Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Urinary System
front 1 Three Functions of the Urinary System | back 1
|
front 2 Excretion | back 2
|
front 3 Elimination | back 3
|
front 4 Homeostatic Regulation | back 4
|
front 5 Organs of the Urinary System | back 5 
|
front 6 Kidneys (2) | back 6 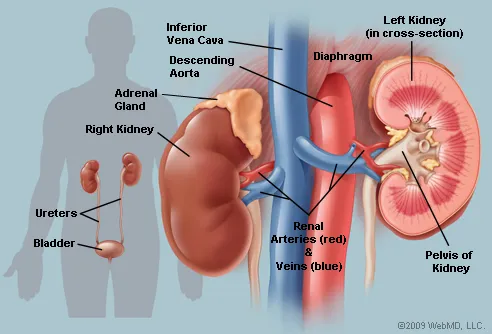
|
front 7 Urine | back 7
|
front 8 Urinary Tract | back 8 
|
front 9 Ureters | back 9  paired tubes |
front 10 Urinary Bladder | back 10  muscular sac for temporary storage of urine |
front 11 Urethra | back 11 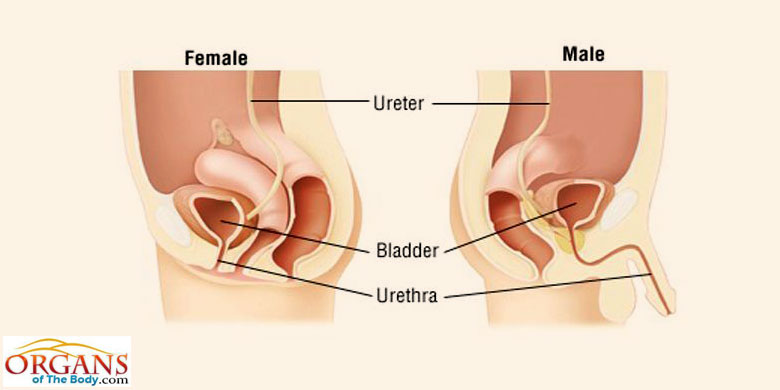 exit tube |
front 12 Urination | back 12
|
front 13 Homeostatic Functions of the Urinary System | back 13
|
front 14 The left kidney lies slightly ___________ to the right kidney. | back 14  superior |
front 15 The superior surface of each kidney is capped by an ______ ______. | back 15  adrenal gland |
front 16 Three Concentric Layers of Connective Tissue that Protect &
| back 16
|
front 17 Fibrous Capsule | back 17 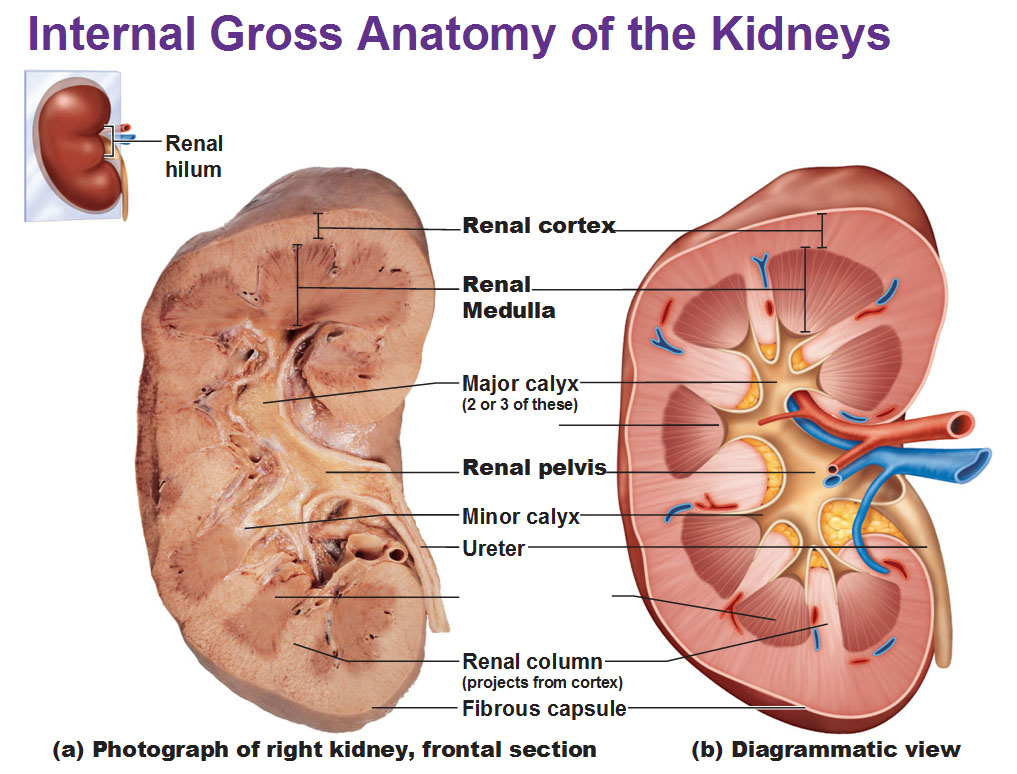 layer of collagen fibers covers outer surface of the |
front 18 Perinephric Fat | back 18 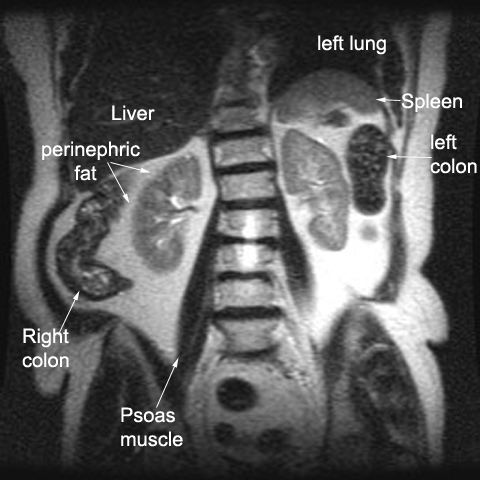 thick layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the fibrous |
front 19 Renal Fascia | back 19 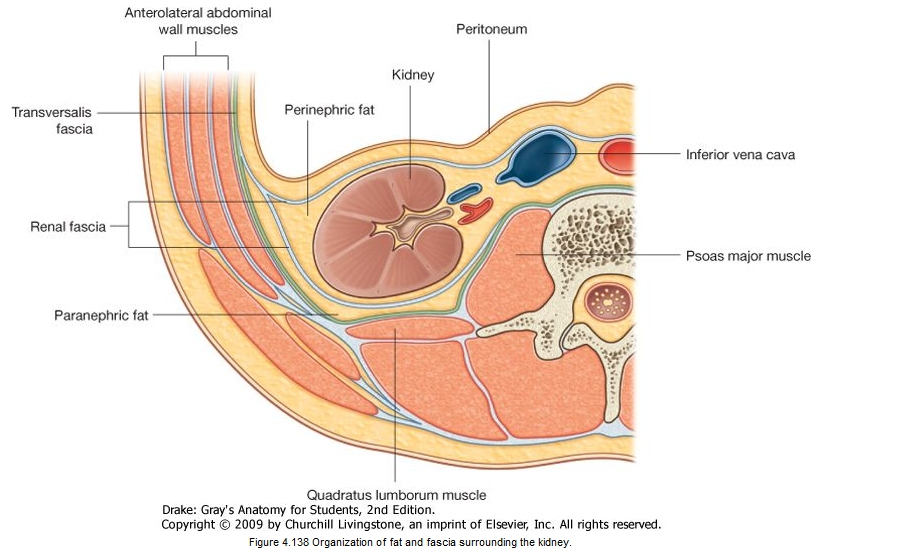 a dense, fibrous outer layer that anchors the kidney to |
front 20 Typical Adult Kidney | back 20 
|
front 21 Hilum | back 21 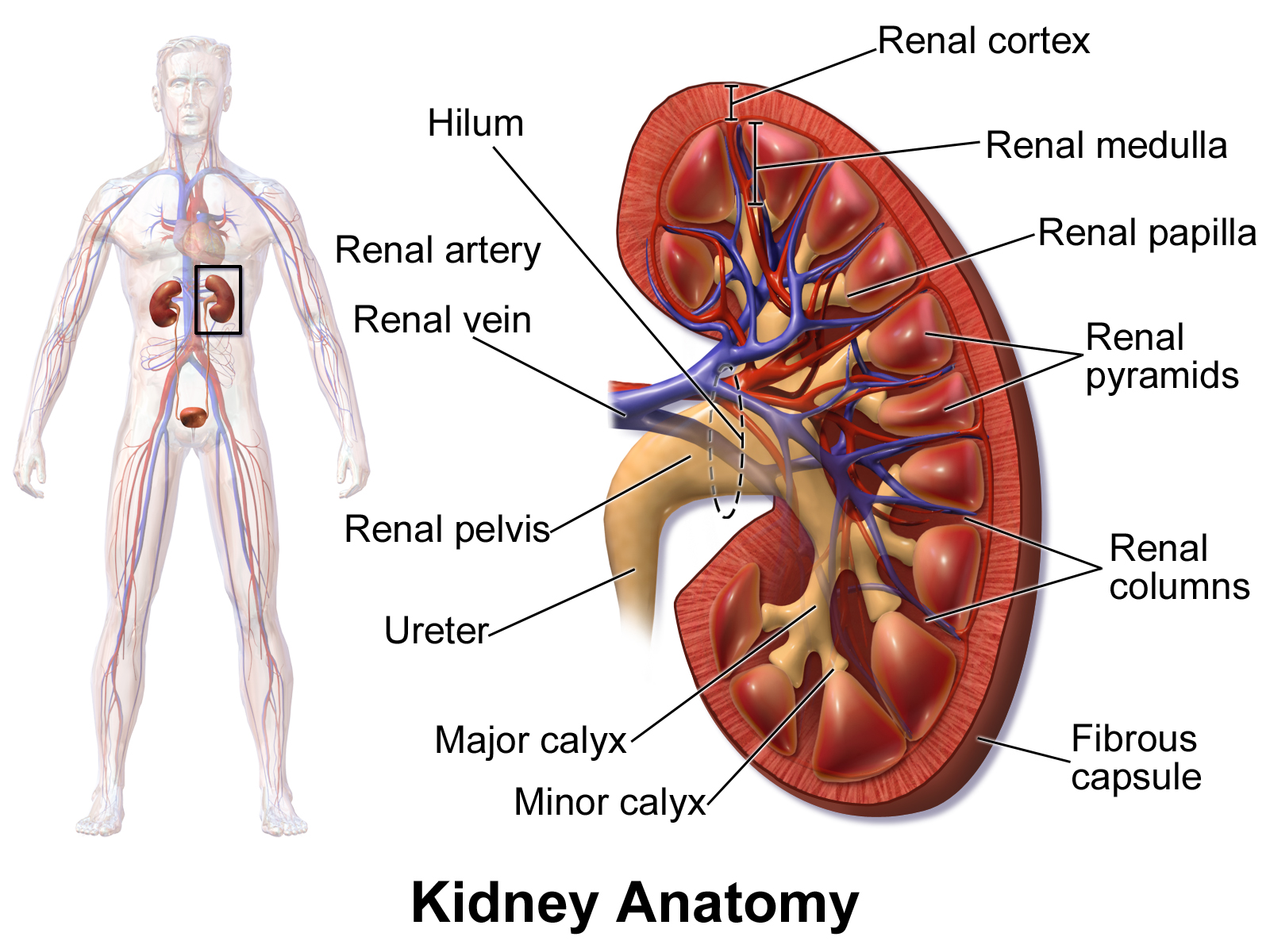
|
front 22 Renal Sinus | back 22  an internal cavity within the kidney lined by fibrous |
front 23 Renal Cortex | back 23 
|
front 24 Renal Medulla | back 24  consists of 6 to 18 triangular structures |
front 25 Renal Pyramids | back 25 
|
front 26 Renal Columns | back 26 
|
front 27 Renal Lobe | back 27 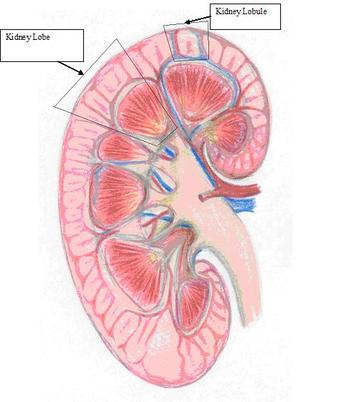
|
front 28 Urine is produced in the ____ _____. | back 28 kidney lobes |
front 29 Renal Papilla | back 29  ducts discharge urine into minor calyx |
front 30 Minor Calyx | back 30  cup shaped drain |
front 31 Major Calyx | back 31  formed by four or five minor calyces |
front 32 Renal Pelvis | back 32 
|
front 33 Nephrons | back 33 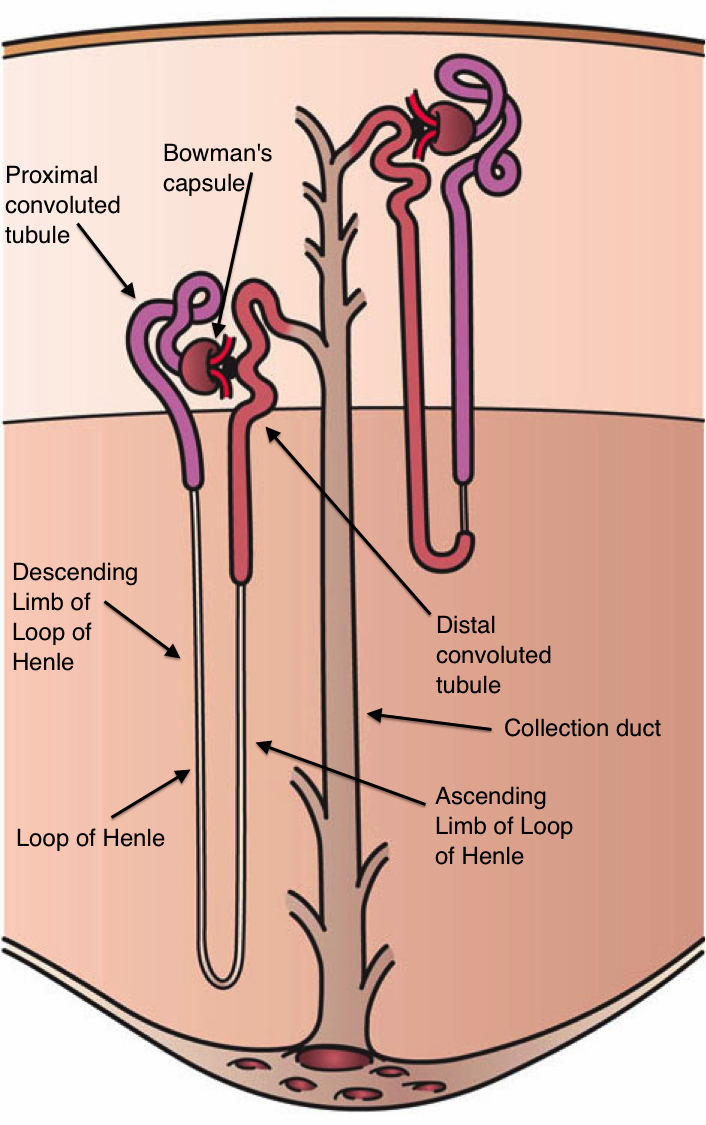
|
front 34 Blood Supply to Kidneys | back 34
|
front 35 Kidney receives blood through the _______ _______. | back 35  renal artery |
front 36 Segmental Arteries | back 36 
|
front 37 Interlobular Arteries | back 37 
|
front 38 Arcuate Arteries | back 38 
|
front 39 Afferent Arterioles | back 39 
|
