Three Functions of the Urinary System
- Excretion
- Elimination
- Homeostatic
Regulation
Excretion
- the removal of organic wastes from body fluids
Elimination
- Discharge of waste products into the environment
Homeostatic Regulation
- Of blood plasma volume and solute concentration
Organs of the Urinary System

- kidneys (2)
- ureters (2)
- urinary bladder
- urethra
Kidneys (2)
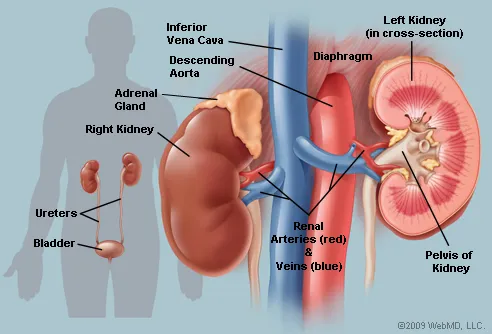
- perform the excretory functions of the urinary system
- produces urine located on either side of the vertebral
column - left kidney lies slightly superior to the right kidney
because of liver
Urine
- fluid that contains ions, water, and small soluble
compunds
Urinary Tract

- organs that eliminate urine
- ureters (2)
- Urinary Bladder
- Urethra
Ureters

paired tubes
Urinary Bladder

muscular sac for temporary storage of urine
Urethra
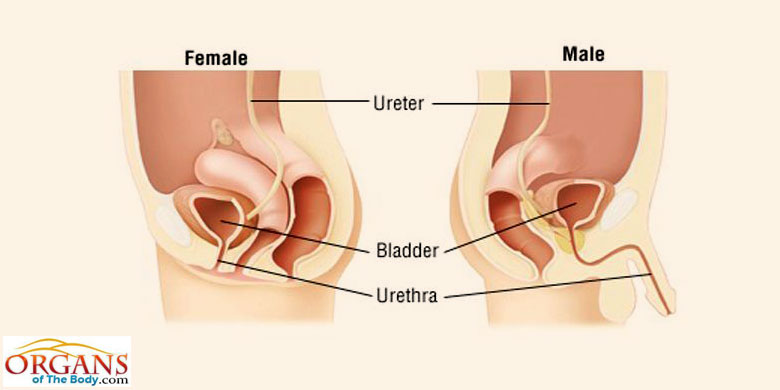
exit tube
Urination
- process of eliminating urine
- the muscular urinary
bladder contracts and forces urine through the urethra
Homeostatic Functions of the Urinary System
- Regulates blood volume & blood pressure
- by
adjusting the volume of water lost in urine
releases erythropoietin and renin
- by
adjusting the volume of water lost in urine
- Regulates plasma
concentrations of sodium, potassium, and
chloride- by
controlling quantities lost in
urine the kidneys - also control calcium ion levels through
the synthesis of calcitriol
- by
controlling quantities lost in
- Helps stabilize blood pH
- by controlling
loss of hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions in urine
- by controlling
- Conserves
valuable nutrients
- by preventing
their loss in urine while removing organic wastes - especially (nitrogenous wastes) urea and uric acid
- by preventing
- Assists the liver in detoxifying
poisons
The left kidney lies slightly ___________ to the right kidney.

superior
The superior surface of each kidney is capped by an ______ ______.

adrenal gland
Three Concentric Layers of Connective Tissue that Protect &
Stabilize Each Kidney
- Fibrous Capsule
- Perinephric Fat
- Renal
Fascia
Fibrous Capsule
layer of collagen fibers covers outer surface of the
entire organ
Perinephric Fat
thick layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the fibrous
capsule
Renal Fascia
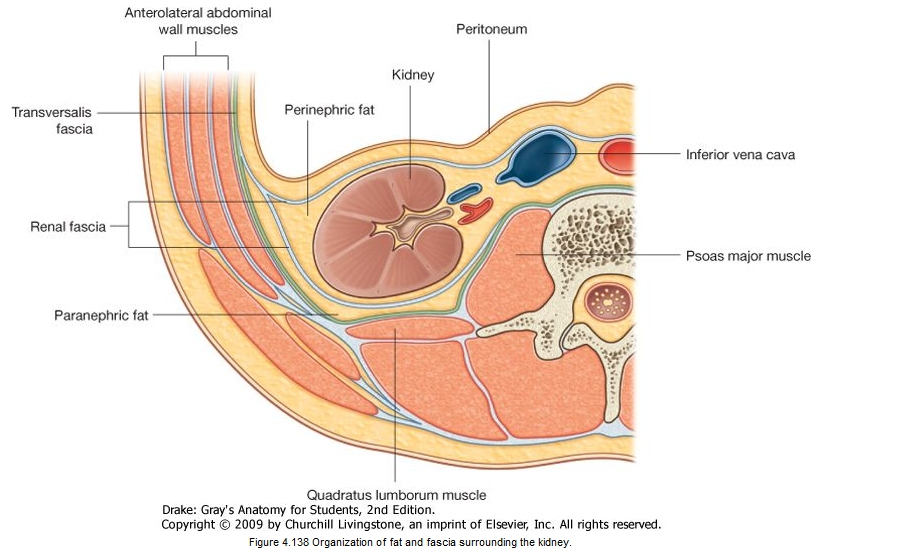
a dense, fibrous outer layer that anchors the kidney to
surrounding structures
Typical Adult Kidney

