Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Digestive System
front 1  Identify the letter that indicates the cardiac region of the
stomach. | back 1 A |
front 2  Identify the letter that indicates the region of the stomach that
regulates the passage of chyme | back 2 E |
front 3  Identify the letter that indicates folds that allow for expansion of
the stomach. | back 3 C |
front 4  Identify the letter that indicates the curvature where the greater
omentum attaches. | back 4 D |
front 5  Identify the letter that indicates the fundus of the stomach. | back 5 B |
front 6  Identify the letter that indicates the cystic duct. | back 6 C |
front 7  Identify the letter that indicates the hepatic ducts as they exits
the porta hepatis. | back 7 A |
front 8 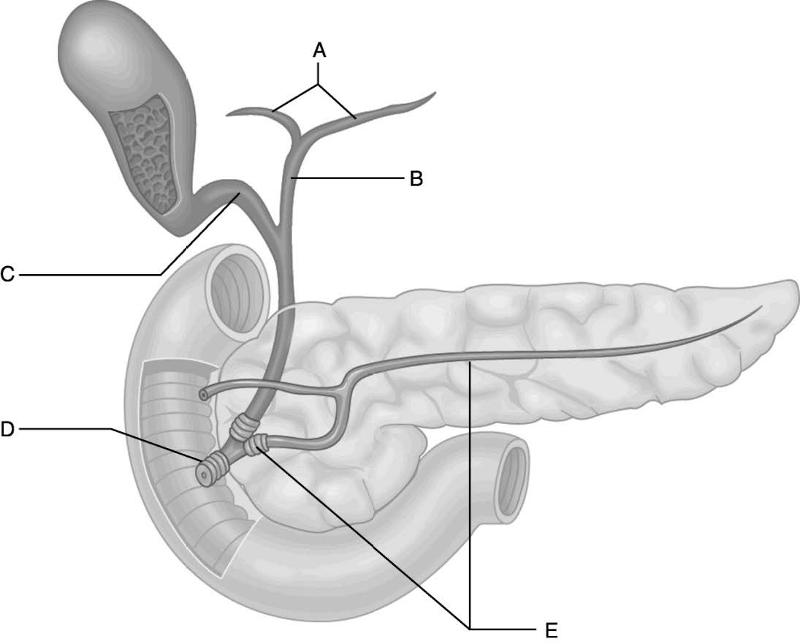 Identify the letter that indicates the duct that carries digestive
enzymes from acinar cells in the | back 8 E |
front 9  Identify the letter that indicates the duct that directs both
digestive enzymes and bile to the | back 9 D |
front 10  Identify the letter that indicates the duct formed by the union of
the right and left hepatic | back 10 B |
front 11  Identify the letter that indicates the root canal. | back 11 E |
front 12  Identify the letter that indicates the crown. | back 12 A |
front 13  Identify the letter that indicates the root. | back 13 C |
front 14  Identify the letter that indicates the surface of the tooth that is
coated with the hardest | back 14 D |
front 15  Identify the letter on the diagram that represents the neck of the
tooth. | back 15 B |
front 16 Retroperitoneal organs have a serosa facing the peritoneal cavity and
a(n) ________ on the | back 16 B |
front 17 Infoldings of the sarcolemma of smooth muscle fibers. | back 17 E |
front 18 Junction of the transverse and ascending colon. | back 18 C |
front 19 The union of the cystic and common hepatic ducts. | back 19 D |
front 20 Smooth muscle constriction between the ileum and cecum. | back 20 D |
front 21 Attaches the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach. | back 21 E |
front 22 Attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and
diaphragm. | back 22 C |
front 23 Layer of the GI tract responsible for peristalsis and
segmentation. | back 23 B |
front 24 Bulblike union of the main pancreatic duct and bile duct. | back 24 D |
front 25 Three strips of longitudinal muscles of the muscularis of the colon
causing it to pucker into | back 25 C |
front 26 Which layer of the digestive tract is responsible for the peristaltic
waves that propel materials | back 26 A |
front 27 Which of the following choices correctly pairs a type of cell in the
stomach with its | back 27 B |
front 28 Which of the following is not a characteristic of the large
intestine? | back 28 C |
front 29 The digestive organ primarily responsible for the absorption of water
is the | back 29 D |
front 30 Another name for serosa is | back 30 C |
front 31 Medial to both midclavicular lines and superior to the subcostal
plane lies the | back 31 D |
front 32 To say someone is "tongue-tied" means that the | back 32 D |
front 33 The lesser omentum extends between the | back 33 B |
front 34 The splenic, or left colic, flexure of the colon is located within
the | back 34 A |
front 35 Which of the following is not contained in saliva? | back 35 A |
front 36 How many deciduous teeth are there? | back 36 B |
front 37 Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) is primarily located within
the | back 37 A |
front 38 What is the function of the hepatopancreatic sphincter? | back 38 A |
front 39 Secretions of the parotid gland empty | back 39 C |
front 40 The mesentery that suspends the small intestine is the | back 40 D |
front 41 Why are bacteria abundant in the large intestines but not in the
stomach? | back 41 D |
front 42 The stomach | back 42 C |
front 43 Which of the following correctly describes the function of the
greater omentum? | back 43 B |
front 44 Which of the following is a secondarily retroperitoneal
organ? | back 44 A |
front 45 What is the function of the gallbladder? | back 45 D |
front 46 The pancreas contains all of the following regions except a | back 46 C |
front 47 The largest salivary gland is the | back 47 D |
front 48 Which of the following cells produce intrinsic factor? | back 48 B |
front 49 Which of the following is not a function of hepatocytes? | back 49 A |
front 50 Which of the following applies to the small intestine? | back 50 D |
front 51 All of the following structures have all four tissue layers in their
walls except the | back 51 B |
