Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ARTH 1450 Midterm 2
front 1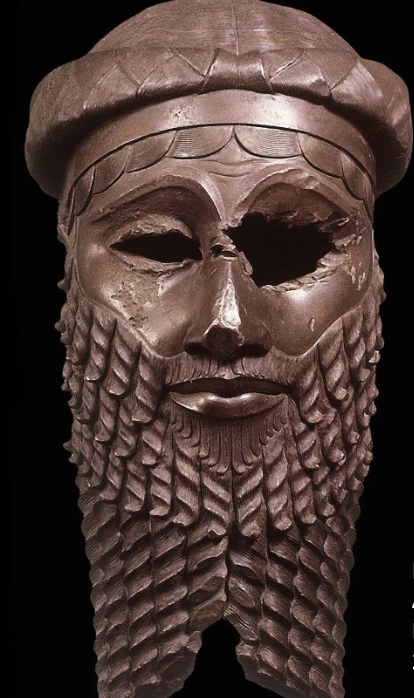  | back 1 Head of an Akkadian Ruler Akkadian (2250 BCE), bronze, 30.7 cm, Akkad do not know where capital of Akkad (maybe Akkad itself?) is Sargon emperor ritual mutilation of senses: eyes and ear --> rely on eyes and ears (damage ability of sight and hearing) done by later people, not Akkadians --> detract rulers power perfect patterned beard --> masculinity / virility / power mask like quality woven hair is marking him as a ruler --> looks like a crown (Princess Leia) |
front 2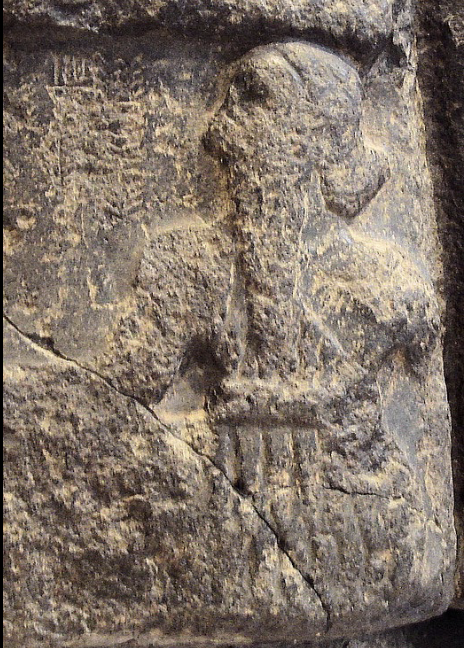  | back 2 Sargon of Akkad Akkadian (2334 - 2284 BCE), diorite, Akkad cuneiform --> sumerian script (not sumerian langauge) |
front 3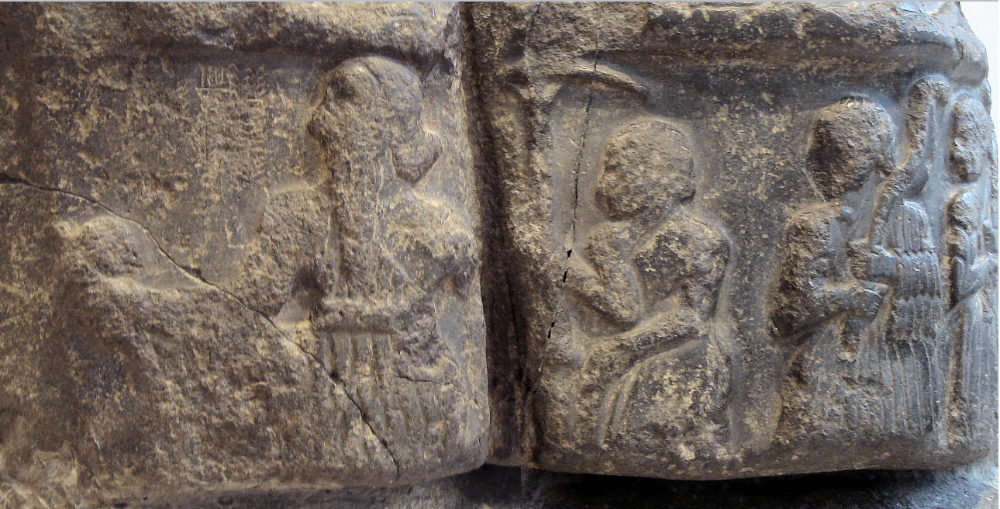  | back 3 Victory Stele of Sargon Akkadian, diorite, Akkad helmet and hair = masculinity |
front 4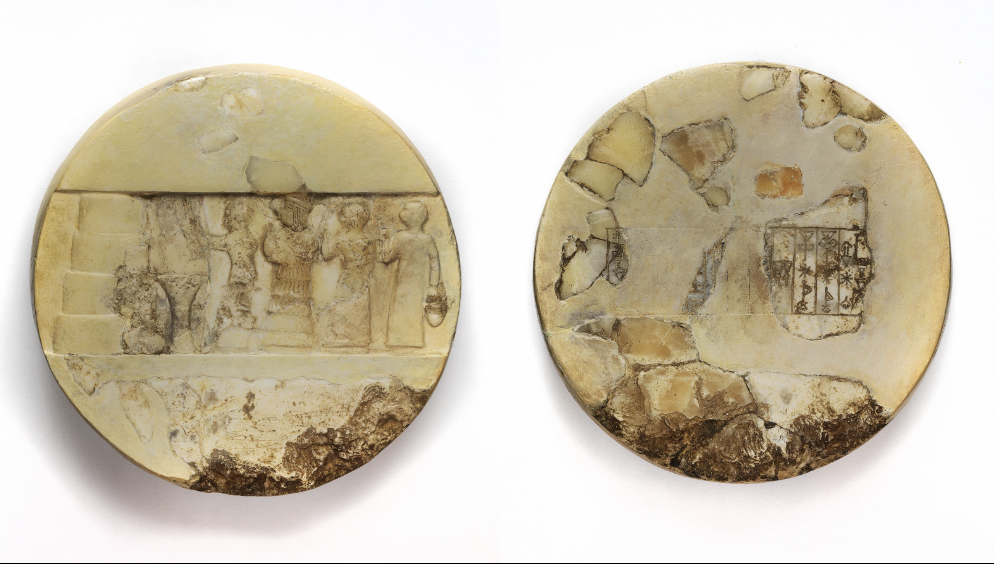  | back 4 Enheduanna Disk Akkadian (2350 - 2300 BCE), limestone and calcite, 25 cm, Akkad wrote first poem first women (and person WOOOHOOO) to sign their name |
front 5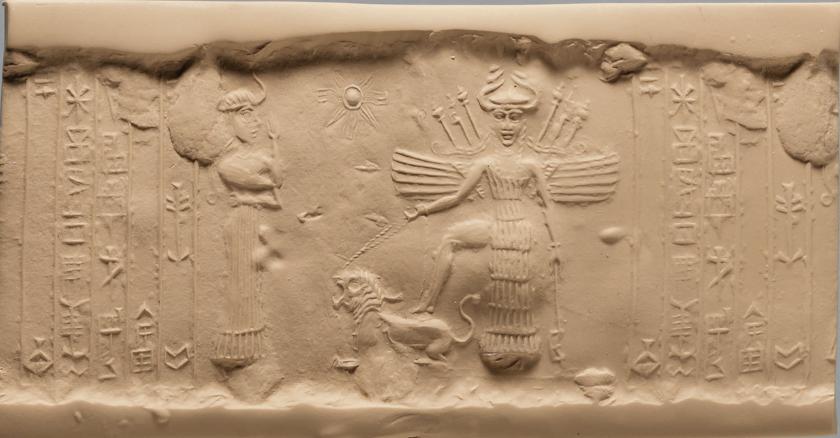  | back 5 Cylinder Seal Akkadian (2350 - 2150 BCE), limestone, Akkad portrait of innana innana scares akkadians innana has wings, full weapons on back, horns = power (more horns = more powerful deity) innana = goddess of love and war --> lion is her sacred animal because they are big and scary but protect their cubs (defensible / fertility) |
front 6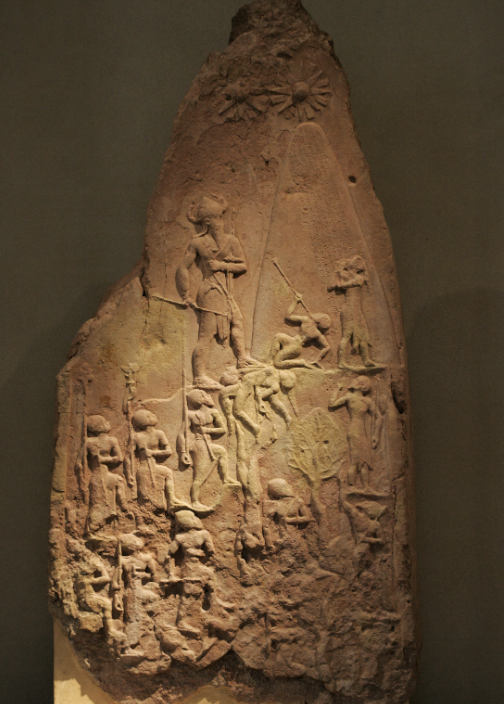  | back 6 Stele of Naram-Sin Akkadian (2250 BCE), limestone, 200 cm (6'7"), Akkad hieratic scale --> Narrar-Sin is bigger and higher than everyone else = more important one set of horns Elammites steal it to appropriate Naram-Sin's victory for their own --> like a trophy original location is Sippar but it was found in Susa Akkad is constantly expanding --> human based cultural destruction |
front 7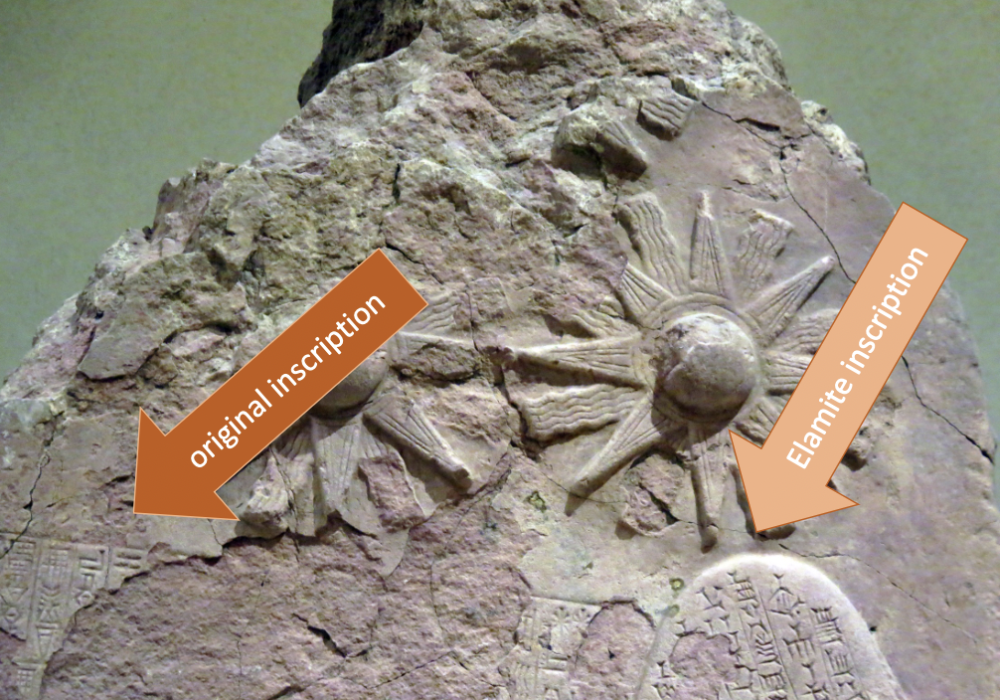  | back 7 proof that Naram-Sin Stele was stolen by Elammites |
front 8 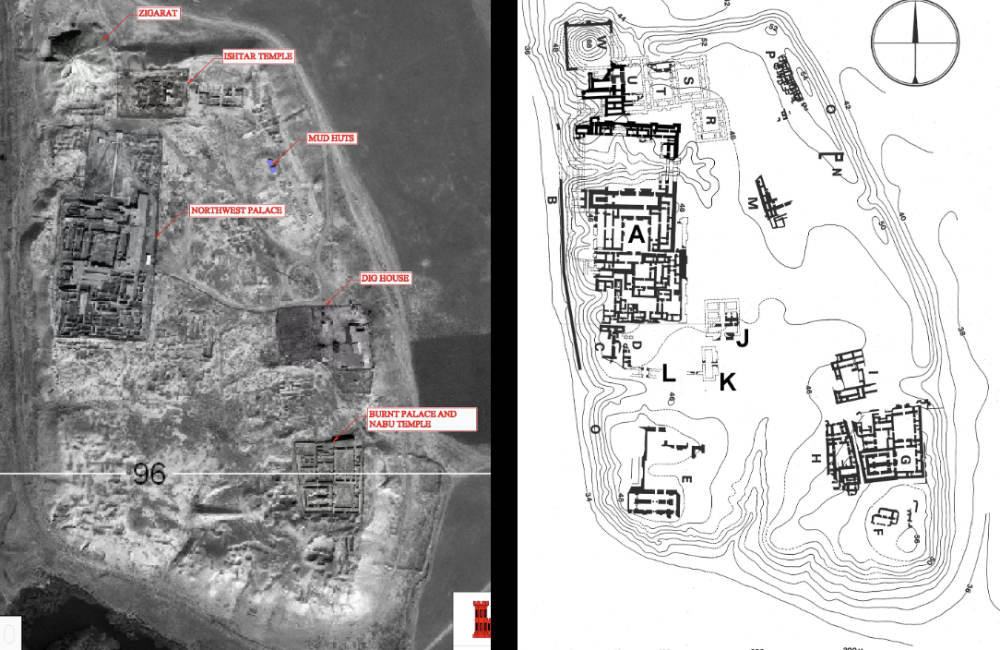 | back 8 Nimrud (879 - 706 BCE) Capital city of Assyirians |
front 9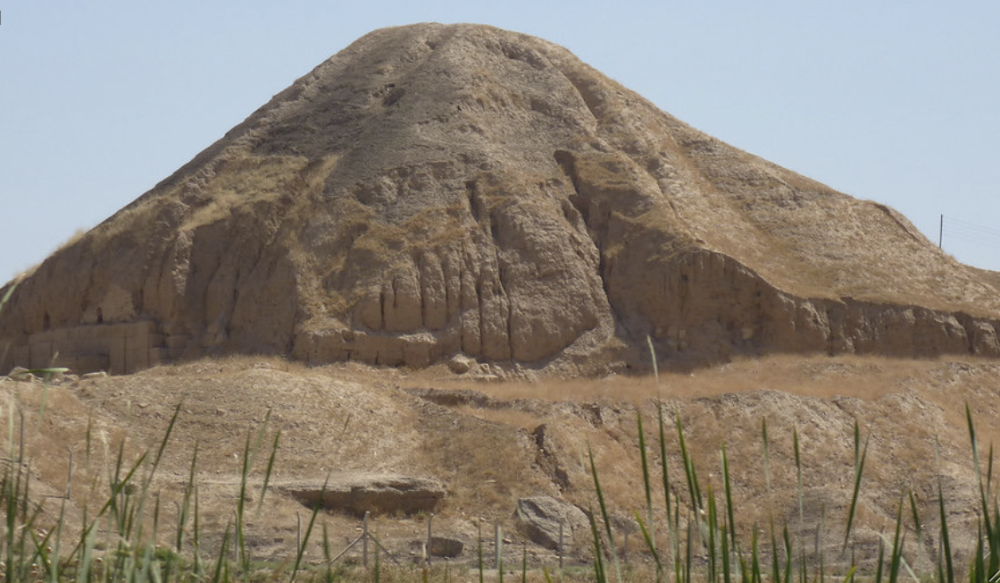  | back 9 Great Ziggurat Assyrian Nimrud Shalmaneser III mud brick --> not well preserved |
front 10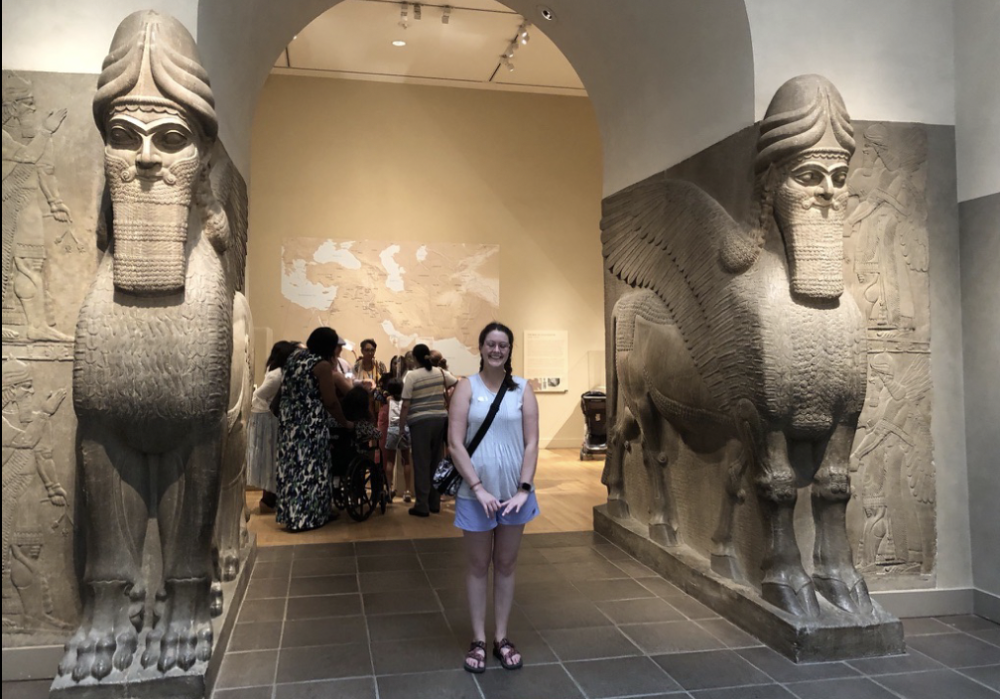  | back 10 Lamassu Assyrian (883 - 859 BCE), Palace of Ashurnasirpal II in Nimrud apotropaic --> guardians of the throne room (intimidate you and keep bad things away) one is a bull body, the other is a lion body 3 horns and five legs --> side it looks like walking with you, front it looks like they are standing still ISIS destroys many artwork int his area |
front 11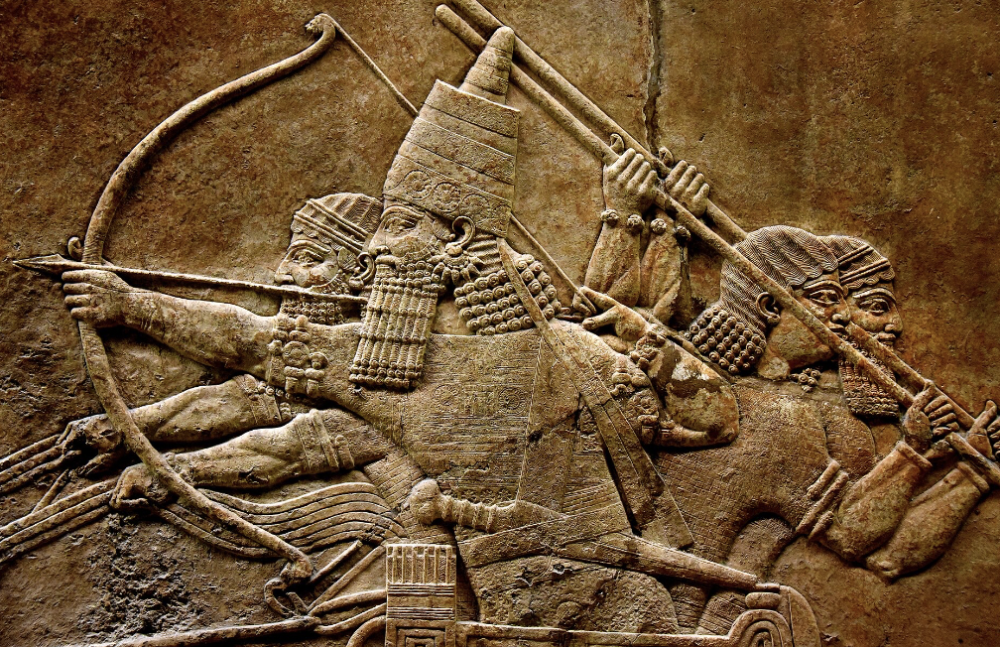  | back 11 Relief depicting Ashurbanipal Assyrian (669 - 631 BCE), Assyria Ash has a hat on Ash is hunting lions --> proves he is more powerful than a lion and intimidate enemies but lions were pre-captured in order to let the king kill them --> king is actually weak |
front 12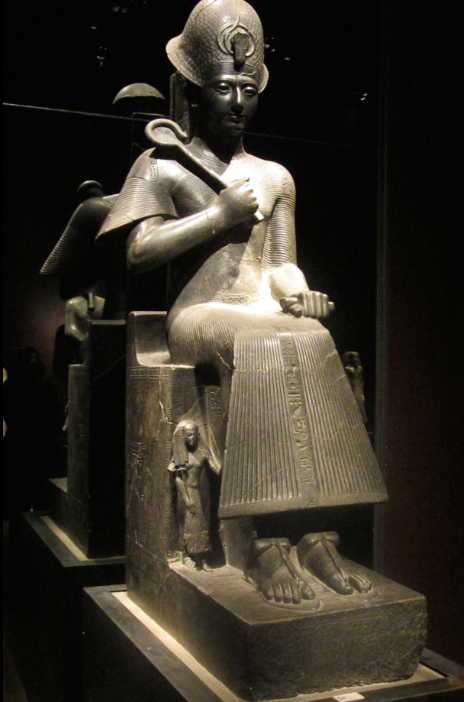  | back 12 Ramses II Dynasty 19 (1292 - 1189 BCE), granodiorite, Karnak Temple in Egypt feminine --> was it more prominent and not ripped Ramses will always look truthful and perfect not intimidating --> face lacks emotion presence = power --> calm but in control child on the side (children are bald except for ponytail) --> hieratic scale = Ramses is most important Ramses has 5 names (more names = more accomplishments) one being Ra ms sw, child of Ra, never lost a battle (lie) graffiti under statue reads sema-tawy = unification of Egypt |
front 13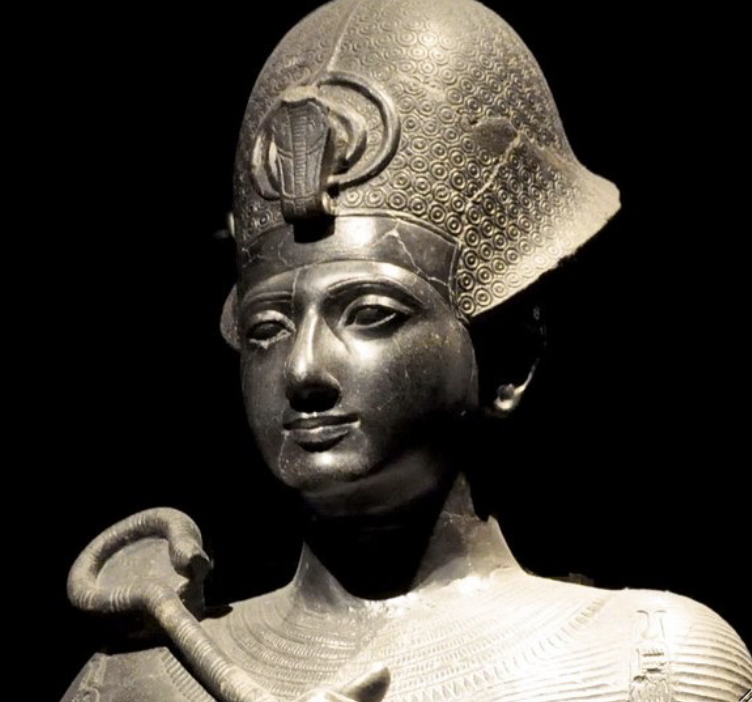  | back 13 Ramses II --> more specifically the crown no physical representation of crown --> know it exists because of statues likely valuable and stolen would've been woven out of reeds (basket like) khepresh = blue crown --> wear when go to war (Ramses wears this constantly) |
front 14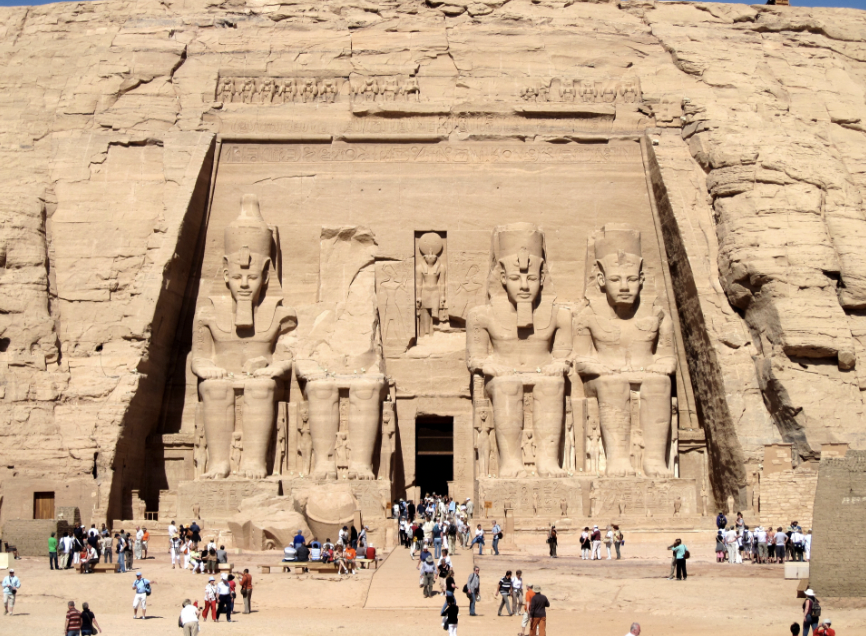  | back 14 Temple of Ramses, beloved of Amun 19th Dynasty (1264 - 1244 BCE), 67 ft tall, Egypt dedicated to Amum = fertility, Ptah, Re-Horakhty, and Ramses II all big statues are Ramses moved Temple piece by piece (lifted and reassembled) --> build a fake mountain for it and tried to maintain as much of the go location as possible wife on right leg and child in between --> hieratic scale |
front 15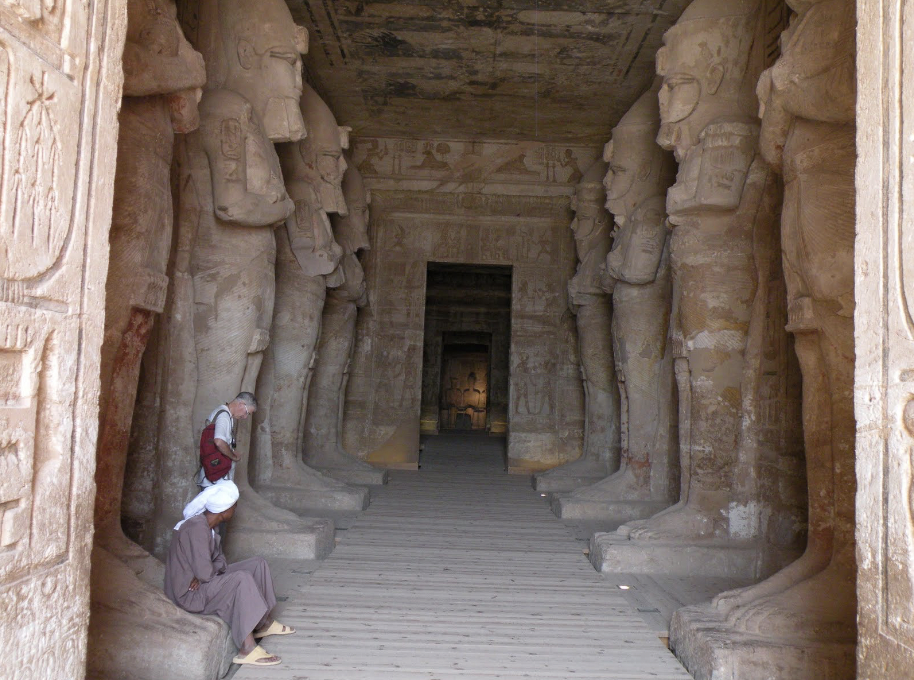  | back 15 Great Hall of the Temple of Ramses II Egypt |
front 16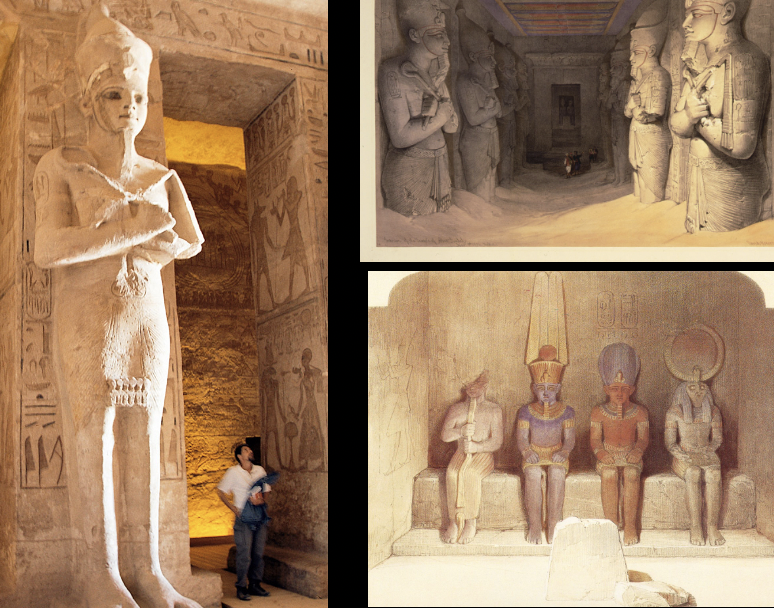  | back 16 Great Hall and Sanctuary in the Temple of Ramses II Egypt the temple is big when you enter and gets smaller the further you go in Ramses will always have a big space in between big tow and other toes (cause he's a freak) |
front 17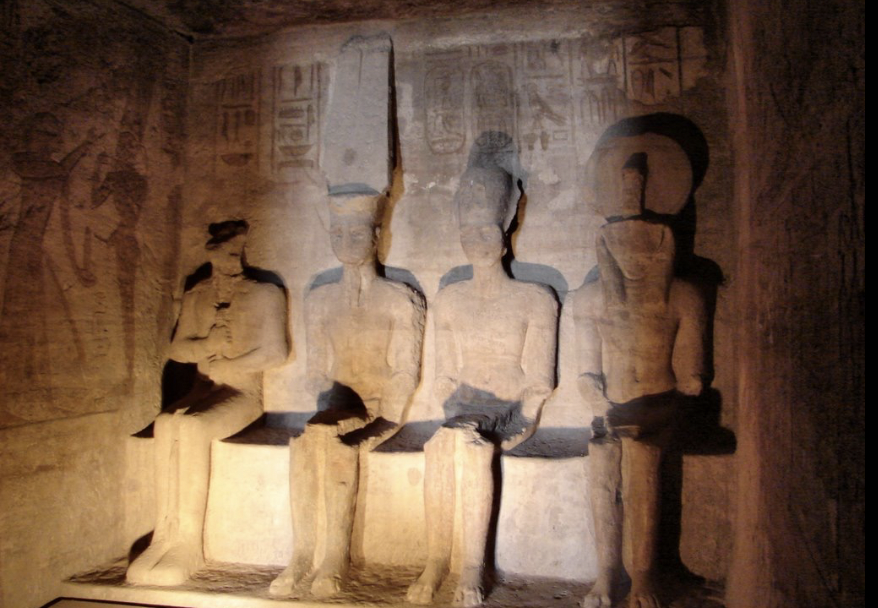  | back 17 Inner Sanctuary in the Temple of Ramses II Ramses (the third figure) and other figures 2 days a year, 3 of the figures are lit with natural light (not Ptah) --> Feb 21 (Ramses birthday) and Oct 21 (his coronation) |
front 18  | back 18 Ramses during the battle from Abu Simbel Battle of Kadesh Ramses winning --> stabbing position both ramses and general getting stabbed are both big for respect (no hieratic scale) stepping on dead enemies |
front 19 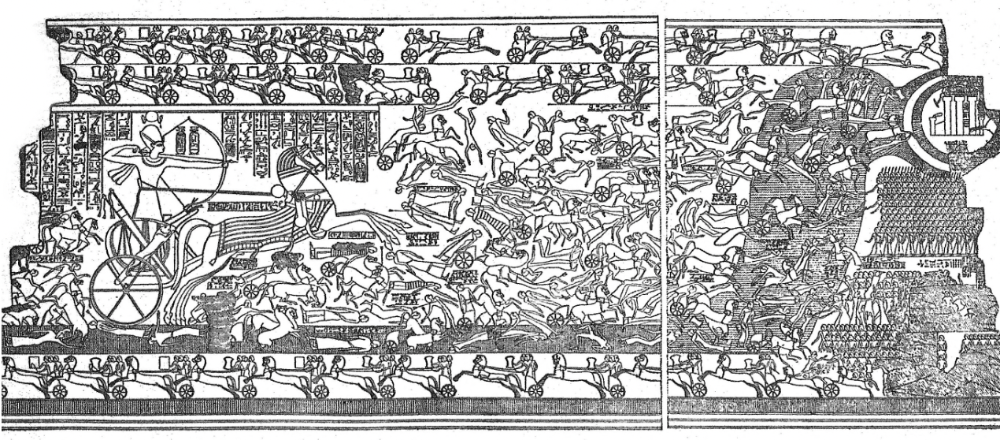 | back 19 Battle Scene from the Great Kadesh Reliefs of Ramses II on the walls of the Ramessuem less noise around Ramses (and Egyptian army) --> more easily identifiable Hitites full of chaos and messy need 3 to drive a chariot --> Ramses only needs himself (demonstrates perfectness) |
front 20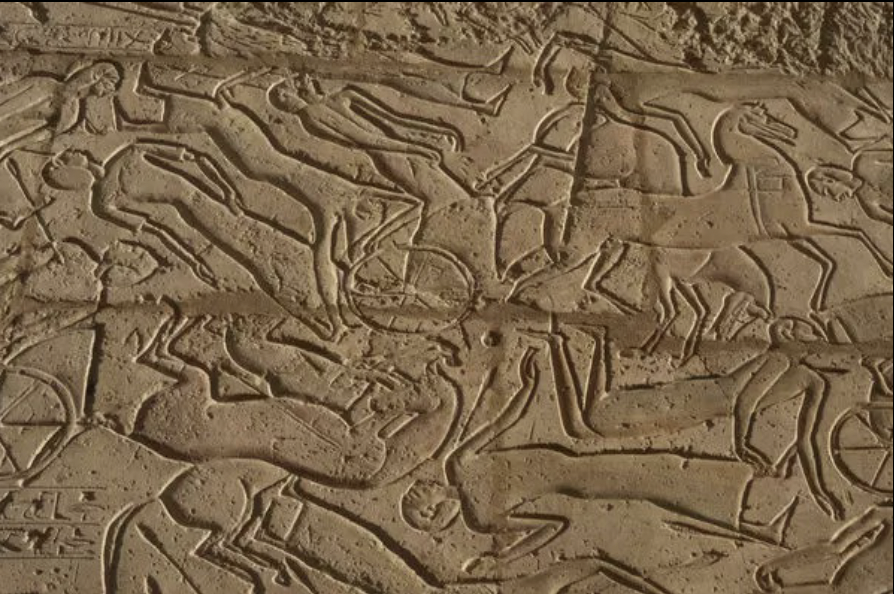  | back 20 Depiction of the Battle from Ramasseum diplomatic piece Ramses did not actually win the war diplomatic victory! not a military victory! |
front 21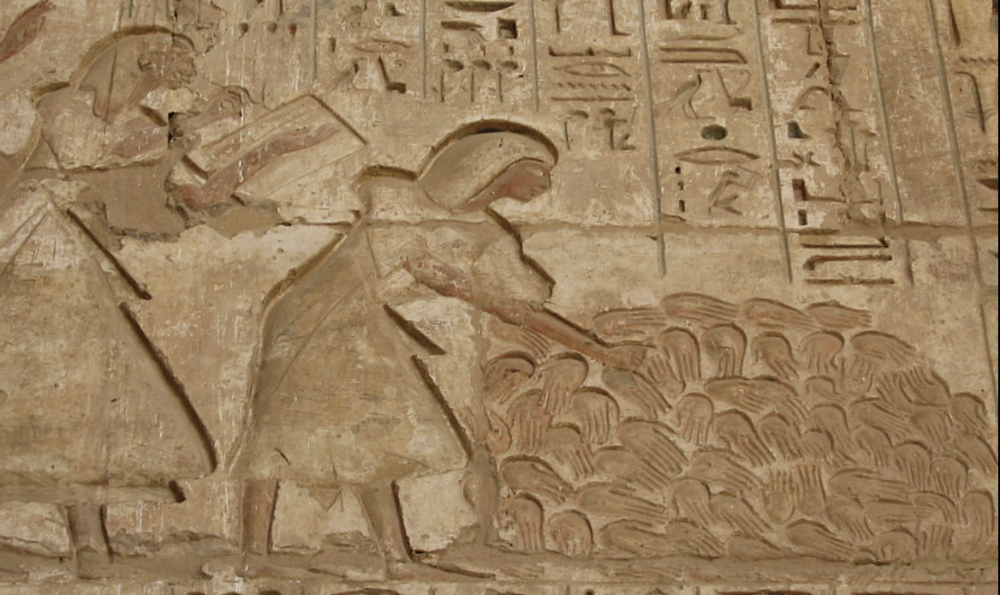  | back 21 Medinet Habu Relief Dynasty 20, Egypt Ramses III count dead by hands or pp --> hands easily doubles body count demonstrates brutality |
front 22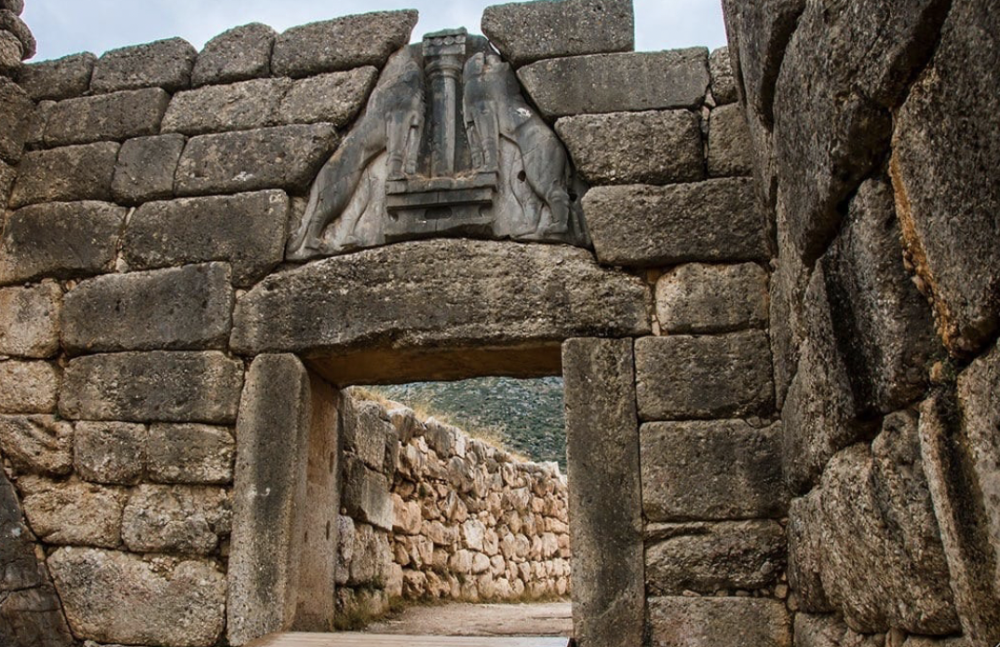  | back 22 Lion Gate Mycenaean (1250 BCE), ashlar masonry, Mycenae main entrance cyclopean masonry --> called this because did not believe ancestors had ability to make them so cyclops had lions --> relieving triangle (receives pressure from lentel) lions are strong and top of the food chain missing their heads --> but if they did have a head there would be no mane |
front 23 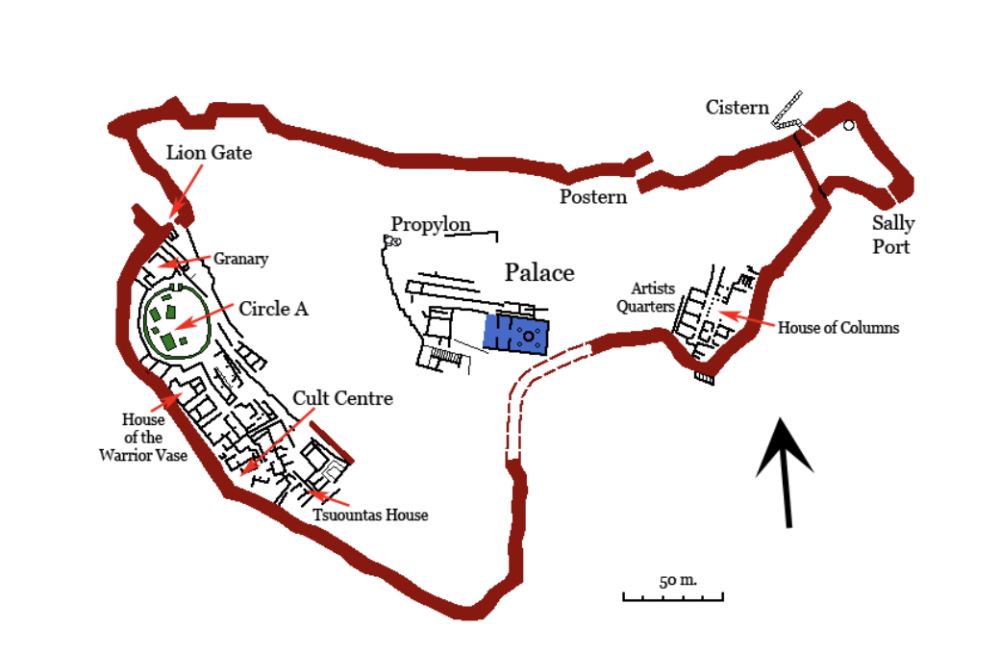 | back 23 City of Mycenae walls --> defensible (constantly preparing for attack, aerie is achieved through militaristic needs) where there is "no wall" there is actually a cliff made for seige |
front 24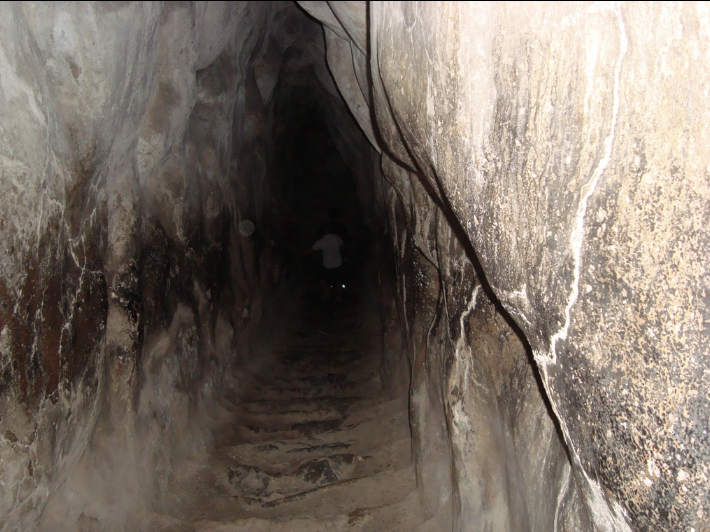  | back 24 Cistern Mycenaean, Mycenae very dark help with potential siege |
front 25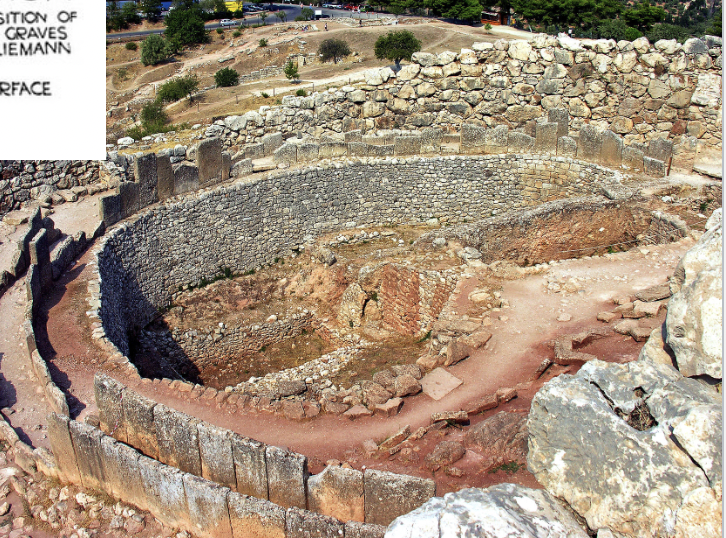  | back 25 Grave Circle A 16th century BCE, Mycenae 6 shaft graves --> 19 bodies |
