
Identify the letter that indicates the cardiac region of the
stomach.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A

Identify the letter that indicates the region of the stomach that
regulates the passage of chyme
into the small intestine.
A)
A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E

Identify the letter that indicates folds that allow for expansion of
the stomach.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C

Identify the letter that indicates the curvature where the greater
omentum attaches.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D

Identify the letter that indicates the fundus of the stomach.
A)
A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B

Identify the letter that indicates the cystic duct.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C

Identify the letter that indicates the hepatic ducts as they exits
the porta hepatis.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
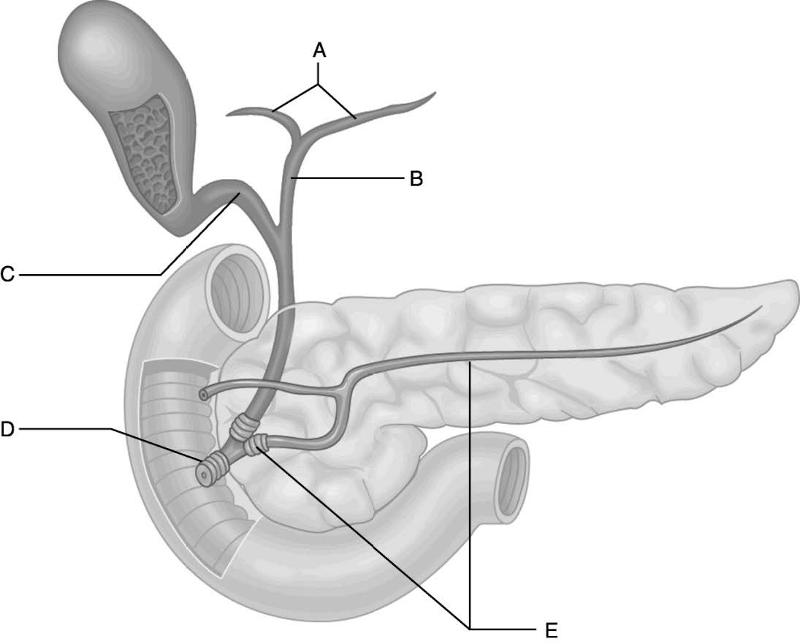
Identify the letter that indicates the duct that carries digestive
enzymes from acinar cells in the
pancreas.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E

Identify the letter that indicates the duct that directs both
digestive enzymes and bile to the
duodenum.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D

Identify the letter that indicates the duct formed by the union of
the right and left hepatic
ducts.
A) A
B) B
C)
C
D) D
E) E
B

Identify the letter that indicates the root canal.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E

Identify the letter that indicates the crown.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A

Identify the letter that indicates the root.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C

Identify the letter that indicates the surface of the tooth that is
coated with the hardest
substance in the body.
A) A
B)
B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D

