-soluble hormones to get from the cell membrane to the nuclear pores B)large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate cascade effects C)proteins that can reach into the nucleus of a cell to affect transcription D)relay proteins that orient receptors and their ligand in appropriate directions to facilitate their complexing. | back 181 B)large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate cascade effects |
front 182 Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because they _____. A)counter the harmful effects of phosphatases B)are species specific C)amplify the original signal many times D)always lead to the same cellular response | back 182 C)amplify the original signal many times |
front 183 Which of the following describes the events of apoptosis? A)the cells DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the cells parts are packaged in vesicles are digested by specialized cells B)the cells nucleus and organelles are lysed, then the cell enlarged and burst C)the cell dies, it is lysed, its organelles are phagocytozed, and its contents are recycled D)the cells DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell dies, and its phagocytized | back 183 A)the cells DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the cells parts are packaged in vesicles are digested by specialized cells |
front 184 Apoptosis involves all butt which of the following? A)digestion of cellular contents by scavenger cells B)fragmentation of the DNA C)lysis of the cell D)activation of cellular enzymes | back 184 C)lysis of the cell |
front 185 Cells that are infected, damaged, or have reached the end of their functional life span often undergo programmed cell death. This controlled cell suicide is called apoptosis. Select the appropriate description of this event on a cells life cycle A)apoptosis is regulated by cell surface receptors that signal when a cell has reached its density-dependent limits B)during apoptosis, cellular agents chop up DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell C)during apoptosis, dying cells leak out their contents including digestive enzymes that also destroy healthy cells D)each cell organelles has protein signals that initiate the breakdown of the organelles components which lead to cell death | back 185 B)during apoptosis, cellular agents chop up DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell |
front 186  Which of the following types of signaling is represented in the figure A)synaptic B)autocrine C)hormonal D)paracrine | back 186 A)synaptic |
front 187  In the figure, the dots in the space between the two strictures represent which of the following? A)hormomes B)neurotransmitters C)receptor molecules D)signal transducers | back 187 B)neurotransmitters |
front 188 Which of the following is true of steroid receptors? A)the receptor molecuoes are themselves lipids or glycolipids B)steroid receptors are typically bound to the external surface of the nuclear envelope C)the receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell D)the unbound steroid receptors are quickly recycled by lysosomes | back 188 C)the receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell |
front 189 What is the name of the signaling molecule that binds to a receptor to cause a respone? A)integrin B)transductor C)ligand D)hormone | back 189 C)ligand |
front 190 Which of the following is NOT an example of a second messenger? A)PEP B)IP3 C)DAG D)Ca+2 | back 190 A)PEP |
front 191 When a signal molecule leaves a receptor, the receptor does what? A)response is activated B)signal is amplified C)response is terminated D)signal is transduced | back 191 C)response is terminated |