front 26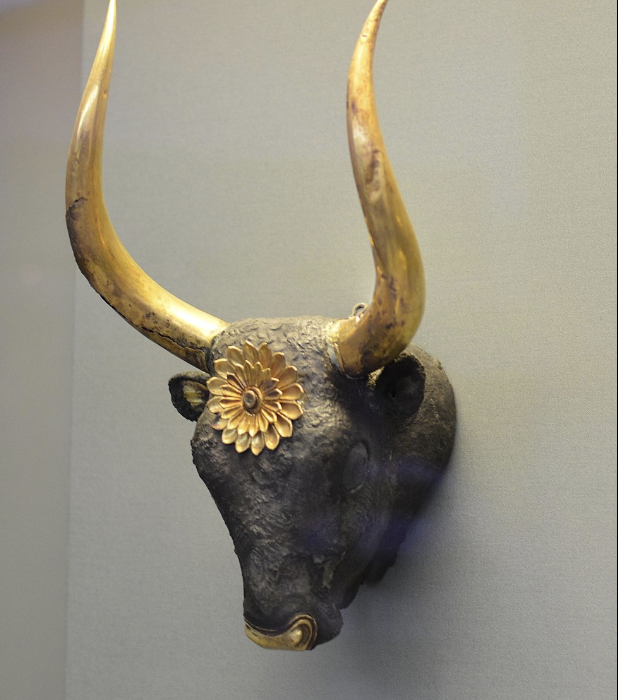  | back 26 Bull's head Rhyton Mycenaean, gold and silver, Grave IV in Grave Circle A, Mycenae used for liquid offerings --> poured out of mouth |
front 27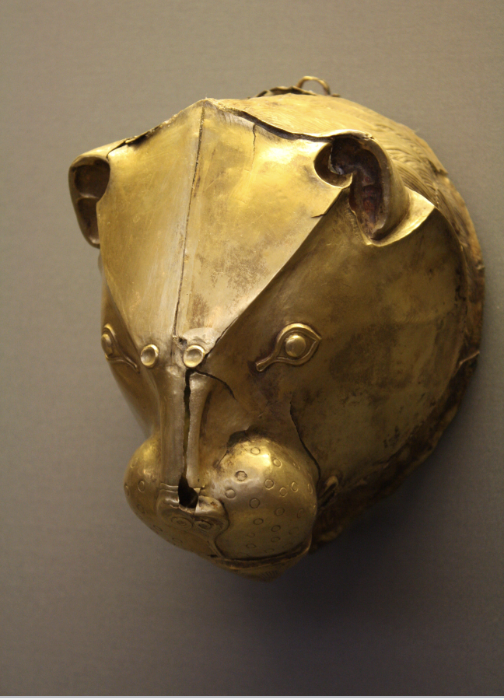  | back 27 Lion's head rhyton Mycenaean, hammered gold, Grave Circle A, Mycenae |
front 28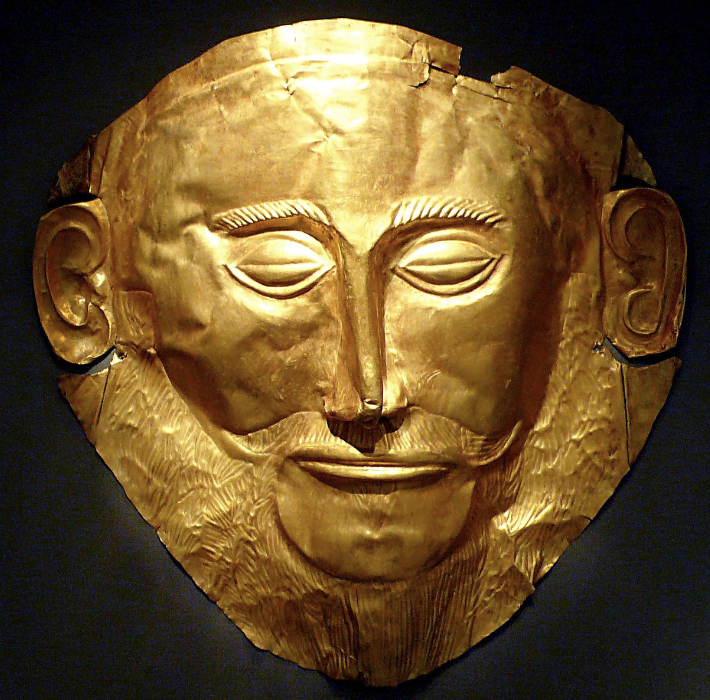  | back 28 Mask of Agamemmon Mycenaean (1550-1500 BCE), gold sheet, Grave V in Grave Circle A peaceful --> closed eyes / grave smile repousse for face and beard is chasing gaslight Keiser Wilhem that he looks like this mask and make him believe he was destined to be a leader / king to get on his good side |
front 29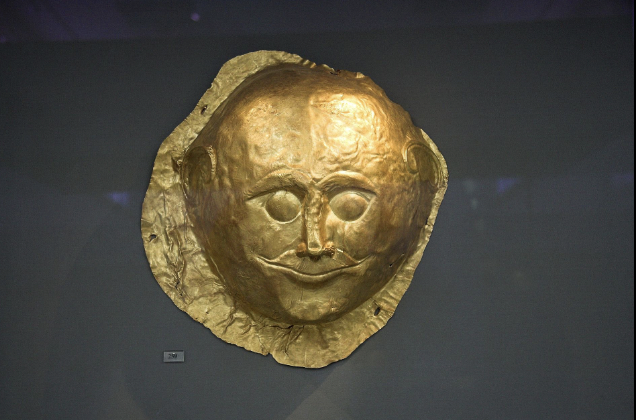  | back 29 Death Mask Mycenaean (1650 BCE), gold, Grave Circle A looks happy to be dead |
front 30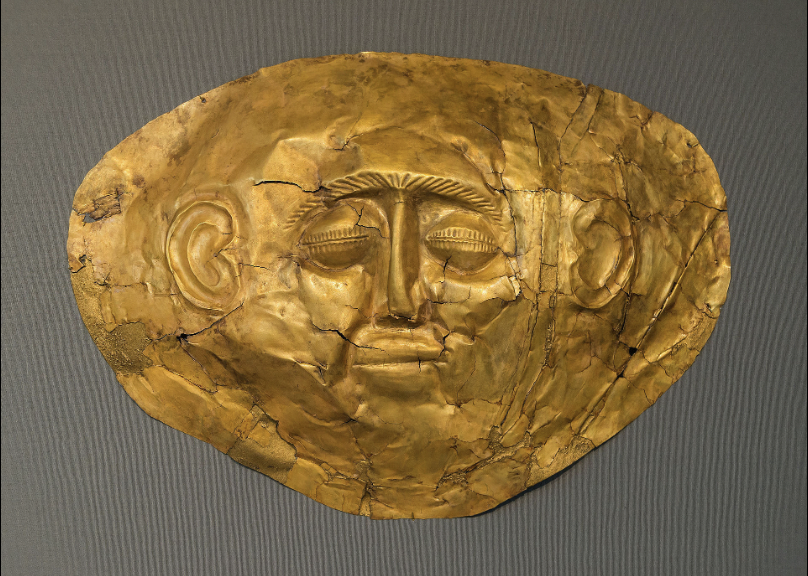  | back 30 Death Mask Mycenaean, gold, Grave Circle A most detailed --> has eyelashes and lips |
front 31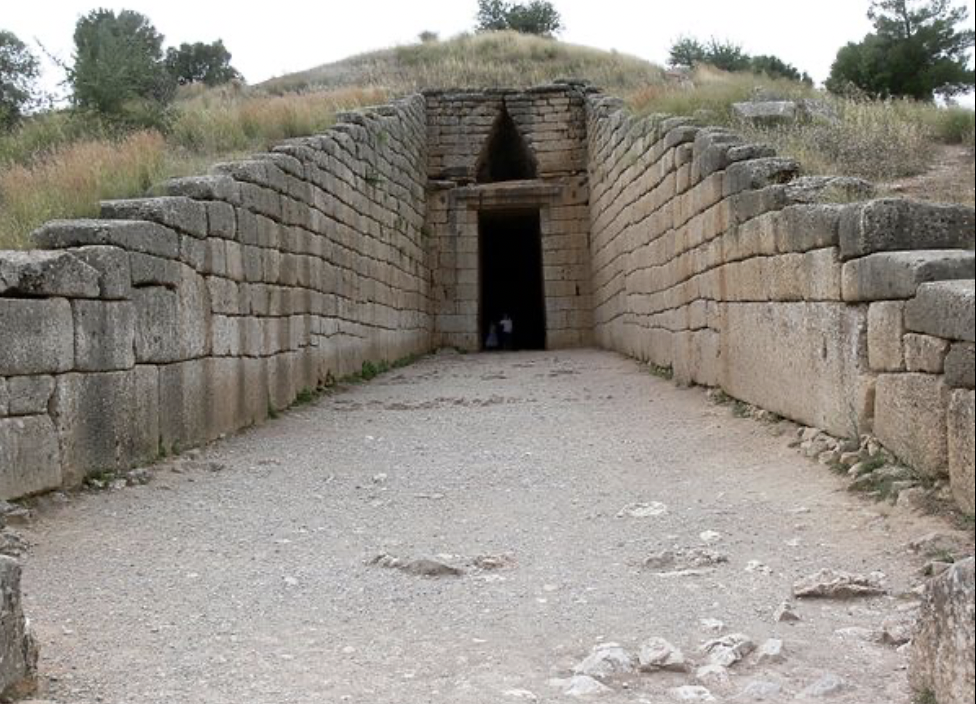  | back 31 Treasury of Atreus Mycenaean (1250 BCE), Mycenae dromos = road that leads to tomb --> like lion gate not actually a treasury, a tomb --> tools tomb or beehive tomb in domestic monastery earth built on top of structure interior 13.5m high and 14.5m in diamter corbel vault |
front 32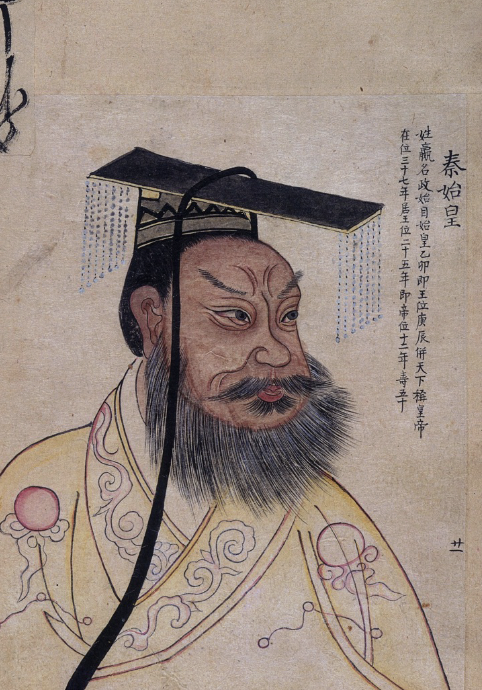  | back 32 posthumous 19th century CE portrait of Emperor Qin Qin rules from 259-210 BCE --> believes legalism is law Qin Dynasty (221-206 BCE) --> first unified state in China with centralized power and collapsed after his death (dies at 49 due to drinking mercury as medicine |
front 33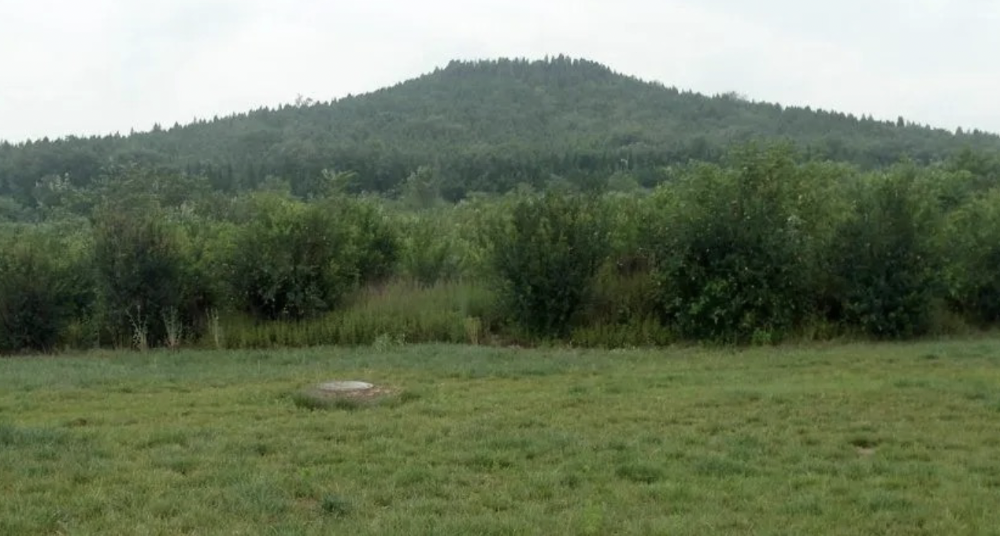  | back 33 Burial of Qin 1974, China looks like a fake mountain built earth structure massive labor effort |
front 34 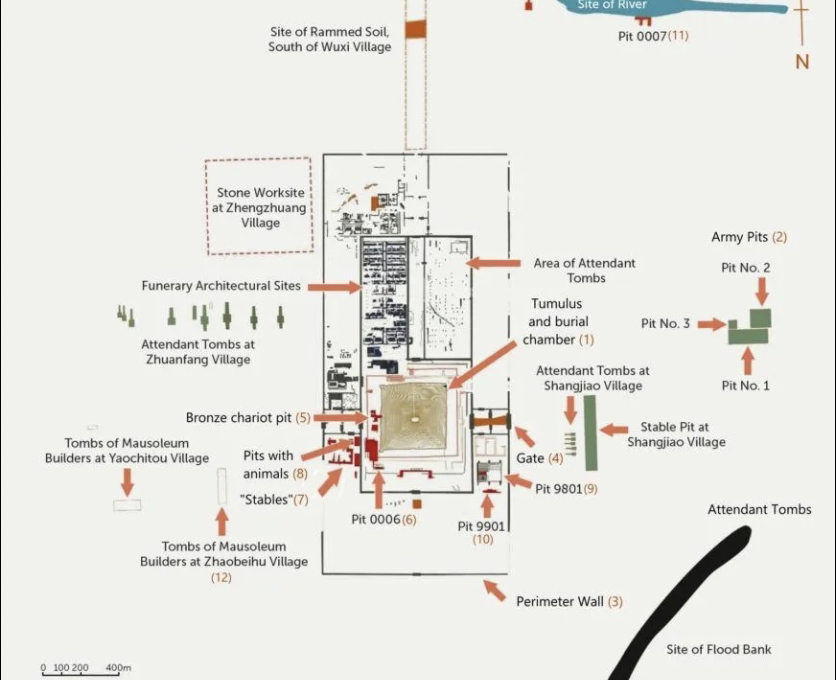 | back 34 Plan of Necropolis Qin Dynasty, China have not opened Qin tomb in central burial chamber --> would have to damage tomb otherwise get in, there is lots of mercury ion tomb, our air could damage it necro = dead, polis = city also tombs for attendant workers, animals, etc --> workers with Qin forever as soon as state unified, this was built walls were defensible whole structure is apotropaic |
front 35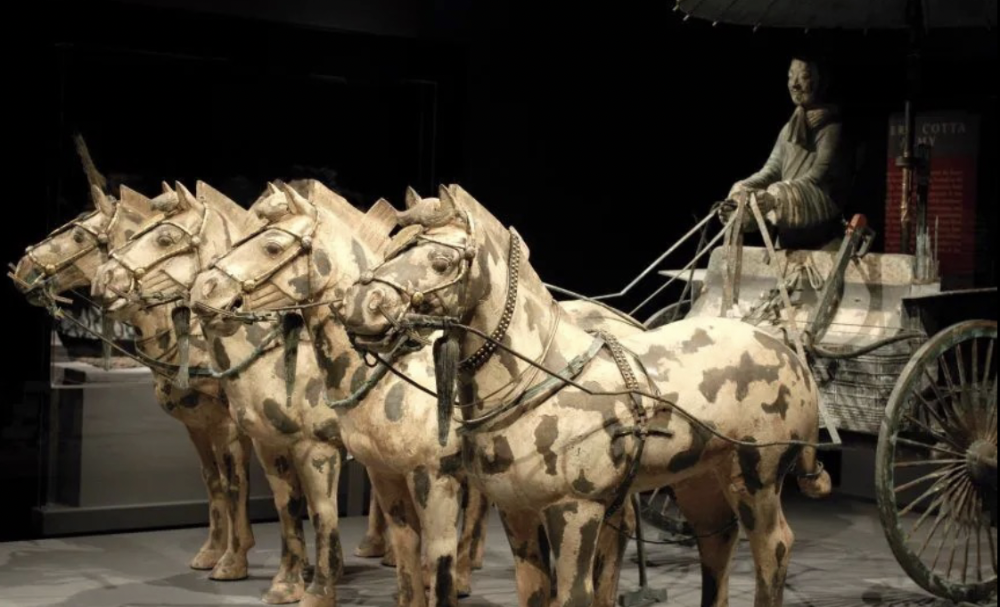  | back 35 War Chariot Qin Dynasty (210 BCE), bronze, Mausoleum of Emperor Qin, China similar to Buddha's riderless horse mostly reconstructed --> brown spots are original as close to burial chamber as possible --> easy access to after life |
front 36  | back 36 Terracotta Soldiers Qin Dynasty, baked clay, China in sita --> still where they were placed plumbers likely builders of these soldiers everything mold made, wait to mold becomes leather hard to add details, put pieces together, bake, then glaze and color soldiers were polychrome --> paint fell off within seconds it touched our air all soldiers individualized --> modular production (many different parts to mix and match --> maximizes variety) not all life size, generally close to life size |
front 37 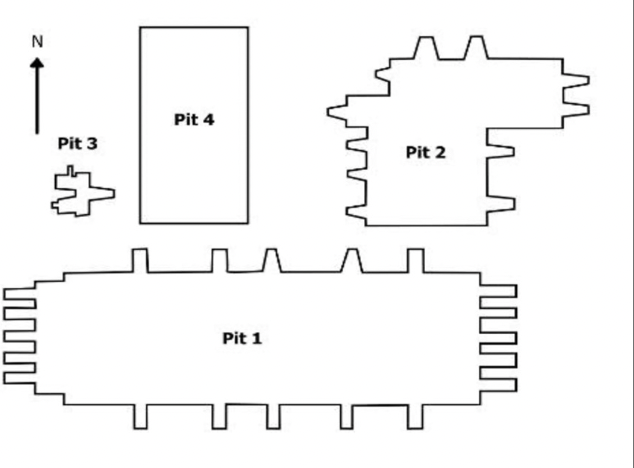 | back 37 Terracotta soldier army pits |
front 38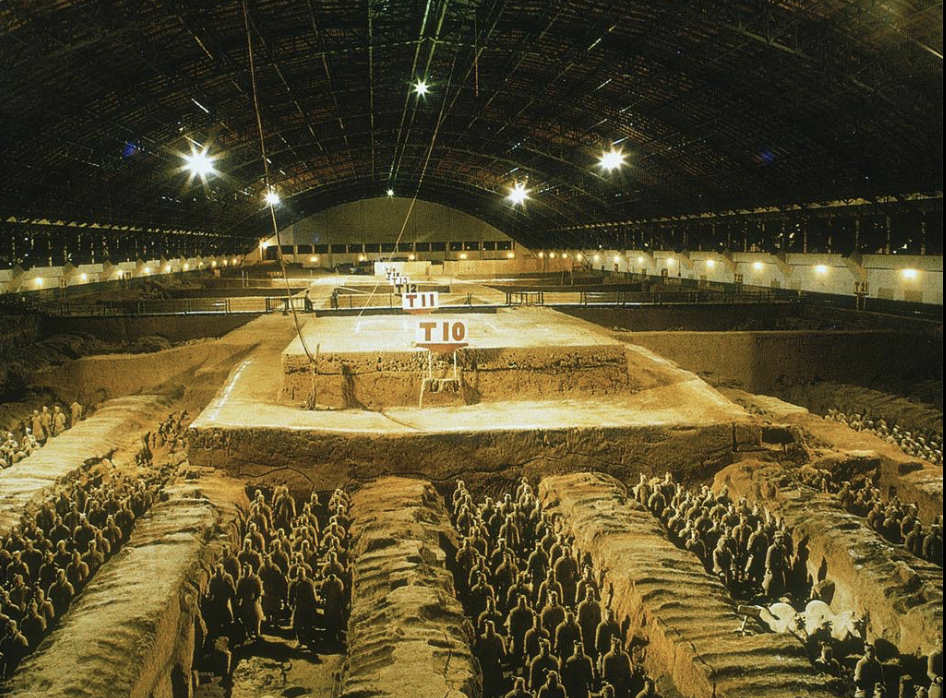  | back 38 Terracotta Army Pit 1 Qin Dynasty, baked clay, China 6,000 soldiers in military position with real weapons --> way to maintain order outside in defensible edge front is unarmored --> sacrifice / martyr horseman always wins |
front 39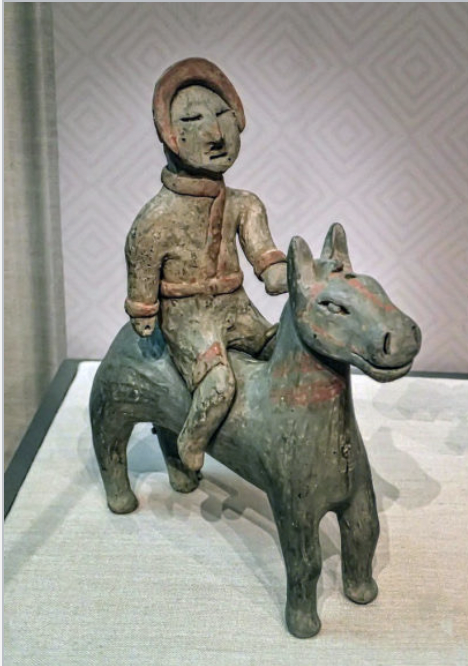  | back 39 Horseman Qin Dynasty (5th - 3rd century BCE), China |
front 40  | back 40 Terracotta Army Pit 2 Qin Dynasty, baked clay, China 1300 figures specialized forces --> archers, chariots, cavalries |
front 41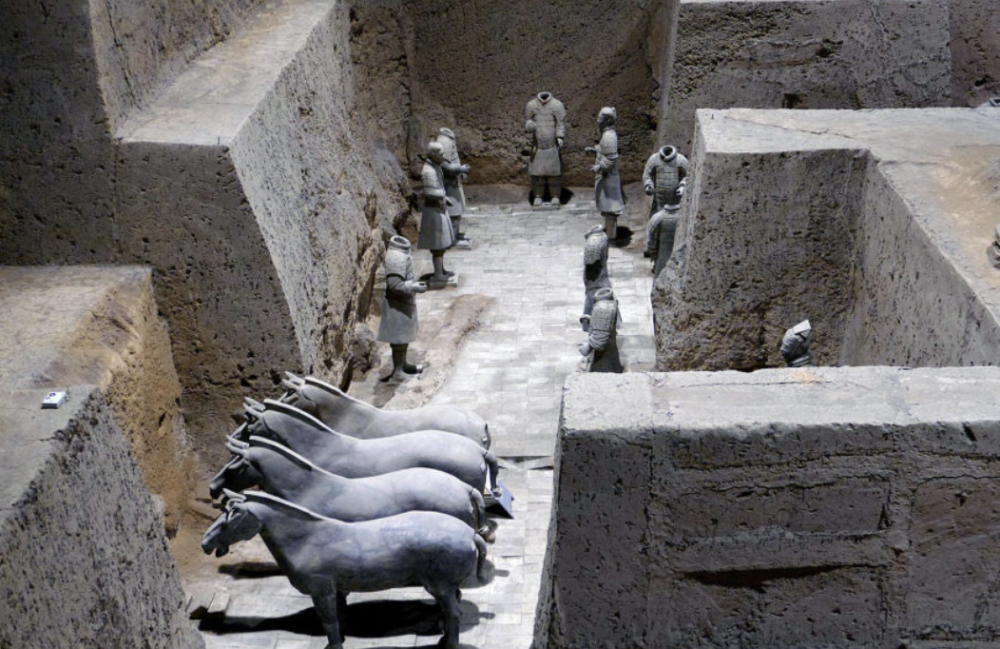  | back 41 Terracotta Army Pit 3 Qin Dynasty, baked clay, China 68 soldiers seems to be talking to each other / waiting to greet their commander |
front 42  | back 42 Terracotta "strongman" Qin Dynasty, baked clay, China likely an acrobat? 4th pit of Terracotta Army is entertainment / stuff for soldiers to do in their downtime keep army happy --> keep following leader |
front 43 describe the history of Greco-Persian war | back 43 classical period (480 - 300 BCE) right after archaic --> Greco-Persian war started this transition since Persians burned down Athens many lived in Ionia --> Athens and Sparta support Ionia, but Persians get angry and invade in 490 unified Greeks meet Persians in marathon city (Greek city and marathon city are 26.2 miles apart) Greeks beat Persia --> Greece not unified, but unify to fight (similar to Trojan war) only about 300 go and all die because Athenians do not fight during Olympics Persians are in Athens from 480 - 479 BCE --> clear burn layer that shows when Persians were invading |
front 44  | back 44 Perserchutt Classical Period, Athens Greece burn layer excavated in 1866 |
front 45  | back 45 Old Temple of Athena Classical (480 BCE), Athens Greece foudations destroyed by army of Xerxes I not rebuilt because its like a graveyard of people that died |
front 46 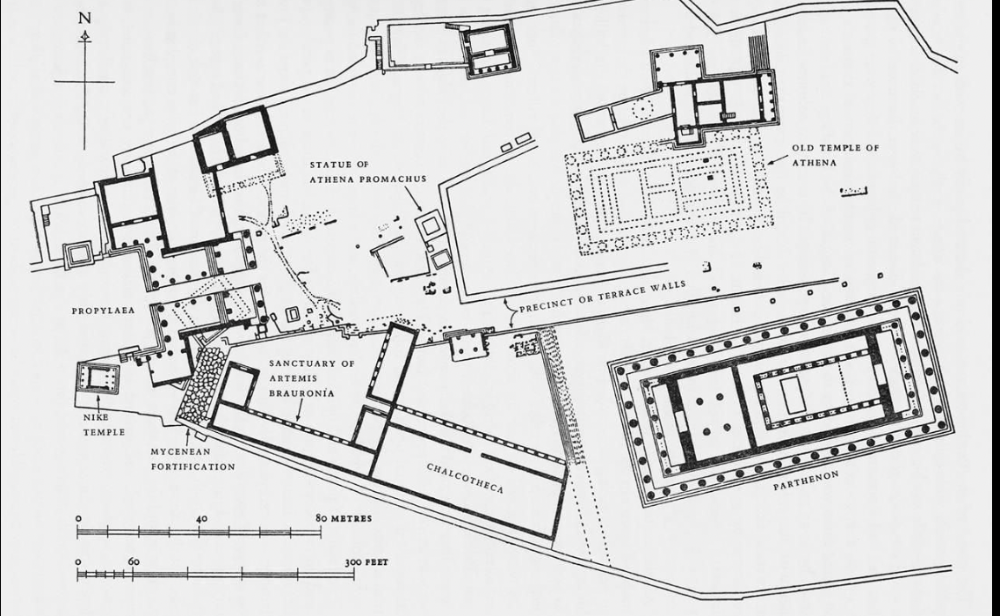 | back 46 Plan of Acropolis Classical (4th century), Athens Greece parthenon --> dedicated to Athen Parthenon (Athena the virgin) Athen pops out of Zeus' head in full armor |
front 47 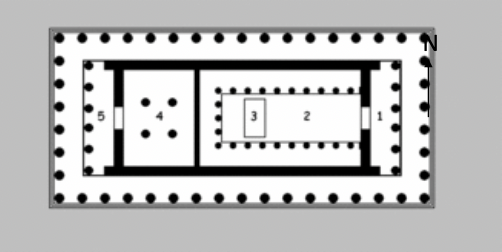 | back 47 Plan of Parthenon Classical, Athens Greece 1) Pronaos --> front porch 2) noas --> main room 3) chryselephantine Athena Parthenon --> cult statute room 4) treasury --> all wealth of Athens 5) adyton --> back porch |
front 48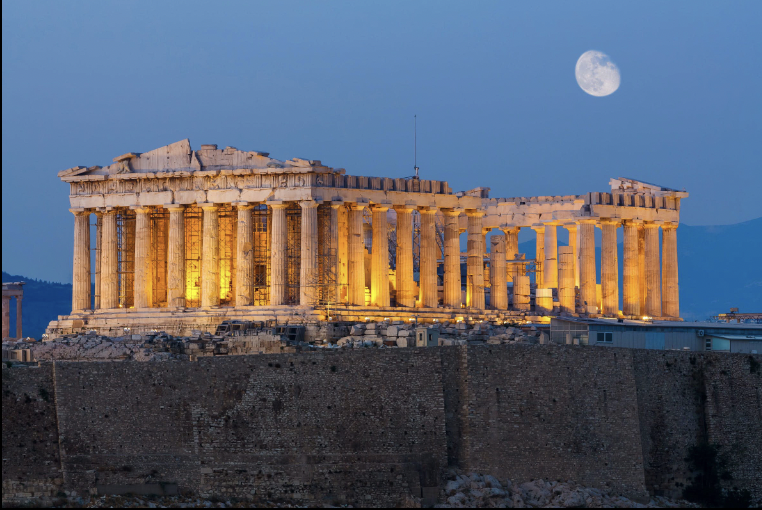  | back 48 Parthenon Classical (447-431 BCE), marble (local Greek stone), Athens Greece Artists = Iktinos and Kallikrates dedicated to Athena the virgin built four decades after destruction straight lines do not look straight to naked eye because our eyes are curved --> columns have entasis (bottom is subtly bigger than the top of column in order to look straight --> without this the parenthenon would look like it is caving in on itself) obstacle refinement would've been painted |
front 49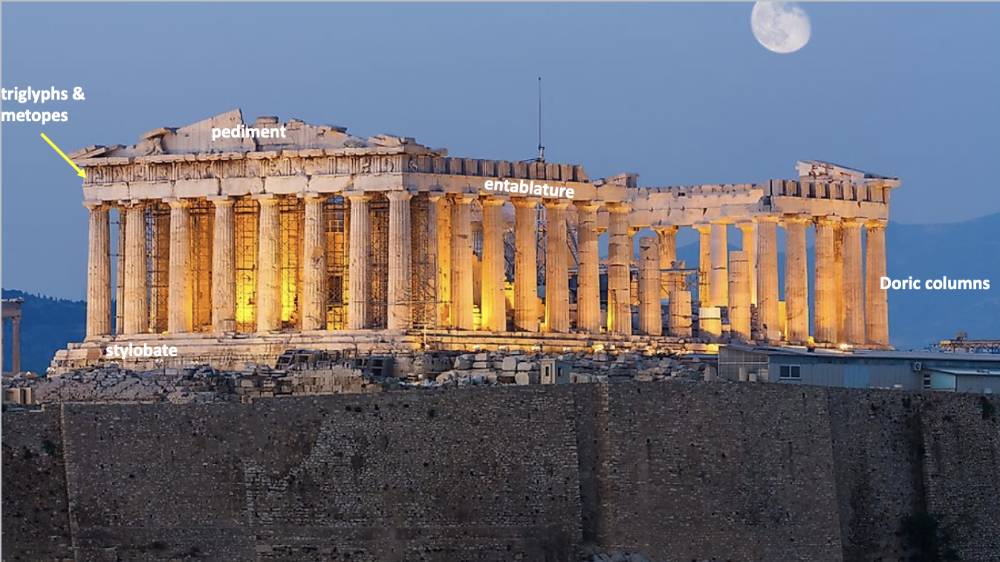  What kind of style is this? what are the functions of these structures? | back 49 Octastyle --> 8 pillars in front style = column stylobate = base doric columns = column entablature = mental that connects posts of column triglyphs and metopes = decorative pediment = ? |
front 50  | back 50 Roman Copy of Phidias Classical, chryselephantine (ivory and gold), 11m, Athens Greece literary inscription of Pausanias Athena Parthenos Erichthonius = early king of Athens contrapposto = right leg hold most of weight (bent) --> more natural than archaic stance (one foot in front of the other) and is NOT SEEN BEFORE 480 BCE contrapposto = classical, archaic stance = one foot in front of other |
front 51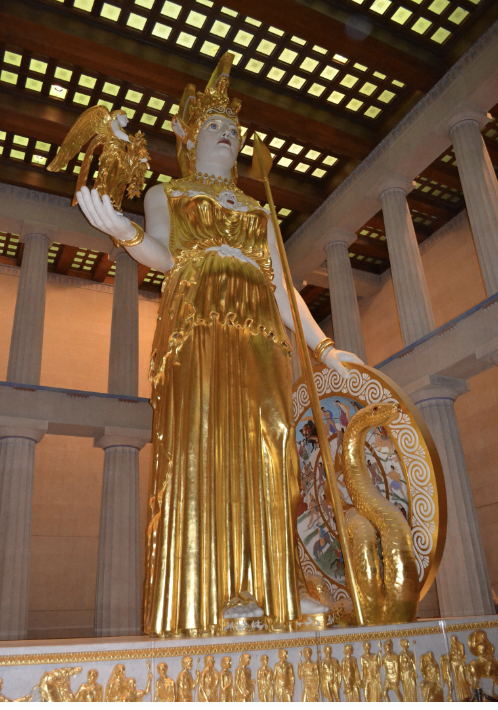  | back 51 Reproduction of Athena Parthenos Nashville Tennessee just gold 40 feet tall = intimidation |
front 52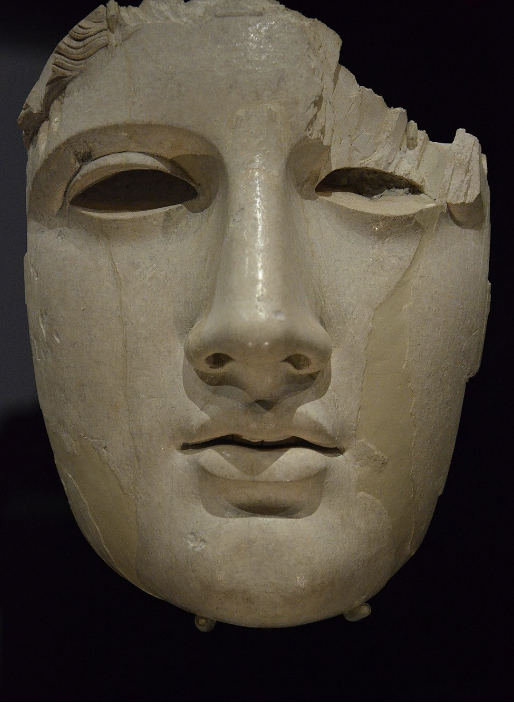  | back 52 Ivory Head of Apollo 1995 possibly carved by Phidias no emotion --> want to absolute control of emotions (no archaic smile!) |