Identify the letter on the diagram that represents the neck of the
tooth.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
Retroperitoneal organs have a serosa facing the peritoneal cavity and
a(n) ________ on the
posterior side embedded in the abdominal
wall.
A) mesothelium
B) adventitia
C) muscularis
externa
D) vasa vasorum
E) caveolae
B
Infoldings of the sarcolemma of smooth muscle fibers.
A)
mesothelium
B) adventitia
C) muscularis externa
D) vasa
vasorum
E) caveolae
E
Junction of the transverse and ascending colon.
A) splenic
flexure
B) cecum
C) hepatic flexure
D) ileocecal
valve
E) haustra
C
The union of the cystic and common hepatic ducts.
A) accessory
pancreatic duct
B) main pancreatic duct
C) hepatopancreatic
ampulla
D) common bile duct
E) bile canaliculi
D
Smooth muscle constriction between the ileum and cecum.
A)
splenic flexure
B) cecum
C) hepatic flexure
D)
ileocecal valve
E) haustra
D
Attaches the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach.
A)
haustra
B) hepatopancreatic ampulla
C) porta hepatis
D)
greater omentum
E) lesser omentum
E
Attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and
diaphragm.
A) greater omentum
B) lesser omentum
C)
falciform ligament
D) ligamentum teres
E) porta hepatis
C
Layer of the GI tract responsible for peristalsis and
segmentation.
A) muscularis mucosae
B) muscularis
externa
C) lamina propria
D) submucosa
E) serosa
B
Bulblike union of the main pancreatic duct and bile duct.
A)
cystic duct
B) hepatic duct
C) porta hepatis
D)
hepatopancreatic ampulla
E) accessory pancreatic duct
D
Three strips of longitudinal muscles of the muscularis of the colon
causing it to pucker into
sacs.
A) ileocecal
junction
B) haustra
C) teniae coli
D) muscularis
mucosae
E) pyloric sphincter
C
Which layer of the digestive tract is responsible for the peristaltic
waves that propel materials
from one portion to another?
A)
muscularis externa
B) serosa
C) submucosa
D) mucosa
A
Which of the following choices correctly pairs a type of cell in the
stomach with its
secretion?
A) parietal cell;
pepsinogen
B) chief cell; pepsinogen
C) parietal cell;
mucus
D) enteroendocrine; hydrochloric acid
B
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the large
intestine?
A) It includes the ascending, transverse, and
descending colon.
B) It contains an abundant bacterial
flora.
C) It is the main site of nutrient absorption.
D) It
absorbs much of the water and salts remaining in the wastes.
C
The digestive organ primarily responsible for the absorption of water
is the
A) ileum.
B) duodenum.
C) anus.
D) large intestine.
D
Another name for serosa is
A) parietal peritoneum.
B)
serous gland.
C) visceral peritoneum.
D) mucosa.
C
Medial to both midclavicular lines and superior to the subcostal
plane lies the
A) appendix.
B) cecum.
C)
jejunum.
D) pyloric sphincter.
D
To say someone is "tongue-tied" means that the
A) lips
are exceptionally immobile.
B) tongue muscles are weak.
C)
salivary glands produce little lubricant.
D) lingual frenulum is short.
D
The lesser omentum extends between the
A) greater curvature of
the stomach and the posterior abdominal wall.
B) lesser curvature
of the stomach and the porta hepatis of the liver.
C) transverse
colon and the posterior abdominal wall.
D) sigmoid colon and the
posterior pelvic wall.
B
The splenic, or left colic, flexure of the colon is located within
the
A) left hypochondriac region.
B) left lumbar
region.
C) right hypochondriac region.
D) right lumbar region.
A
Which of the following is not contained in saliva?
A) enzymes
that begin the digestion of proteins
B) enzymes that initiate the
digestion of carbohydrates
C) bicarbonate buffer
D)
bactericidal enzymes
A
How many deciduous teeth are there?
A) 18
B) 20
C)
32
D) It varies from person to person.
B
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) is primarily located within
the
A) lamina propria.
B) muscularis mucosa.
C)
serosa.
D) submucosa.
A
What is the function of the hepatopancreatic sphincter?
A) It
controls the entry of bile and pancreatic juices into the alimentary
canal.
B) As it contracts, it squeezes pancreatic secretions into
the duodenum.
C) It inhibits defecation in the upper alimentary
canal while the anal sphincters do the same in
the lower
regions.
D) It prevents the movement of bile into the gallbladder.
A
Secretions of the parotid gland empty
A) anterior to the
frenulum of the tongue.
B) between the lingual tonsil and
epiglottis.
C) lateral to the upper molars.
D) through 10
ducts on the floor of the oral cavity.
C
The mesentery that suspends the small intestine is the
A)
falciform ligament.
B) lesser omentum.
C) greater
omentum.
D) mesentery proper.
D
Why are bacteria abundant in the large intestines but not in the
stomach?
A) Food enters the stomach first and does not spend much
time there.
B) The intestine is much warmer and moister,
encouraging bacterial growth.