- reddish brown
- 10 cm long
- 5.5 cm wide
- 3 cm thick
- weighs about 150 g
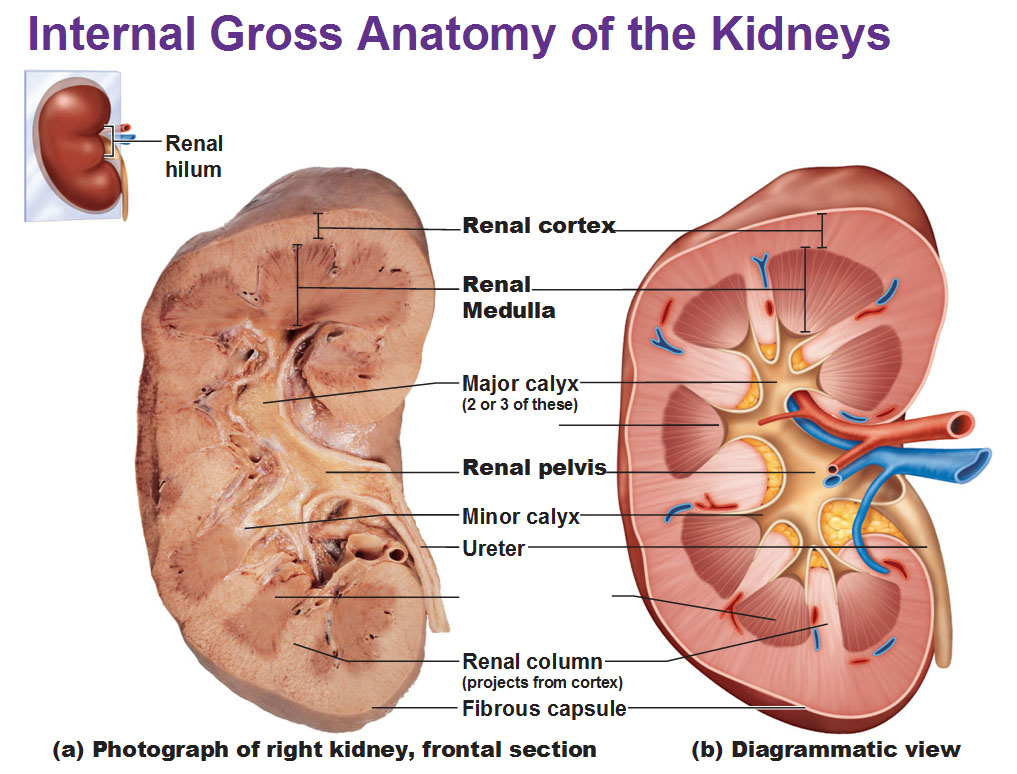
Hilum
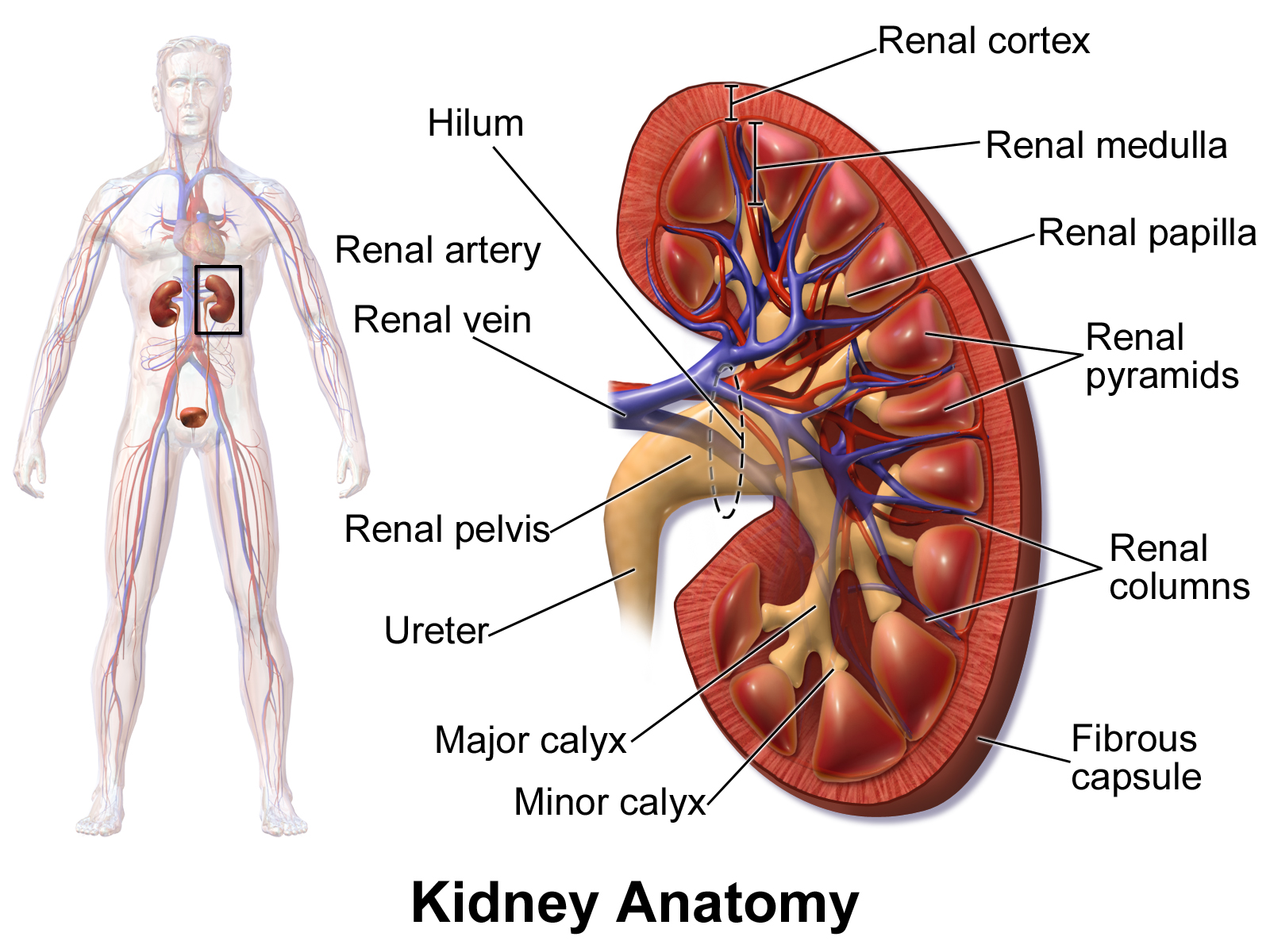
- medial indentation point of entry for the renal artery
and renal nerves
- point of exit for renal vein and
ureter
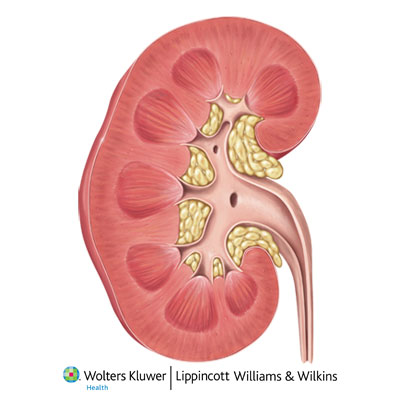
Renal Sinus

an internal cavity within the kidney lined by fibrous
renal capsule
Renal Cortex

- superficial portion of the kidney, in contact with the renal
capsule - reddish-brown and granular
Renal Medulla

consists of 6 to 18 triangular structures
Renal Pyramids

- 6 to 18 distinct triangular structures in renal medulla
- base abuts cortex tip (renal papilla projects into
renal sinus
Renal Columns

- bands of cortical tissue separates adjacent renal pyramids
extend into medulla granular tissue
Renal Lobe
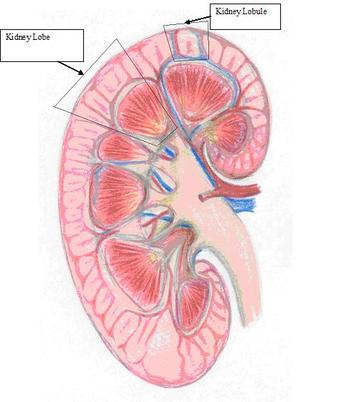
- consists of:
- renal pyramid overlying area of
renal cortex - adjacent tissues of renal columns
- produces urine
- renal pyramid overlying area of
Urine is produced in the ____ _____.
kidney lobes
Renal Papilla

ducts discharge urine into minor calyx
Minor Calyx

cup shaped drain
Major Calyx

formed by four or five minor calyces
Renal Pelvis

- formed by 2 or 3 major calyces
- funnel shaped chamber
- fills most of the renal sinus
- connected to
ureters, which drains kidneys
Nephrons
- microscopic, tubular structures in cortex of each renal love
- where urine production begins
Blood Supply to Kidneys
- kidneys receive 20-25% of the total cardiac output
- 1200 mL of blood flow through the kidneys each minute
Kidney receives blood through the _______ _______.

renal artery
Segmental Arteries

- recieves blood from the renal artery
- divides into interlobular arteries
Interlobular Arteries

- radiate outward through the renal columns between the renal pyramids
- supply blood to the arcuate arteries
Arcuate Arteries

- arch along the boundary between the cortex and medulla of the kidney
Afferent Arterioles

- delivers blood to the capillaries supplying individual nephrons
Cortical Radiate Veins/Interlobular Veins

- deliver blood to the arcuate veins
- empty into interlobar veins
Interlobar Veins

- drain directly into renal vein
Renal Nerves

- innervate the kidneys and ureters
- enters each kidney at the hilum
- follows the branches of the renal arteries to reach individual nephrons
Sympathetic Innervation
- Adjusts rates of urine formation
- by changing blood flow and blood pressure at the nephron
- Stimulates the release of renin
- which restricts water and salt loss in urine by stimulation reabsorption by the nephron
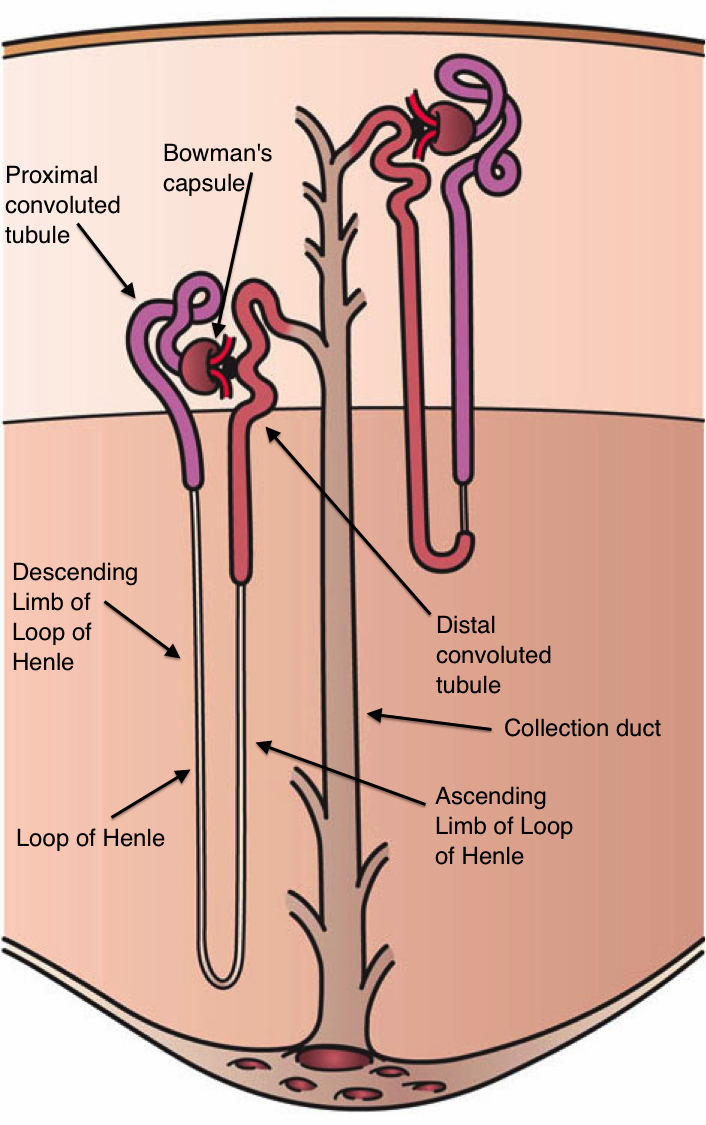
The Nephron