front 40 Cortical Radiate Veins/Interlobular Veins | back 40 
|
front 41 Interlobar Veins | back 41 
|
front 42 Renal Nerves | back 42 
|
front 43 Sympathetic Innervation | back 43
|
front 44 The Nephron | back 44 
|
front 45 Renal Corpuscle | back 45 
|
front 46 Glomerular (Bowman's) Capsule | back 46 
|
front 47 Renal Tubule | back 47 
|
front 48 Glomerulus | back 48 
|
front 49 Efferent Arteriole | back 49 
|
front 50 The process of filtration takes place in the _______ ________. | back 50  renal corpuscle |
front 51 Blood Pressure | back 51
|
front 52 Filtration | back 52 
|
front 53 Filtrate | back 53 
|
front 54 Three Functions of the Renal Tubule | back 54 
|
front 55 Proximal Convoluted Tubule | back 55 
|
front 56 Distal Convoluted Tubule | back 56 
|
front 57 Descending Limb of Loop of Henle | back 57 
|
front 58 Ascending Limb of Loop of Henle | back 58 
|
front 59 As the filtrate travels along the renal tubule, it is now called ______ _____. | back 59 tubular fluid |
front 60 Collecting System | back 60 
|
front 61 Each nephron empties into the __________ _________. | back 61 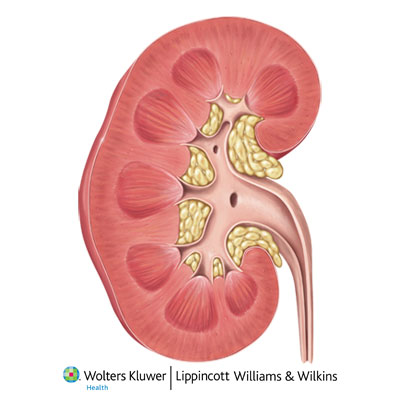 collecting system |
front 62 Collecting Ducts | back 62 
|
front 63 Papillary Ducts | back 63 
|
front 64 Cortical Nephrons | back 64 
|
front 65 Juxtamedullary Nephrons | back 65 
|
front 66 Vasa Recta | back 66 
|
front 67 The Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle) | back 67 
|
front 68 The Juxtaglomerular Complex | back 68 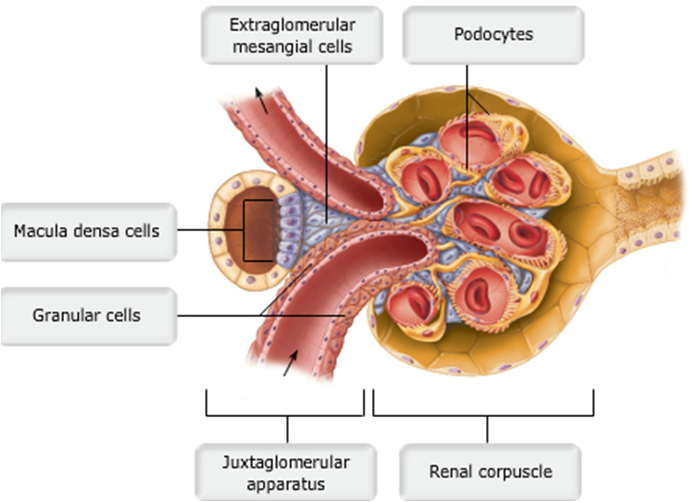
|
front 69 Macula Densa | back 69 
|
front 70 The of Urine Production | back 70
|
front 71 Three Organic Waste Products | back 71
|
front 72 Organic Waste Products | back 72
|