A bacterial chromosome consists of:
- a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
- a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
- a circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
- a linear DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
- a linear or circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of:
- circular DNA molecules complexed with positively charged nonhistone proteins.
- circular DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
- linear DNA molecules complexed with positively charged histone proteins.
- linear
DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
circular DNA molecules.
linear DNA molecules complexed with positively charged histone proteins.
Nucleosomes are best described as:
- eukaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
- prokaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
- eukaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
- prokaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
- eukaryotic DNA associated with scaffolding proteins.
eukaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
What is the function of nucleosomes?
- To prevent DNA strands from tangling.
- To help DNA replicate.
- To make RNA synthesis possible.
- To prevent RNA from tangling with DNA during transcription.
- To prevent histones from tangling.
To prevent DNA strands from tangling.
Nucleosomes are organized into large coiled loops held together by:
- histones.
- centromeres.
- kinetochore proteins.
- scaffolding proteins.
- condensins.
scaffolding proteins.
The cell cycle of a typical somatic cell consists of __________ and M phase.
- interphase
- meiosis I
- crossing-over
- meiosis II
- mitosis
interphase
The M phase of the cell cycle involves two main processes:
- mitosis and cytokinesis.
- meiosis I and meiosis II.
- homologous pairing and crossing-over.
- interphase and mitosis.
- mitosis and meiosis.
mitosis and cytokinesis
Once nerve cells become mature, they don't usually undergo cell division. Based on your knowledge of the cell cycle, you would predict that mature nerve cells become arrested in the __________ of the cell cycle.
- G0 phase
- S phase
- prophase
- G1 phase
- G2 phase
G0 phase
Chromosomes are duplicated during __________ of the cell cycle.
- G1 phase
- G2 phase
- S phase
- metaphase
- prophase
S phase
Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
- interphase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase - telophase
- anaphase - telophase - metaphase - prophase - interphase
- interphase - prophase - anaphase - metaphase - prometaphase
- metaphase - telophase - prometaphase - anaphase - prophase
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
If a cell is in G2:
- it has twice the amount of DNA present in a telophase nucleus.
- it has visibly distinct chromosomes.
- it lacks a visible nuclear membrane.
- it is in mitosis.
- it is in cytokinesis.
it has twice the amount of DNA present in a telophase nucleus.
During prophase, __________ is(are) compacted into visible chromosomes.
- chromatin
- centrioles
- centromeres
- kinetochores
- colchicine
chromatin
The __________ is responsible for the separation of the chromosomes during __________ of mitosis.
- cell wall; anaphase
- flagellum; metaphase
- mitotic spindle; anaphase
- kinetochore; prophase
- centromere; telophase
mitotic spindle; anaphase
__________ contain identical DNA sequences and are held together by __________ during mitosis.
- Daughter chromosomes; hydrogen bonding
- Daughter chromosomes; ionic bonding
- Sister chromatids; spindle fibers
- Sister chromosomes; histone proteins
- Sister chromatids; centromeres
Sister chromatids; centromeres
The mitotic spindle is made of:
- collagen.
- condensin.
- histones.
- keratin.
- microtubules.
microtubules.
Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
- interphase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase - telophase
- anaphase - telophase - metaphase - prophase - interphase
- interphase - prophase - anaphase - metaphase - prometaphase
- metaphase - telophase - prometaphase - anaphase - prophase
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
All of the following events occur during prometaphase EXCEPT:
-
the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- the nucleoli disappear.
- the mitotic spindle is completely assembled.
- the spindle fibers "capture" chromosomes.
- the duplicated chromosomes become visible with the light microscope.
the duplicated chromosomes become visible with the light microscope.
A cell is in metaphase if:
-
the chromosomes are visible as threadlike structures.
- the nuclear envelope is clearly visible.
- the chromosomes are aligned at the midplane of the cell.
- the chromosome are separated into distinct groups at opposite poles of the cell.
- cytokinesis is occurring.
the chromosomes are aligned at the midplane of the cell.
Duplicated centrioles move to opposite poles of a dividing __________ cell during __________ of the cell cycle.
- plant; metaphase
- plant; anaphase
- prokaryotic; metaphase
- animal; interphase
- animal; prophase
animal; prophase
The chromosome makeup of an individual organism is called a:
- kinetochore.
- chromosome plot.
- centromere.
- karyotype.
- centriole.
karyotype.
Chromosomes are condensed to their greatest extent during __________ of mitosis.
- metaphase
- prophase
- telophase
- interphase
- anaphase
metaphase
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves contraction of a ring of __________ microfilaments.
- tubulin plus actin
- actin plus myosin
- cyclin plus myosin
- keratin plus actin
- cyclin plus actin
actin plus myosin
Cytokinesis in plant cells occurs via the formation of a(n):
- aster.
- mitotic spindle.
- Golgi complex.
- cell wall.
- cell plate.
cell plate.
If a cell is dividing by binary fission then you know that:
- mitosis has taken place without cytokinesis.
- homologous chromosomes have already paired.
-
the cyclin-Cdk complex is no longer phosphorylating enzymes.
- the cell cycle is out of control.
- the cell is prokaryotic.
the cell is prokaryotic.
To prevent disastrous consequences, the eukaryotic cell cycle is controlled by:
- the mitochondria.
- helper viruses.
- environmental signals.