- consists of:
- renal tubule
- renal corpuscle
Renal Corpuscle

- a spherical structure consisting of:
- glomerular
(Bowman's) capsule
- cup shaped chamber
- glomerulus
- a capillary network
- glomerular
(Bowman's) capsule
- squamous cells
Glomerular (Bowman's) Capsule

- cup shaped chamber
Renal Tubule

- begins at renal corpuscle
- long tubular passageway
Glomerulus

- consists of 50 intertwined capillaries
- projects into the glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
- blood leaves the glomerulus in an efferent arteriole
Efferent Arteriole

- flows into a network of capillaries called peritubular capillaries
- drain into small venules that return blood to the venous system
The process of filtration takes place in the _______ ________.

renal corpuscle
Blood Pressure
- forces water and dissolved solutes out of the glomerular capillaries into capsular space
Filtration

- takes place in the renal corpuscle
- produces protein
free solution (aka filtrate)
- similar to blood plasma
Filtrate

- protein-free solution (similar to blood plasma)
- moves from renal corpuscle to renal tubule
Three Functions of the Renal Tubule

- Reabsorb useful organic nutrients that enter filtrate
- Reabsorb more than 90% of water that enter filtrate
- Secrete waste products that failed to enter renal corpuscle through filtration at glomerulus
Proximal Convoluted Tubule

- reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic matter
- cuboidal cells with abundant microvilli
Distal Convoluted Tubule

- secretion of ions, acids, drugs, and toxins
- variable reabsorption of water, sodium ions, and calcium ions
- cuboidal cells with few microvilli
Descending Limb of Loop of Henle

- further reabsorption of water
- squamous cells
Ascending Limb of Loop of Henle

- reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions
- low cuboidal cells
As the filtrate travels along the renal tubule, it is now called ______ _____.
tubular fluid
Collecting System

- series of tubes that carry tubular fluid away from the nephron
- collecting ducts
- papillary ducts
Each nephron empties into the __________ _________.
collecting system
Collecting Ducts

- receives fluid from many nephrons
- carried fluid to papillary ducts that drain into a minor calyx
- cuboidal to columnar cells
- reabsorption of water, sodium ions
Papillary Ducts

- columnar cells
- conducts tubular fluid to minor calyx
Cortical Nephrons

- 85% of all nephrons
- located mostly in superficial cortex of kidney
- nephron loop is short
- efferent arteriole delievers blood to a network of peritubular capillaries
Juxtamedullary Nephrons

- 15% of nephrons
- long nephron loops that extend deep into the medulla
- peritubular capillaries are connected to the vasa recta
Vasa Recta

- long straight capillaries that parallel the nephron loop
The Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle)

- descending limb
- fluid flows toward the renal pelvis
- ascending limb
- fluid flows toward the renal cortex
The Juxtaglomerular Complex
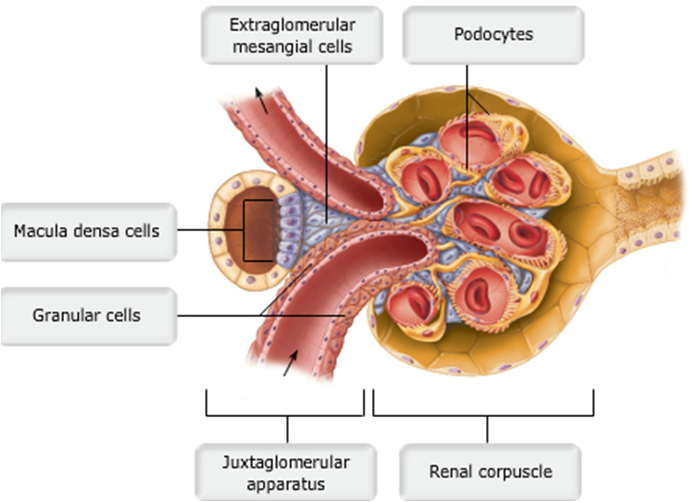
- an endocrine structure that secretes:
- hormone erythropoietin
- enzyme renin
- formed
by:
- macula densa
- juxtaglomerular cells
Macula Densa

- epithelial cells of DCT
- near renal corpuscle
- tall cells with densely clustered nuclei
The of Urine Production
- maintain homeostasis
- by regulating volume and composition of blood
- including excretion of metabolic waste products
Three Organic Waste Products
- Urea
- Creatinine
- Uric Acid
Organic Waste Products
- dissolved in bloodstream
- are eliminated only while dissolved in urine
- removal is accompanies by water loss