Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 10
front 1 A bacterial chromosome consists of:
| back 1 a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. |
front 2 Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of:
| back 2 linear DNA molecules complexed with positively charged histone proteins. |
front 3 Nucleosomes are best described as:
| back 3 eukaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins. |
front 4 What is the function of nucleosomes?
| back 4 To prevent DNA strands from tangling. |
front 5 Nucleosomes are organized into large coiled loops held together by:
| back 5 scaffolding proteins. |
front 6 The cell cycle of a typical somatic cell consists of __________ and M phase.
| back 6 interphase |
front 7 The M phase of the cell cycle involves two main processes:
| back 7 mitosis and cytokinesis |
front 8 Once nerve cells become mature, they don't usually undergo cell division. Based on your knowledge of the cell cycle, you would predict that mature nerve cells become arrested in the __________ of the cell cycle.
| back 8 G0 phase |
front 9 Chromosomes are duplicated during __________ of the cell cycle.
| back 9 S phase |
front 10 Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
| back 10
|
front 11 If a cell is in G2:
| back 11 it has twice the amount of DNA present in a telophase nucleus. |
front 12 During prophase, __________ is(are) compacted into visible chromosomes.
| back 12 chromatin |
front 13 The __________ is responsible for the separation of the chromosomes during __________ of mitosis.
| back 13 mitotic spindle; anaphase |
front 14 __________ contain identical DNA sequences and are held together by __________ during mitosis.
| back 14 Sister chromatids; centromeres |
front 15 The mitotic spindle is made of:
| back 15 microtubules. |
front 16 Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
| back 16
|
front 17 All of the following events occur during prometaphase EXCEPT:
| back 17 the duplicated chromosomes become visible with the light microscope. |
front 18 A cell is in metaphase if:
| back 18 the chromosomes are aligned at the midplane of the cell. |
front 19 Duplicated centrioles move to opposite poles of a dividing __________ cell during __________ of the cell cycle.
| back 19 animal; prophase |
front 20 The chromosome makeup of an individual organism is called a:
| back 20 karyotype. |
front 21 Chromosomes are condensed to their greatest extent during __________ of mitosis.
| back 21 metaphase |
front 22 Cytokinesis in animal cells involves contraction of a ring of __________ microfilaments.
| back 22 actin plus myosin |
front 23 Cytokinesis in plant cells occurs via the formation of a(n):
| back 23 cell plate. |
front 24 If a cell is dividing by binary fission then you know that:
| back 24 the cell is prokaryotic. |
front 25 To prevent disastrous consequences, the eukaryotic cell cycle is controlled by:
| back 25 a series of cell cycle checkpoints. |
front 26 Which of the following statements concerning the cell cycle is FALSE?
| back 26 M-Cdk inhibits mitosis. |
front 27 The correct number of chromosomes is maintained during sexual reproduction by:
| back 27 meiosis, which reduces the chromosome number by half. |
front 28 Animal cells are stimulated to divide by mitosis by:
| back 28 growth factors. |
front 29 If meiosis did not occur in sexually reproducing organisms, then:
| back 29 chromosome number would double in each generation. |
front 30 What evolutionary advantage is provided by sexual reproduction?
| back 30 increased genetic diversity |
front 31 Plant hormones known as __________ stimulate mitosis.
| back 31 cytokinins |
front 32 Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis during:
| back 32 prophase I. |
front 33 A maternal homologue and a paternal homologue synapse to form:
| back 33 a tetrad. |
front 34 During which phase does crossing-over occur?
| back 34 prophase I |
front 35 A zygote contains the __________ number of chromosomes.
| back 35 diploid |
front 36 In a human cell at prophase I, there are __________ tetrads.
| back 36 23. |
front 37 An animal with a diploid number of 36 chromosomes will have __________ chromosomes in its gametes and __________ chromosomes in its somatic cells.
| back 37 18;36 |
front 38 During prophase I, each chiasma represents:
| back 38 a site of crossing-over. |
front 39 During which of the following stages of meiosis do the sister chromatids separate?
| back 39 anaphase II |
front 40 Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
| back 40
|
front 41 The sources of genetic variation during meiosis are:
| back 41 crossing-over and the random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes. |
front 42 Which of the following events does not occur during meiosis I?
| back 42 separation of sister chromatids |
front 43  Figure 10-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-1. Which of the following combinations of letters accurately represents two sister chromatids?
| back 43 A and C |
front 44  Figure 10-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-1. Which of the following combinations of letters accurately represents two homologous chromatids?
| back 44 A and D |
front 45 The formation of female gametes is termed:
| back 45 oogenesis |
front 46 Which of the following are NOT produced by meiosis?
| back 46 zygotes |
front 47 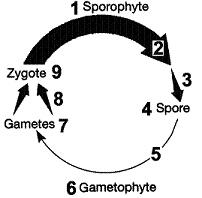 Figure 10-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-2. The chromosome complement of item 6 in the life cycle is:
| back 47 haploid |
front 48 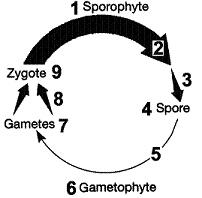 Figure 10-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-2. The process occurring at arrow 3 in the associated figure is:
| back 48 meiosis |
front 49 Gametophyte plants produce gametes using:
| back 49 mitosis |
front 50 Sporophyte plants produce spores using:
| back 50 meiosis |