Typical Prenatal Development
- begins with fertilization and ends with birth
- takes between 266 to 280 days (38 to 40 weeks)
- divided into
three periods:
- germinal
- embryonic
- fetal
The Germinal Period
- takes place in the first two weeks after conception
- includes the creation of the fertilized egg (called a zygote), cell division, and the attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall
Blastocyst
- the inner layer of cells that develops during the germinal period
- these cells later develop into the embryo
Trophoblast
- the outer layer of cells that develops in the germinal period
- these cells provide nutrition and support the embryo
Implantation
- the attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall
- takes place 11 to 15 days after conception
The Embryonic Period
- the period of prenatal development that occurs from two to eight weeks after conception
- begins as the blastocyst attached to the uterine wall
- the rate of cell differentiation intensifies
- support system for cells form
- organs appear
-
three layers of cells:
- endoderm
- mesoderm
- ectoderm
Embryo
- mass of cells
Endoderm

- inner layer of cells
- will develop into the digestive and respiratory systems
Mesodem

- middle layer of cells
- will develop into the circulatory system, bones, muscles, excretory and reproductive system
Ectoderm

- outermost layer of cells
- will become the nervous system and brain, sensory receptors and skin parts
Amnion

- the life support system
- bag-like
- contains a clear fluid (amniotic fluid) in which the developing embryo floats
Amniotic Fluid
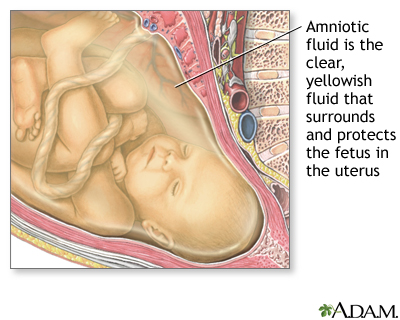
- provides an environment that is temperature and humidity controlled
- shook proof
Umbilical Cord
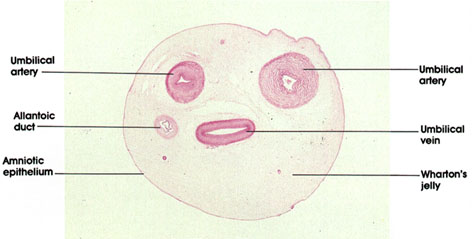
- a life support system
- contains 2 arteries and one vein
- connects the baby to the placenta
Placenta

- life support system
- consists of disk-shaped group of tissues in which small vessels from the mother and offspring interwine
Organogenesis
- organ formation
- takes place during the first two months of prenatal development
- organs are especially vulnerable during this time
- third week after conception = neural tube that eventually becomes spinal cord forms
- about 21 days: eyes begin to appear
- 24 days: the cells of the heart begin to differentiate
Fetal Period
- lasts about seven months
- prenatal period between 2 months after conception to birth
The Brain & Prenatal Development
- neurons handle information processing at the cellular level in the brain
- babies have approx 100 billion neurons by the time they are born
- the third trimester of prenatal development and the first 2 years of postnatal life are characterized by connectivity and functioning of neurons
Neurons
- nerve cells, which handle information processing at the cellular level in the brain
Nervous System & Prenatal Development
- the nervous system begins forming as a long, hollow tube located in the embryos back
- forms about 18 to 24 days after conception
Anencephaly

- the highest regions of the brain fail to develop
- or when head end of the neural tube fails to close
- baby dies in the womb, during childbirth or shortly after birth
Spina Bifida

- results in varying degrees of paralysis of the lower limbs
- usually needs assistive devices: such as crutches, braces, or wheelchairs
- risk factors: maternal diabetes and obesity
- preventive measures: mother take adequate amounts of vitamin B folic acid
Neurogenesis
- the generation of new neurons
Neuronal Migration
- involves cells moving from their point of origin to their appropriate location
- occurs at approx. 6 to 24 weeks
- Once a cell has migrated to its target destination, it must mature and develop a more complex structure
Teratogen
- any agent that can potentially cause a birth defect or negatively affect cognitive and behavioral outcomes
-
Ex:
- food
- drugs
- chemical toxins
Teratogen Influence
-
Dose
- the greater the dose of an agent the greater the effect
-
Gene Susceptibility
- the type or severity of abnormalities caused by a teratogen is linked to both the genotype of the pregnant mother and fetus/embryo
-
Time of Exposure
- exposure to teratogens does more damage when it occurs at some points int development that at others
Critical Period
- a fixed time period very early in development during which certain experiences or events can have a long-lasting effecting on development
Teratology
- field of study that investigates the causes of birth defects
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
- a cluster of abnormalities that appear in the offspring of mothers who drink alcohol heavily during pregnancy
-
Abnormalities
- facial deformities
- defective limbs, face, and heart
- learning problems
Normal Gestational Weight Gain
- 11 to 20 pounds
Prenatal Care
- involves a defined schedule of visits for medical care
-
includes:
- screening for manageable conditions & treatable diseases (that can affect the baby or mother)
- comprehensive educational, social, and nutritional services
- exercise regularly
- helps prevent constipation
- conditions the body
- reduces excessive weight gain
- positive mental state
Stages of Birth
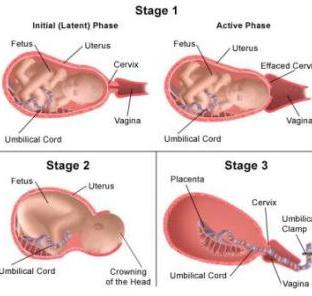
- (first stage)
- uterine contractions are 15 to 20 minutes apart and last up to a minute
- these contractions cause the woman's cervix to stretch and open
- at the end of the first birth stage, contractions dilate the cervix to an opening of about 10 cm (4 in)...so baby can move from the uterus to the birth canal
- lasts an average of 6 to 12 hours
- (second stage)
- begins when the baby's head starts to move through the cervix and the birth canal
- typically lasts 45 mins to 1 hr
- (third stage)
- afterbirth
- the placenta, umbilical cord, and other membranes are detached and expelled
- lasts only a few minutes
- afterbirth
Childbirth Setting & Attendants
- in the US 99% of births take place in hospitals
-
Midwife
- a person qualified to deliver babies and to care for women before, during, and after childbirth
-
Doula
- a caregiver who provides continuous physical, emotional, and educational support for the mother before, during, and after childbirth
Midwife