front 53  | back 53 West Pediment of Parthenon Classical (447-431 BCE), marble (local Greek stone), Athens Greece all figures on pediment are same scale --> not are shrunk or made bigger to fit inside the pediment west pediment is poorly reserved shows contest between Athena and Poseidon --> Athen offers Olive Garden and Poseidon offers salt water Athen wins (Athens) |
front 54 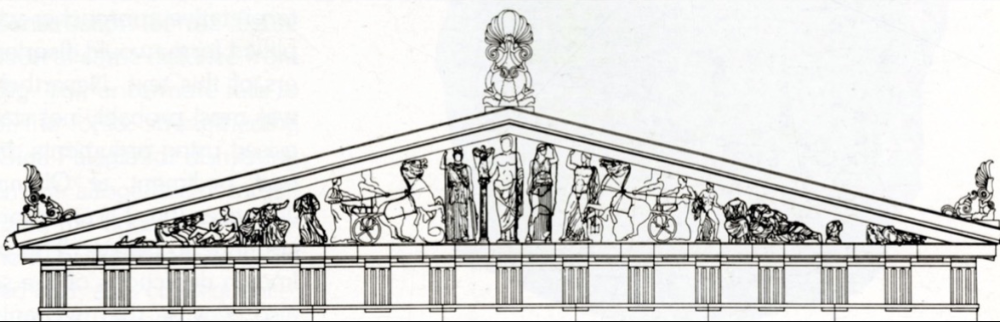 | back 54 East Pediment of Parthenon Classical (447-431 BCE), marble (local Greek stone), Athens Greece shows birth of Athena --> rising sun on one side, moon setting on other no nude women until 320 BCE |
front 55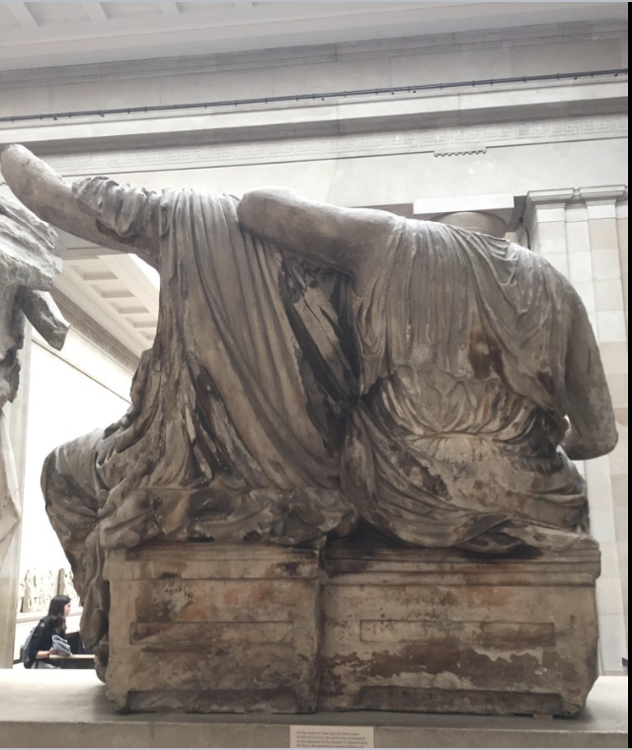  what is this type of architecture called? | back 55 wet drappery --> conceals everything but is also very revealing backs are carved and not left blank --> shows respect to gods but also strive for optical perfection this is a temple for Athena, it needs to be perfect, although humans can't fly up to see the backs of the statues, Athena could |
front 56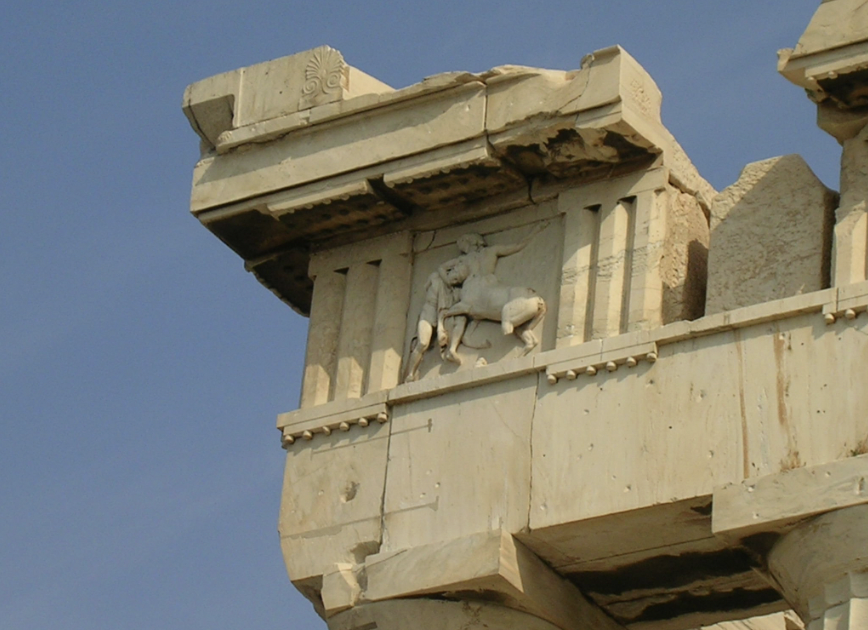  | back 56 Metope on Parthenon west = amazon ally --> woman warrior south = Lapiths and centaur east = gigantomachy north = trojan war |
front 57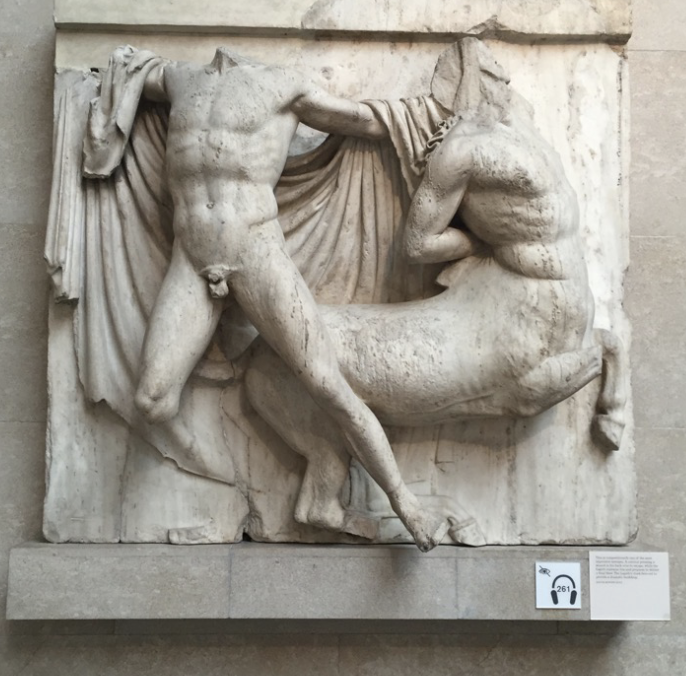  | back 57 Metope of Lapith and Centaur |
front 58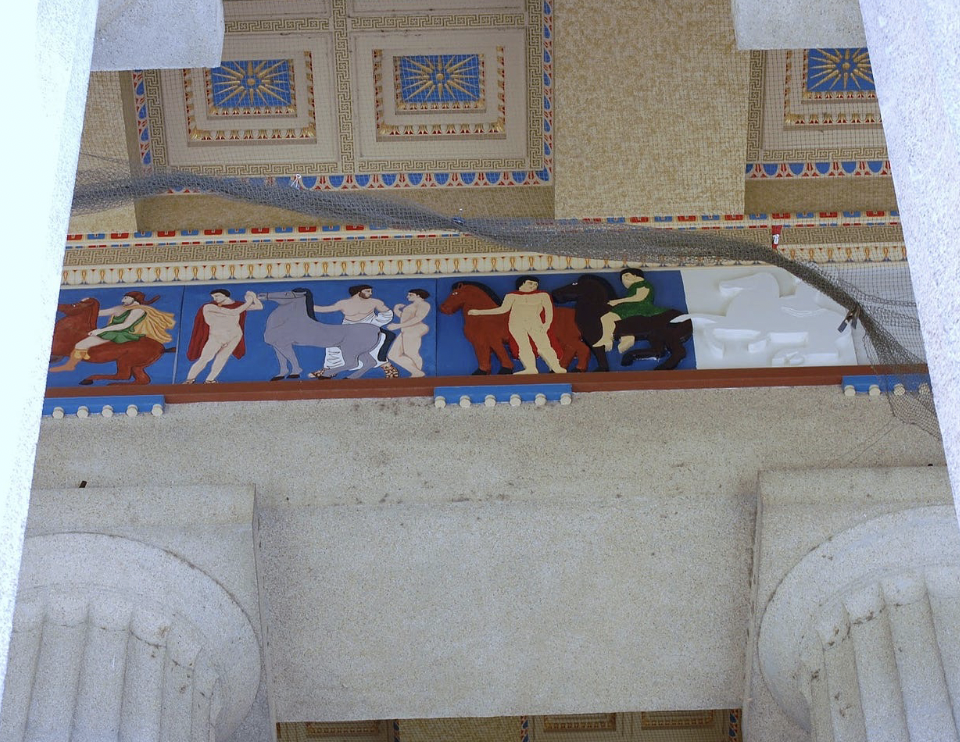  | back 58 Frieze of Parthenon everyone participate in ritual of procession pan-artheraic parade |
front 59 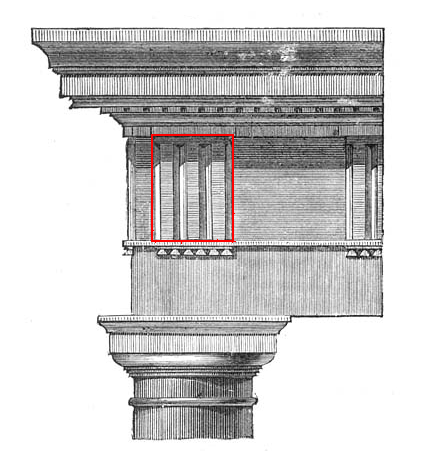 | back 59 Trioglyph of parthenon |
front 60 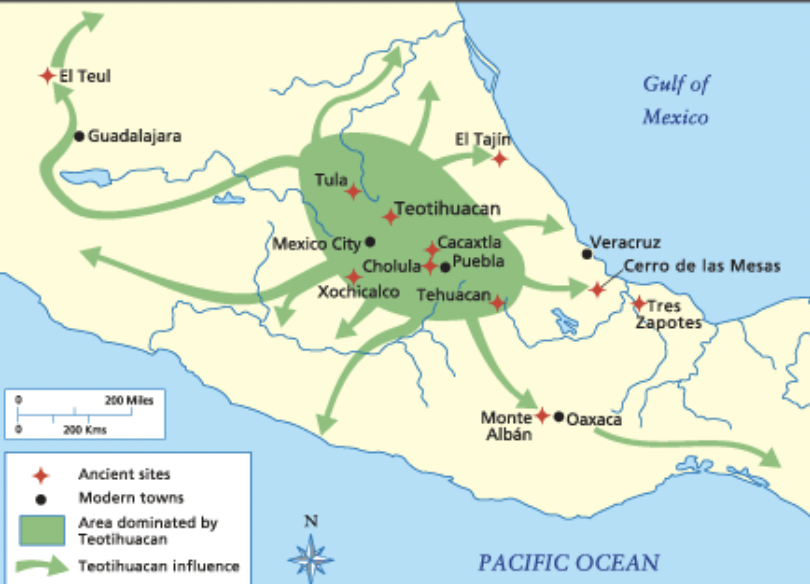 briefly explain the history of Teotihuacan | back 60 200 BCE massively burned in 650 CE when the Aztecs arrive in 1325 it is abandoned no writing system in Teotihuacan so all the names are Aztec influenced |
front 61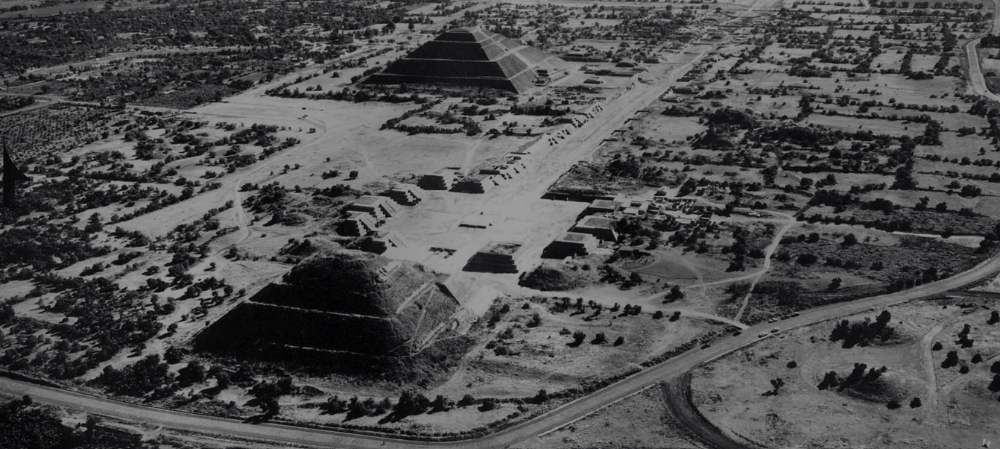  | back 61 Teotihuacan city teatl = Nahuatl (Aztec language) signifying defied entitiy divided into ethnic neighborhoods |
front 62 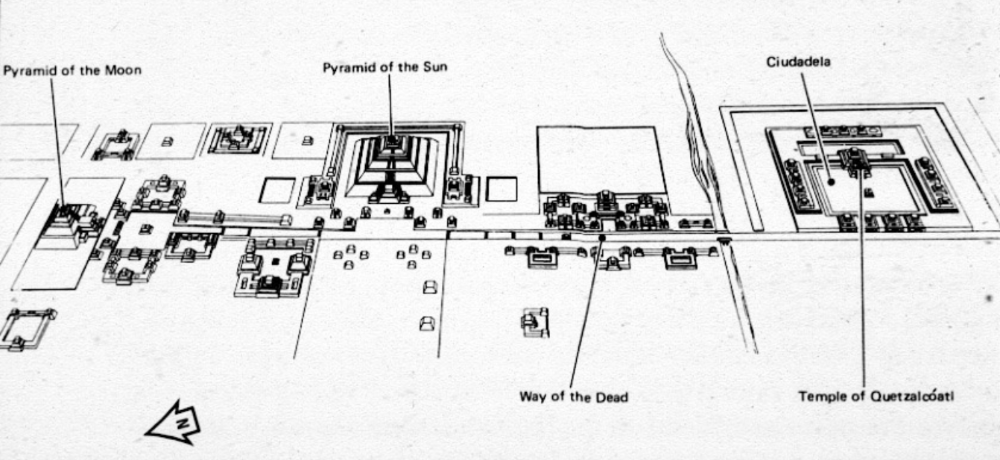 | back 62 "Avenue (or Way) of the Dead" Teotihuacan, Mexico 4 miles that that leads to the Temple of the Moon niches in the wall for mummies to lay standing up 3 types of people that live there --> super-elites, elites, and everyone else richer people lived closer to way of the dead 650 houses burned down in this area --> none were poor (poor class burned down the houses) |