- a very detailed, rigid genetic program.
- a series of cell cycle checkpoints.
a series of cell cycle checkpoints.
Which of the following statements concerning the cell cycle is FALSE?
- The activity of Cdks increases and decreases during the cell cycle.
- Cyclins fluctuate during the cell cycle.
- are active only when they bind to cyclins.
- The anaphase-promoting complex stimulates the separation of sister chromatids.
- M-Cdk inhibits mitosis.
M-Cdk inhibits mitosis.
The correct number of chromosomes is maintained during sexual reproduction by:
- a process by which one half of the chromosomes in gametes are removed.
- chromosome doubling in the newly formed zygote.
- meiosis, which reduces the chromosome number by half.
- mitosis, which maintains the original chromosome number.
- replication of chromosomes twice during meiosis.
meiosis, which reduces the chromosome number by half.
Animal cells are stimulated to divide by mitosis by:
- colchicines.
- magnetic fields.
- mating.
- growth factors.
- nutrients.
growth factors.
If meiosis did not occur in sexually reproducing organisms, then:
- growth of the zygote would be halted.
- mitosis would be sufficient.
- gametes would remain haploid.
- chromosome number would double in each generation.
- eggs would be haploid, but sperm would be diploid.
chromosome number would double in each generation.
What evolutionary advantage is provided by sexual reproduction?
- increased genetic diversity
- making clones
- making diploidy possible
- making polyploidy possible
- being able to work with chromosomes
increased genetic diversity
Plant hormones known as __________ stimulate mitosis.
- gametophytes
- kinesin and dynein
- cytokinins
- colchicines
- kinetochores
cytokinins
Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis during:
- anaphase I.
- prophase I.
- anaphase II.
- telophase II.
- prophase II.
prophase I.
A maternal homologue and a paternal homologue synapse to form:
- a tetrad.
- a parental pair.
- a paternal pair.
- sister chromatids.
- a maternal pair.
a tetrad.
During which phase does crossing-over occur?
- interphase
- prophase I
- metaphase I
- prophase II
- metaphase II
prophase I
A zygote contains the __________ number of chromosomes.
- haploid
- diploid
- polyploid
- spermatogenesis
- none of these
diploid
In a human cell at prophase I, there are __________ tetrads.
- 92
- 46
- 23
- 2
- 4
23.
An animal with a diploid number of 36 chromosomes will have __________ chromosomes in its gametes and __________ chromosomes in its somatic cells.
- 18; 18
- 18; 36
- 36; 18
- 36; 36
- 36; 72
18;36
During prophase I, each chiasma represents:
- the remnants of the nuclear membrane.
- the remnant of the nucleolus.
- a newly formed haploid gamete.
- a site of crossing-over.
- the site where sister chromatids are connected.
a site of crossing-over.
During which of the following stages of meiosis do the sister chromatids separate?
- metaphase I
- anaphase I
- metaphase II
- anaphase II
- telophase II
anaphase II
Which of the following represents the overall sequence of events during mitosis?
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
- interphase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase - telophase
- anaphase - telophase - metaphase - prophase - interphase
- interphase - prophase - anaphase - metaphase - prometaphase
- metaphase - telophase - prometaphase - anaphase - prophase
- prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase -telophase
The sources of genetic variation during meiosis are:
- crossing-over and the random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
- crossing-over and random pairing of tetrads.
- random pairing of tetrads and mutations.
- polyploidy and random pairing of tetrads.
- random pairing of tetrads and random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
crossing-over and the random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Which of the following events does not occur during meiosis I?
- DNA exchange
- pairing of homologous chromosomes
- separation of sister chromatids
- separation of homologous chromosomes
- crossing-over between homologous chromosomes
separation of sister chromatids

Figure 10-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-1. Which of the following combinations of letters accurately represents two sister chromatids?
- A and B
- A and C
- A and D
- A and E
- B and F
A and C

Figure 10-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-1. Which of the following combinations of letters accurately represents two homologous chromatids?
- A and B
- A and C
- A and D
- B and F
- D and E
A and D
The formation of female gametes is termed:
- oogenesis.
- macrogenesis.
- spermatogenesis.
- ovogenesis.
- microgenesis.
oogenesis
Which of the following are NOT produced by meiosis?
- polar bodies
- animal eggs
- animal sperm
- plant spores
- zygotes
zygotes
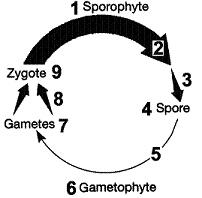
Figure 10-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-2. The chromosome complement of item 6 in the life cycle is:
- twenty.
- haploid.
- diploid.
- forty-eight.
- four.
haploid
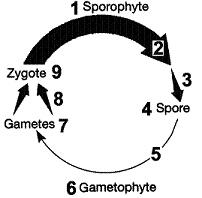
Figure 10-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 10-2. The process occurring at arrow 3 in the associated figure is:
- fertilization.
- G1.
- meiosis.
- mitosis.
- fusion.
meiosis
Gametophyte plants produce gametes using:
- mitosis.
- meiosis.
- fertilization.
- polyploidy.
- sporogenesis.
mitosis
Sporophyte plants produce spores using:
- mitosis.
- meiosis.
- fertilization.
- macrogenesis.
- microgenesis.
meiosis