- a person qualified to deliver babies and to care for women before, during, and after childbirth
Doula

- a caregiver who provides continuous physical, emotional, and educational support for the mother before, during, and after childbirth
Methods of Childbirth
- Medication
- Natural and Prepared Childbirth
- Cesarean Delivery
Medication (methods of childbirth)
-
Analgesia
- used to relieve pain
-
Anesthesia
- used in late first stage of labor
- blocks sensation in an area of the body
- or block consciousness
- epidural block
- regional anesthesia that numbs the woman's body from the waist down
-
Oxytocin
- a synthetic hormone
- used to stimulate contractions
- pitocin (example)
Natural Childbirth

- method that aims to reduce the mother's pain by decreasing her fear
- done through education about childbirth
- teaching breathing methods and relaxation techniques during delivery
Prepared Childbirth

- special breathing technique to control pushing in the final stages of labor
- detailed anatomy and physiology course
Cesarean Delivery

- surgical procedure in which the baby is removed from the mother's uterus through an incision made in her abdomen
Breech Position
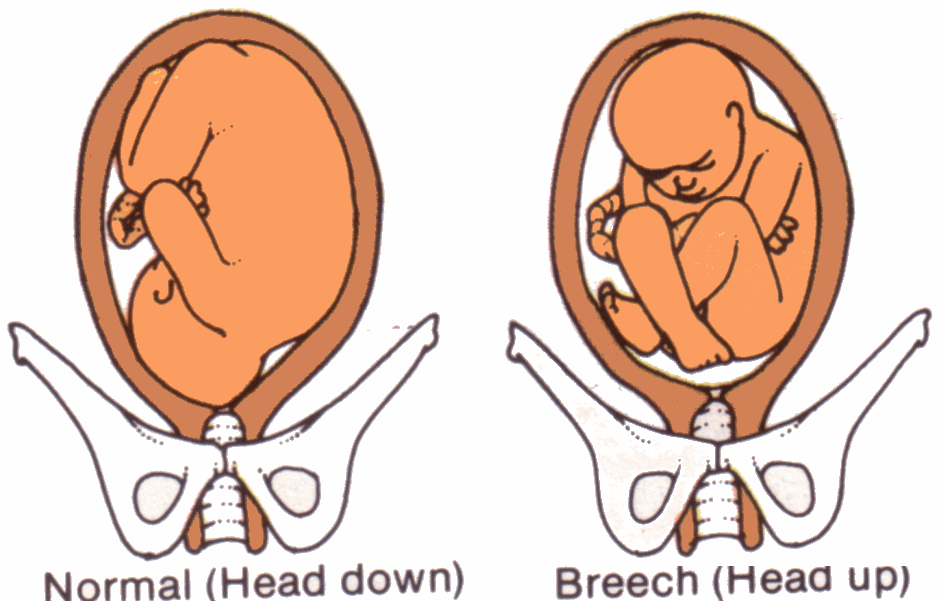
- the baby's position in the uterus causes the buttocks to be the first part to emerge from the vagina
Apgar Scale

- scale used assess the health of newborns at one and five minutes after birth
- evaluates an infants heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, body color, and reflex irritability
- total score of 7 - 10 indicates that the newborn is in good condition
Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS)
- a measure that is used in the first month of life to assess the newborn's neurological development, reflexes, and reactions to people and objects
Low Birth Weight Infants

- weigh less than 5½
Preterm Infants

- infants born before the completion of 37 weeks of gestation
Small for Date Infants
- infants whose birth weights are below normal when the length of pregnancy is considered
Nurturing Low-Weight and Preterm Infants
- kangaroo care
- massage therapy
Kangaroo Care

- involves skin to skin contact between baby and mother
- 2 to 3 hours per day
- helps to stabilize the preterm infant's heartbeat, temperature, and breathing
Postpartum Period
- the period after childbirth when the mother adjusts both physically and psychologically, to the process of childbirth
Physical (postpartum adjustments)
- fatigue
- hormonal changes
Emotional & Psychological (postpartum adjustments)
- Postpartum Depression
- major depression episode
- typically occurs about 4 wks after delivery
- strong feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair