Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Prenatal Development and Birth
front 1 Typical Prenatal Development | back 1
|
front 2 The Germinal Period | back 2
|
front 3 Blastocyst | back 3
|
front 4 Trophoblast | back 4
|
front 5 Implantation | back 5
|
front 6 The Embryonic Period | back 6
|
front 7 Embryo | back 7
|
front 8 Endoderm | back 8 
|
front 9 Mesodem | back 9 
|
front 10 Ectoderm | back 10 
|
front 11 Amnion | back 11 
|
front 12 Amniotic Fluid | back 12 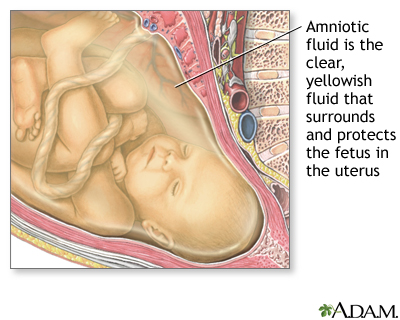
|
front 13 Umbilical Cord | back 13 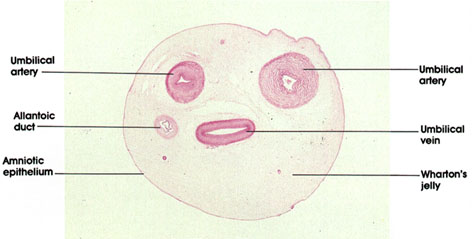
|
front 14 Placenta | back 14 
|
front 15 Organogenesis | back 15
|
front 16 Fetal Period | back 16
|
front 17 The Brain & Prenatal Development | back 17
|
front 18 Neurons | back 18
|
front 19 Nervous System & Prenatal Development | back 19
|
front 20 Anencephaly | back 20 
|
front 21 Spina Bifida | back 21 
|
front 22 Neurogenesis | back 22
|
front 23 Neuronal Migration | back 23
|
front 24 Teratogen | back 24
|
front 25 Teratogen Influence | back 25
|
front 26 Critical Period | back 26
|
front 27 Teratology | back 27
|
front 28 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder | back 28
|
front 29 Normal Gestational Weight Gain | back 29
|
front 30 Prenatal Care | back 30
|
front 31 Stages of Birth | back 31 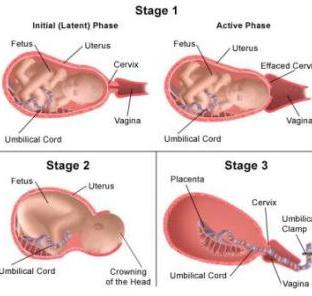
|
front 32 Childbirth Setting & Attendants | back 32
|
front 33 Midwife | back 33 
|
front 34 Doula | back 34 
|
front 35 Methods of Childbirth | back 35
|
front 36 Medication (methods of childbirth) | back 36
|
front 37 Natural Childbirth | back 37 
|
front 38 Prepared Childbirth | back 38 
|
front 39 Cesarean Delivery | back 39 
|
front 40 Breech Position | back 40 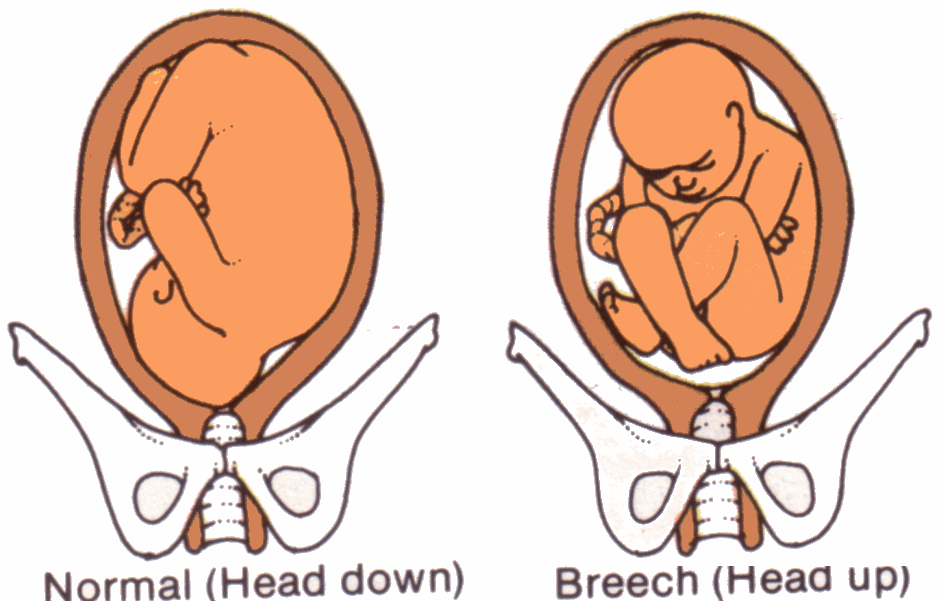
|
front 41 Apgar Scale | back 41 
|
front 42 Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) | back 42
|
front 43 Low Birth Weight Infants | back 43 
|
front 44 Preterm Infants | back 44 
|
front 45 Small for Date Infants | back 45
|
front 46 Nurturing Low-Weight and Preterm Infants | back 46
|
front 47 Kangaroo Care | back 47 
|
front 48 Postpartum Period | back 48
|
front 49 Physical (postpartum adjustments) | back 49
|
front 50 Emotional & Psychological (postpartum adjustments) | back 50
|