Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch.9 BICH
front 1 Lipids and proteins are mobile, and can | back 1 diffuse laterally in the membrane |
front 2 Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogens which means | back 2 they have all single bonds |
front 3 meaning of (n:x) -n= -x= | back 3 -number of carbons -amount of double bonds |
front 4 What is the structure of myristic acid? | back 4 (14:0) |
front 5 What is the structure of palmitic acid? | back 5 (16:0) |
front 6 What is the structure of stearic acid? | back 6 (18:0) |
front 7 Unsaturated fatty acid have | back 7 double bonds |
front 8 Oleic acid structure____ | back 8 (18:1) |
front 9 Linoleic acid structure ___ | back 9 (18:2) |
front 10 Arachidonic acid structure___ | back 10 (20:4) |
front 11 Δx | back 11 x means its the location of the double bonds |
front 12 Double bonds are cis and | back 12 unconjugated |
front 13 When unsaturated fatty acids have one or more unconjugated double bonds, | back 13 the fatty acid can not fully extend |
front 14 Saturated chains optimally pack tightly and form | back 14 more stable, rigid, ordered aggregates |
front 15 Unsaturated chains bend and pack in a less ordered way with greater potential | back 15 greater potential for motion |
front 16 Higher order means more stability and higher | back 16 melting temperature, Tm |
front 17 Triacylglycerols (TAG's) are considered to be | back 17 1. The most reduced form of carbon in nature (oxidation releases energy) 2. No solvation with water (dehydrated, weighs less) 3. Efficient packing (not just because dehydrated, also van Der Waals) |
front 18 TAG's are a major | back 18 energy source for many organisms |
front 19 Most fatty acids in plants and animals exist in the form of | back 19 triacylglycerols |
front 20 If all fatty acids are the same, the molecule is called a | back 20 simple triacylglycerol |
front 21 If two or three fatty acids are different, it is called | back 21 mixed triacylglycerols |
front 22 a 1,2-diacylglycerol that has a phosphate group esterified at C3 of the glycerol backbone is a | back 22 glycerophospholipid |
front 23 Glycerophospholipid are ____lipids and are essential components of cell membranes | back 23 structural |
front 24 All head groups start with | back 24 -OH groups |
front 25 Look at table 9-2 | back 25 no data |
front 26 Phospholipases A1 and A2 cleave fatty acids from glycerophospholipids producing | back 26 lysophospholipids |
front 27 Phospholipases C and D hydrolyze on either side of the phosphate in | back 27 the polar head group |
front 28 Phospholipids play important roles such as | back 28 giving chemical signals in and on cells |
front 29 Lipid signals act _______, and have short lifetimes | back 29 locally within or near the cell |
front 30 Ether glycerophospholipids (PAF) properties: | back 30 1. a potential mediator in inflammation, allergic response, and shock 2. Has a beneficial effect on toxic shock syndrome 3. involved in implantation of the egg in the uterine wall 4. stimulates production of fetal lung surfactant |
front 31 Sphingolipids are frequently present in | back 31 animal cell membranes |
front 32 Has 18-carbon alcohol, forms the backbone of these lipids | back 32 sphingosine |
front 33 A fatty acid that is joined to sphingosine is linked in | back 33 amide group and is called a ceramide |
front 34 Are ceramides with one or more sugars in beta glycosidic linkage at the hydroxyl group | back 34 Glycosphingolipids |
front 35 Glycosphingolipids with one sugar and a single sugar headgroup | back 35 cerebrosides |
front 36 Glycosphingolipids with 3 or more sugars, and one of which is a sialic acid | back 36 Gangliosides |
front 37 Sphingolipids increase Tm, and | back 37 pack together well |
front 38 Terpenes are a class of lipids formed from combinations of | back 38 isoprene units |
front 39 Isoprene units have two possible linkages | back 39 1) head-to-tail 2) tail-to-tail |
front 40 Steroids are isoprene-based molecules built on a core structure of | back 40 three 6-membered ring and one 5-membered ring fused together |
front 41 What is the most common steroid in animals and precursor for all other steroids? | back 41 Cholesterol |