front 52 The portion of the large intestine closest to the liver is
the | back 52 C |
front 53 Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the
bile-secreting liver | back 53 B |
front 54 The duodenum contains these structures whose products neutralize the
acidic chyme. | back 54 A |
front 55 Which of the following statements about the duodenum is
false? | back 55 D |
front 56 Which of the following layers is present in the mucosa of the stomach
and intestines, but not | back 56 C |
front 57 The "mostly mucous" extrinsic salivary gland is the
________ gland. | back 57 C |
front 58 Which of the following are the only mucosal folds that do not flatten
out at all when the | back 58 C |
front 59 The bare area of the liver | back 59 C |
front 60 The epithelial lining of the mouth derives from | back 60 A |
front 61 The liver and pancreas form as part of the embryonic | back 61 A |
front 62 Of the basic digestive processes, the one in which nutrients enter
capillaries is called | back 62 D |
front 63 Which of the following is not a characteristic of the rectum? | back 63 B |
front 64 If we say the pancreas is shaped like a tadpole, then the tadpole's
head lies | back 64 C |
front 65 Which of the following is true of the pectinate line of the anal
canal? | back 65 C |
front 66 Which of the following is not a characteristic of enteroendocrine
cells? | back 66 D |
front 67 The splenic flexure is the boundary between the | back 67 B |
front 68 In the stomach, the undifferentiated epithelial stem cells lie near
the junction between the | back 68 D |
front 69 Some bacteria from the intestinal microbiota work their way into the
intestinal wall and start | back 69 B |
front 70 Which of the following is a role of the levator ani muscle in
defecation? | back 70 C |
front 71 In mastication, the relative roles of an incisor versus a molar
are | back 71 C |
front 72 The lamina propria and submucosa of the stomach both derive from
which embryonic layer? | back 72 C |
front 73 Most of the gastrointestinal tract is innervated by the sympathetic
and parasympathetic | back 73 B |
front 74 Which of the following structures neither enters nor leaves the porta
hepatis? | back 74 A |
front 75 The parietal cells in the stomach produce | back 75 C |
front 76 Which of the following is not an accessory digestive organ? | back 76 D |
front 77 In most cases, the accessory pancreatic duct drains into the | back 77 C |
front 78 The lining epithelium of the developing digestive tract (pharynx
through anal canal) comes | back 78 C |
front 79 The terminal portion of the small intestine is the | back 79 B |
front 80 The correct sequence of layers in the wall of the alimentary canal,
from internal to external, | back 80 B |
front 81 The layer of the digestive tube that contains abundant elastin plus
blood vessels, lymphoid | back 81 B |
front 82 Which of the following statements about the large intestine is
false? | back 82 C |
front 83 The vermiform appendix is suspended from the cecum. A) True B) False | back 83 A |
front 84 The terms taste bud and papillae are synonymous. A) True B) False | back 84 B |
front 85 The lesser omentum directly attaches the stomach to the posterior abdominal wall. A) True B) False | back 85 B |
front 86 The pancreas and duodenum are secondarily retroperitoneal organs. A) True B) False | back 86 A |
front 87 Most of the ascending colon lies between the subcostal and transtubercular planes. A) True B) False | back 87 A |
front 88 From the lumen outward, the layers of the gastrointestinal tract are
mucosa, submucosa, A) True B) False | back 88 A |
front 89 The most superficial layer of the esophagus is the serosa. A) True B) False | back 89 B |
front 90 Smooth muscle fibers differ from skeletal muscle in that they do not
contain contractile A) True B) False | back 90 B |
front 91 Stretching of the anal sphincter initiates the defecation reflex. A) True B) False | back 91 B |
front 92 Villi are cytoplasmic projections on the surface of intestinal absorptive cells. A) True B) False | back 92 B |
front 93 Chief cells of the gastric glands secrete pepsinogen. A) True B) False | back 93 A |
front 94 Hepatic portal blood is mixed with blood from the hepatic artery in the liver. A) True B) False | back 94 A |
front 95 The small intestines contain bacteria that synthesize some essential vitamins. A) True B) False | back 95 A |
front 96 A gallstone lodged in the cystic duct may also cause blockage of the pancreas. A) True B) False | back 96 B |
front 97 The sinusoids of the liver lobule receive blood from the portal
arteriole and deliver blood to A) True B) False | back 97 B |