Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Blood and Circulatory System Disorders
front 1 Blood | back 1
|
front 2 Two Separate Circulations | back 2
|
front 3 The Pulmonary Circulation | back 3 
|
front 4 The Systemic Circulation | back 4 
|
front 5 Arteries | back 5 
|
front 6 Arterioles | back 6 
|
front 7 Capillaries | back 7 
|
front 8 Precapillary Sphincters | back 8 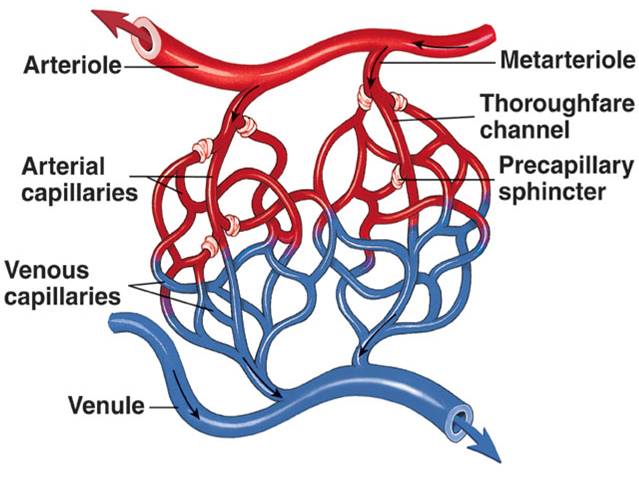
|
front 9 Small Venules | back 9
|
front 10 Veins | back 10
|
front 11 Capacitance Vessels | back 11
|
front 12 Walls of arteries and veins | back 12 
|
front 13 autoregulation | back 13
|
front 14 Causes of local vasodilation | back 14
|
front 15 composition of blood | back 15 
|
front 16 Hematocrit | back 16 
|
front 17 plasma | back 17 
|
front 18 serum | back 18 
|
front 19 Examples of plasma proteins | back 19
|
front 20 albumin | back 20
|
front 21 Fibrinogen | back 21
|
front 22 Red bone marrow | back 22
|
front 23 Erythrocytes or red blood cells | back 23 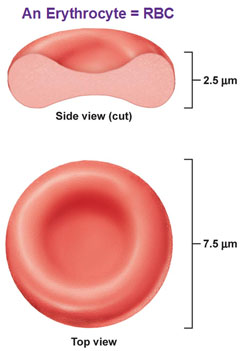
|
front 24 Erythropoietin | back 24
|
front 25 Hemoglobin | back 25 
|
front 26 Oxyhemoglobin | back 26
|
front 27 deoxyhemoglobin | back 27
|
front 28 Leukopoiesis | back 28
|
front 29 leukocytes | back 29
|
front 30 Lymphocytes | back 30
|
front 31 neutrophils | back 31
|
front 32 Basophils | back 32
|
front 33 Eosinophils | back 33
|
front 34 monocytes | back 34
|
front 35 differential count | back 35
|
front 36 Thrombocytes | back 36
|
front 37 Hemostasis (3 steps) | back 37
|
front 38 Heparin | back 38
|
front 39 Blood type | back 39
|
front 40 ABO groups | back 40
|
front 41 type O blood | back 41
|
front 42 type A and B blood | back 42
|
front 43 RH system | back 43
|
front 44 Complete blood count (CBC) diagnostic test for blood | back 44
|
front 45 Leukocytosis | back 45
|
front 46 leukopenia | back 46
|
front 47 increase in eosinophils | back 47
|
front 48 morphology | back 48
|
front 49 Hemoglobin (diagnostic test) | back 49
|
front 50 Reticulocyte Count | back 50
|
front 51 Chemical analysis of the blood | back 51
|
front 52 Bleeding time (diagnostic test) | back 52
|
front 53 prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT) | back 53
|
front 54 partial thromboplastin time | back 54
|
front 55 prothrombin time | back 55
|
front 56 anemia | back 56
|
front 57 Iron deficiency anemia | back 57
|
front 58 Etiology of iron deficiency anemia | back 58
|
front 59 Manifestations of iron deficiency anemia | back 59
* People who have iron deficiency anemia may have unusual craving for nonfood items such as ice, paint, or starch. This craving is called pica |
front 60 Diagnostic tests for Iron deficiency anemia | back 60
|
front 61 Treatment for iron deficiency anemia | back 61
|
front 62 pernicious anemia: vitamin B12 deficiency (megaloblastic anemia) | back 62
|
front 63 Vitamin B12 and nerve cells | back 63
|
front 64 Manifestations of pernicious anemia | back 64
|
front 65 Diagnostic tests for pernicious anemia | back 65
|
front 66 Treatment for Pernicious Anemia | back 66
|
front 67 Aplastic anemia | back 67
|
front 68 Pancytopenia | back 68
|
front 69 Hemolytic Anemia | back 69
|
front 70 What term is used to describe a deficit of all types of blood cells?
| back 70
|
front 71 Capillary walls consist of:
| back 71
|
front 72 Individuals with type O blood are considered to be universal donors because their blood:
| back 72
|
front 73 What causes numbness and tingling in the fingers of individuals with untreated pernicious anemia?
| back 73
|
front 74 What is the cause of oral ulcerations and delayed healing occurring with any severe anemia?
| back 74
|
front 75 Why is pernicious anemia treated with injections of vitamin B12?
| back 75
|
front 76 Why do vascular occlusions and infarcts occur frequently with sickle cell anemia?
| back 76
|
front 77 In cases of polycythemia vera, blood pressure is elevated as a result of:
| back 77
|
front 78 In individuals with pernicious anemia, antibodies form to:
| back 78
|
front 79 Petechiae and purpura are common signs of:
| back 79
|
front 80 Which of the following substances acts as an anticoagulant?
| back 80
|
front 81 Why is excessive bleeding a common occurrence with acute leukemia?
| back 81
|
front 82 Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor involving:
| back 82
|
front 83 The Reed-Sternberg cell is diagnostic for:
| back 83
|
front 84 Which of the following applies to the leukemias?
| back 84
|
front 85 A high percentage of blast cells in the leukocyte population indicates a poor prognosis for an individual with:
| back 85
|
front 86 Which of the following applies to erythropoietin?
| back 86
|
front 87 Microcytic and hypochromic erythrocytes are commonly found as a result of:
| back 87
|