front 42 What are the functions of steroid hormones? | back 42 salt balance, metabolic and sexual function |
front 43 Cortisol provides control of | back 43 carbohydrates, protein, and lipid metabolism |
front 44 testosterone is | back 44 the primary male sex steroid hormone |
front 45 Estradiol is | back 45 the primary female sex steroid hormone |
front 46 Progesterone is a precursor of | back 46 testosterone and estradiol |
front 47 Bile salts/acids including cholic and deoxycholic acid are | back 47 detergent molecules secreted in bile from the gallbladder |
front 48 Are insoluble in water, and serve as water repellant | back 48 waxes |
front 49 Classes of lipids 1. Triacylglycerols: energy storage; fats 2. Glycerophospholipids: structural and signaling 3. Sphingolipids: structural 4. sterols (terpenes): structural and signaling | back 49 no data |
front 50 Functions of membranes : | back 50 - barrier to toxic molecules - Transport and accumulation of nutrients - energy transduction - facilitation of cell motion -reproduction - signal transduction -cell-cell interactions |
front 51 Biological membranes contain as much as ______% protein or as little as _____% protein | back 51 75-80%, 15-20% |
front 52 Lipids self-associate to form membranes because of | back 52 hydrophobic effect |
front 53 Lipids spontaneously form ordered structures in | back 53 water |
front 54 What is the phospholipid bilayer? | back 54 fluid matrix |
front 55 Two classes of proteins: | back 55 -peripheral proteins( extrinsic ) -integral proteins ( intrinsic ) |
front 56 Slow transverse diffusion of lipids and proteins ______. By contrast lateral diffusion is ______. | back 56 preserves membrane asymmetry, rapid |
front 57 Bilayer core dimensions | back 57 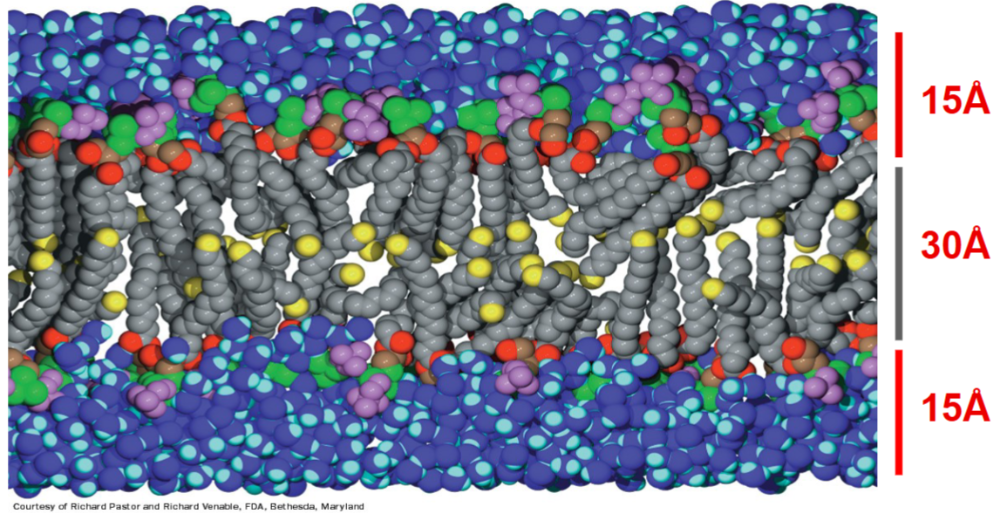 |
front 58 Peripheral membrane proteins: | back 58 -can be dissociated with high salt concentration - insert hydrophobic loop or amphiphilic alpha helix - form ionic interactions and H bonds |
front 59 Integral membrane proteins are strongly embedded in lipid bilayer and | back 59 -can be removed from the membrane by denaturing - secondary structure neutralizes the highly polar N-H and C=O functions of the peptide backbone through H-bond formation |
front 60 Transmembrane segment is alpha-helical and consists of | back 60 19 hydrophobic acids |
front 61 Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) is found in ____ and consists of____ | back 61 purple patches of Halobacterium, 7 transmembrane helical segments |
front 62 The sequence of a transmembrane protein is adapted to the transition from water to the | back 62 hydrophobic core and then to water again |
front 63 Trp, His, and Tyr are mixtures of | back 63 polar and non-polar parts |
front 64 Each alpha helix requires____ per transmembrane strand. Each beta strand requires only ___ per transmembrane strand. | back 64 21-25, 9-11 |
front 65 Four types of lipid-anchored proteins: | back 65 1. Amide-linked myristoyl anchors 2. Thioester-linked fatty acid anchors 3. Thioether-linked prenyl anchors 4. Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchors |
front 66 Amide-linked myristoyl anchors are always linked to the alpha-amino N of Gly residue and | back 66 always myristic acid and N-terminal |
front 67 Thioester-linked and acyl anchors are always linked to Cys and | back 67 myristate, palmitate, stearate, and oleate |
front 68 Ethanolamine link to an oligosaccharide linked in turn to | back 68 inositol of phosphatidyl inositol (PI) |
front 69 Always attached to a C-terminal carboxyl group of a recognized sequence, | back 69 GPI-linked proteins are found on the cell surface where oligosaccharide links are found |
front 70 Membranes are asymmetric structures | back 70 1. Lateral Asymmetry of Proteins 2. Lateral Asymmetry of Lipids 3. Transverse Asymmetry of Proteins 4. Transverse Asymmetry of Lipids |
front 71 ATP flipases move PS from the | back 71 outer leaflets to the inner leaflets: "flip in" |
front 72 ATP flopases move lipids including cholesterol, PC< and sphingomyelin from the | back 72 inner leaflets to the outer leaflet of the membrane: "flop out" |