C) The stomach wall contains so
much lymphoid tissue that it destroys all bacteria there.
D)
Secretions of parietal cells kill bacteria in the stomach.
D
The stomach
A) stores food for later use in the form of
fat.
B) absorbs most of the nutrients in food.
C) churns
food into a paste by mechanical means.
D) dehydrates food
materials before passing them to the small intestine.
C
Which of the following correctly describes the function of the
greater omentum?
A) It is a vestigial structure that has no known
function.
B) It stores fat.
C) It absorbs heat from the
digestive process and radiates it to the outside of the body.
D)
It wraps around most of the large intestine and anchors it to the
anterior abdominal wall.
B
Which of the following is a secondarily retroperitoneal
organ?
A) descending colon
B) ileum
C) sigmoid
colon
D) transverse colon
A
What is the function of the gallbladder?
A) secretion of
bile
B) production of cholesterol
C) secretion of
gastrin
D) storage of bile
D
The pancreas contains all of the following regions except a
A)
head.
B) tail.
C) hilum.
D) body.
C
The largest salivary gland is the
A) intrinsic.
B)
submandibular.
C) sublingual.
D) parotid.
D
Which of the following cells produce intrinsic factor?
A) chief
cells
B) parietal cells
C) mucous neck cells
D)
enteroendocrine cells
B
Which of the following is not a function of hepatocytes?
A)
producing digestive enzymes
B) picking up and processing
nutrients from the portal blood
C) storing some vitamins
D)
detoxifying poisons
A
Which of the following applies to the small intestine?
A) It is
where foodstuffs first encounter protein-splitting enzymes.
B)
Its walls secrete most of the digestive enzymes that are active in its
lumen.
C) It is where carbohydrates and fats but not proteins are
digested.
D) Breakdown products of fats enter its lacteals.
D
All of the following structures have all four tissue layers in their
walls except the
A) esophagus.
B) mouth.
C)
stomach.
D) sigmoid colon.
B
The portion of the large intestine closest to the liver is
the
A) cecum.
B) rectum.
C) transverse colon.
D)
descending colon.
C
Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the
bile-secreting liver
were severely damaged?
A)
carbohydrates
B) lipids
C) proteins
D) nucleic acids
B
The duodenum contains these structures whose products neutralize the
acidic chyme.
A) duodenal glands
B) gastric glands
C)
intestinal glands
D) Peyer's patches
A
Which of the following statements about the duodenum is
false?
A) It receives chyme from the stomach.
B) It is the
site of action of liver and pancreas secretions.
C) It is shorter
than either the ileum or jejunum.
D) It is more movable than the
ileum or jejunum, which are retroperitoneal.
D
Which of the following layers is present in the mucosa of the stomach
and intestines, but not
in the mucosa of the mouth and
pharynx?
A) lining epithelium
B) lamina propria
C)
muscularis mucosae
D) lumen
C
The "mostly mucous" extrinsic salivary gland is the
________ gland.
A) parotid
B) submandibular
C)
sublingual
D) intrinsic
C
Which of the following are the only mucosal folds that do not flatten
out at all when the
organ stretches?
A) longitudinal folds
in the esophagus
B) rugae in the stomach
C) circular folds
in the small intestine
D) mucosal folds in the gallbladder
C
The bare area of the liver
A) contains the ligamentum
teres.
B) is covered with visceral peritoneum.
C) is fused
with the diaphragm.
D) is on the liver's inferior and anterior surface.
C
The epithelial lining of the mouth derives from
A)
ectoderm.
B) mesoderm.
C) endoderm.
D) neural crest.
A
The liver and pancreas form as part of the embryonic
A)
foregut.
B) midgut.
C) hindgut.
D) the hindgut and midgut.
A
Of the basic digestive processes, the one in which nutrients enter
capillaries is called
A) ingestion.
B) propulsion.
C)
mechanical digestion.
D) absorption.
D
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the rectum?
A)
lacks tenia coli
B) has longitudinal folds called columns
C)
is secondarily retroperitoneal
D) has transverse folds called
rectal valves
B
If we say the pancreas is shaped like a tadpole, then the tadpole's
head lies
A) posterior to the fundus of the stomach.
B)
inside the mesentery proper.
C) in the curvature formed by the
duodenum.
D) against the hilum of the spleen.
C
Which of the following is true of the pectinate line of the anal
canal?
A) It lies just below the level of the rectal
valves.
B) It is also called the anal columns.
C) It divides
regions of somatic and visceral innervation.
D) All hemorrhoids
occur there.
C
Which of the following is not a characteristic of enteroendocrine
cells?
A) They are scattered throughout the lining epithelium of
the stomach and intestines.
B) They secrete hormones that help
signal the events of digestion.
C) They never secrete their
product into the lumen of the digestive canal.
D) They are
scattered throughout the lining of the rectum.
D
The splenic flexure is the boundary between the
A) spleen and
stomach.
B) transverse and descending colon.
C) transverse
and ascending colon.
D) descending colon and sigmoid colon.
B
In the stomach, the undifferentiated epithelial stem cells lie near
the junction between the
gastric pits and gastric glands. In the
intestine, the corresponding stem cells occur
A) on the tips of
the villi.
B) where the intestinal crypts meet the villi.
C)
in the duodenal (Brunner's) glands.
D) deep within the intestinal
glands (crypts of Lieberkühn).
D
Some bacteria from the intestinal microbiota work their way into the
intestinal wall and start
to spread through the circulation. Many
of these bacteria are stopped by MALT, while many
more are
destroyed by
A) hepatocytes.
B) hepatic macrophages.
C)
the walling-off action of the greater omentum.
D) megakaryocytes.
B
Which of the following is a role of the levator ani muscle in
defecation?
A) It pushes down on the feces.
B) It has no
role in defecation, only in inhibiting defecation (it is the external
sphincter muscle).
C) It lifts the anal canal superiorly around
the feces.
D) Its stretch and proprioception properties initiate
the defecation reflex.
C
In mastication, the relative roles of an incisor versus a molar
are
A) piercing versus tearing.
B) chewing versus holding
food in the mouth.
C) biting off pieces of food versus
grinding.
D) only incisors function in mastication.
C
The lamina propria and submucosa of the stomach both derive from
which embryonic layer?
A) ectoderm
B) intermediate
mesoderm
C) splanchnic mesoderm
D) somatic mesoderm
C
Most of the gastrointestinal tract is innervated by the sympathetic
and parasympathetic
branches of the nervous system. Which parts
are innervated by the somatic nervous system?
A) esophagus and
stomach
B) pharynx and anal canal
C) pyloric, ileocecal, and
internal anal sphincters
D) small and large intestines
B
Which of the following structures neither enters nor leaves the porta
hepatis?
A) hepatic veins
B) branches of hepatic portal
vein
C) branches of hepatic artery
D) hepatic ducts
A
The parietal cells in the stomach produce
A) mucin.
B)
pepsin.
C) intrinsic factor and HCl.
D) secretin.
C
Which of the following is not an accessory digestive organ?
A)
teeth
B) salivary gland
C) liver
D) spleen
D
In most cases, the accessory pancreatic duct drains into the
A)
common bile duct.
B) common hepatic duct.
C)
duodenum.
D) jejunum.
C
The lining epithelium of the developing digestive tract (pharynx
through anal canal) comes
from
A) ectoderm.
B)
mesoderm.
C) endoderm.
D) neural crest.
C
The terminal portion of the small intestine is the
A)
duodenum.
B) ileum.
C) jejunum.
D) pyloric sphincter.
B
The correct sequence of layers in the wall of the alimentary canal,
from internal to external,
is
A) mucosa, muscularis, serosa,
submucosa.
B) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa.
C)
serosa, muscularis, mucosa, submucosa.
D) submucosa, mucosa,
serosa, muscularis.
B
The layer of the digestive tube that contains abundant elastin plus
blood vessels, lymphoid
nodules, and deep glands is the
A)
adventitia.
B) submucosa.
C) muscularis.
D) serosa.
B
Which of the following statements about the large intestine is
false?
A) It has no villi.
B) It exhibits external muscular
bands called taeniae coli.
C) It is longer than the small
intestine.
D) It has haustra.
C
The vermiform appendix is suspended from the cecum.
A) True
B) False
A
The terms taste bud and papillae are synonymous.
A) True
B) False
B
The lesser omentum directly attaches the stomach to the posterior abdominal wall.
A) True
B) False
B
The pancreas and duodenum are secondarily retroperitoneal organs.
A) True
B) False
A
Most of the ascending colon lies between the subcostal and transtubercular planes.
A) True
B) False
A
From the lumen outward, the layers of the gastrointestinal tract are
mucosa, submucosa,
muscularis, serosa.
A) True
B) False
A
The most superficial layer of the esophagus is the serosa.
A) True
B) False
B
Smooth muscle fibers differ from skeletal muscle in that they do not
contain contractile
myofilaments.
A) True
B) False
B
Stretching of the anal sphincter initiates the defecation reflex.
A) True
B) False
B
Villi are cytoplasmic projections on the surface of intestinal absorptive cells.
A) True
B) False
B
Chief cells of the gastric glands secrete pepsinogen.
A) True
B) False
A
Hepatic portal blood is mixed with blood from the hepatic artery in the liver.
A) True
B) False
A
The small intestines contain bacteria that synthesize some essential vitamins.
A) True
B) False
A
A gallstone lodged in the cystic duct may also cause blockage of the pancreas.
A) True
B) False
B
The sinusoids of the liver lobule receive blood from the portal
arteriole and deliver blood to
the portal venule.
A) True
B) False
B