front 63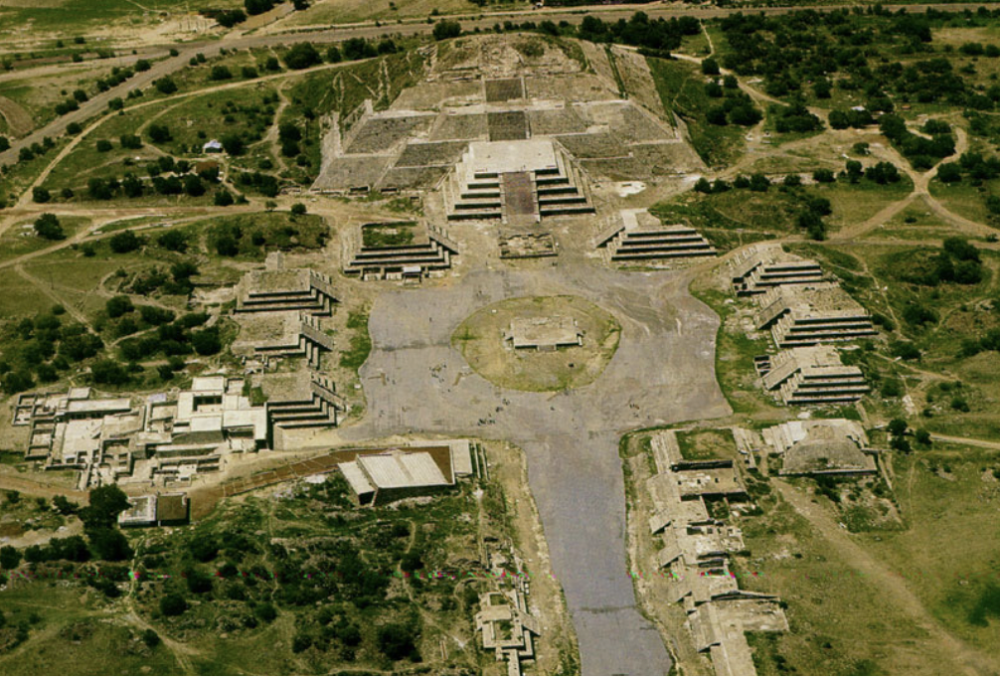  | back 63 Temple of the Moon Teotihuacan, Mexico Performance / ritual area --> stage and smaller pyramids (very big on being seen and public spectacle) pyramid mimics the earth --> geomancy = built environment aligns with natural world solar alignments (makes good astronomical observations --> like Stonehenge) --> high up and raised and when standing on platform there is no obstruction of view 7 construction phases --> all built around old temple (build outwards and in between each phase is buttressing stone and rubble past phases are preserved |
front 64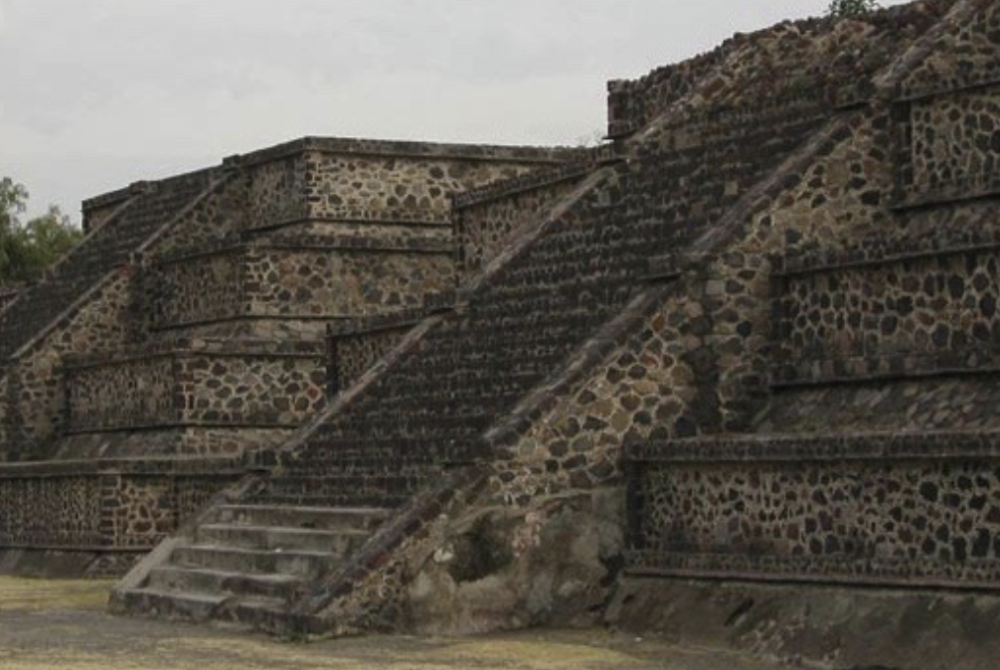  | back 64 Talud-Tablero Teotihuacan, Mexico diagnostic indicator of Teotihuaconic presence see influence of architectural style discreet terraces --> each platform of pyramid talud = slope --> less exaggerated on inside tablero = table / flat surface |
front 65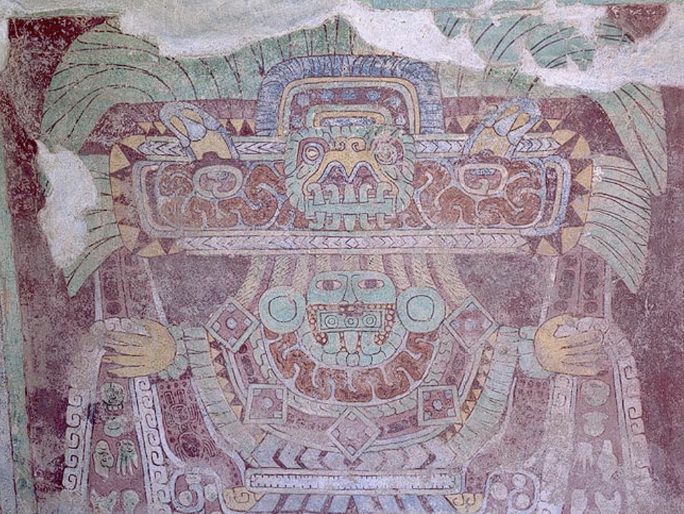  | back 65 Tetitla Great Goddess Teotihuacan (500 CE), Mexico interested in nature, not naturalism looks like a human dressed up as goddess --> real human face polychromatic color palette --> green / blue / red = fertility on talud ear spools, green / blue bird headers, water issuing from hands, and fangs hybridized goddess |
front 66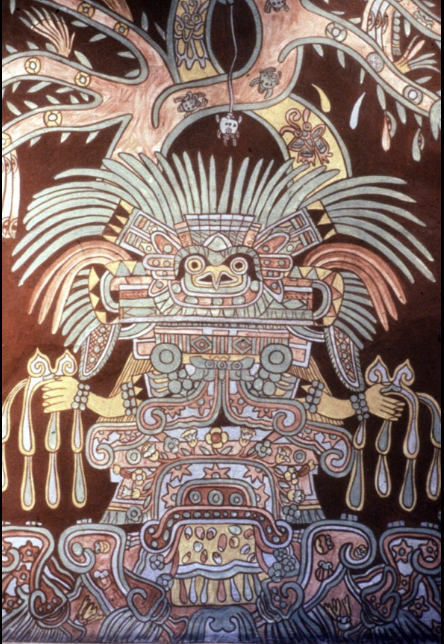  | back 66 Tepantitla Great Goddess Teotihuacan, Mexico sitting in fertility cave / tree growing out = fertility goddess shows actual deity great spider goddess --> creation and destruction (gods sacrifice themselves in order to create ear spools, green / blue bird headers, water issuing from hands, and fangs |
front 67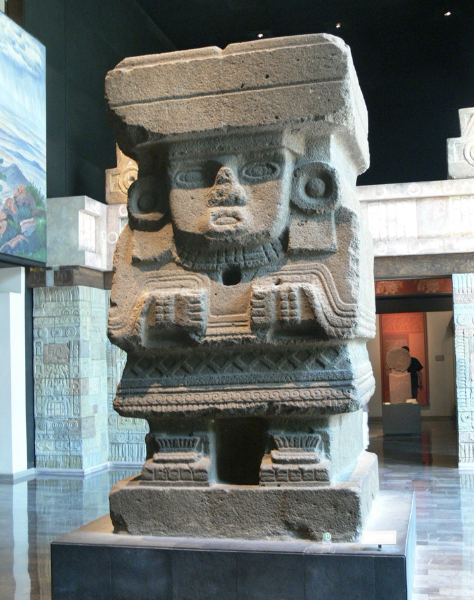  | back 67 Great Goddess Sculpture Teotihuacan very simple |
front 68  | back 68 Tlaloc Teotihuacan, Mexico bug eyes and barbs like catfish mini version of himself in his hadns on tablero in realm of tlaloc --> dancing and singing = swirls out of mouth |
front 69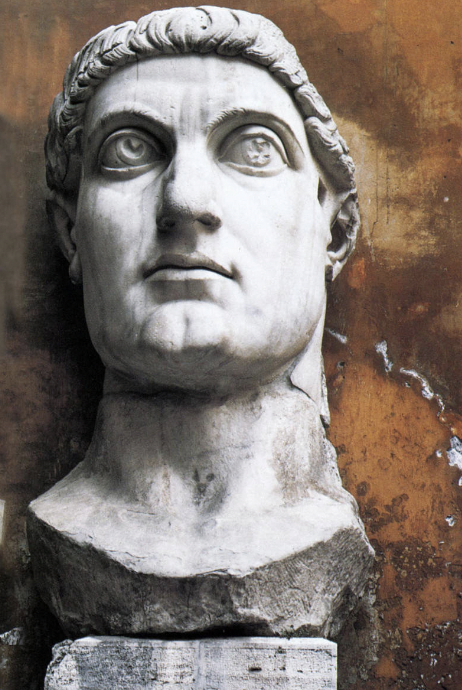  | back 69 Colossal Statue of Constantine the Great 325 CE, marble, Rome first emperor to be christian --> had to be hidden, not allowed to be Christian before him big eyes --> look heavenward like Alexander (also a dedication to heaven) braided hair crown --> bowl cut beardless and cleft chin |
front 70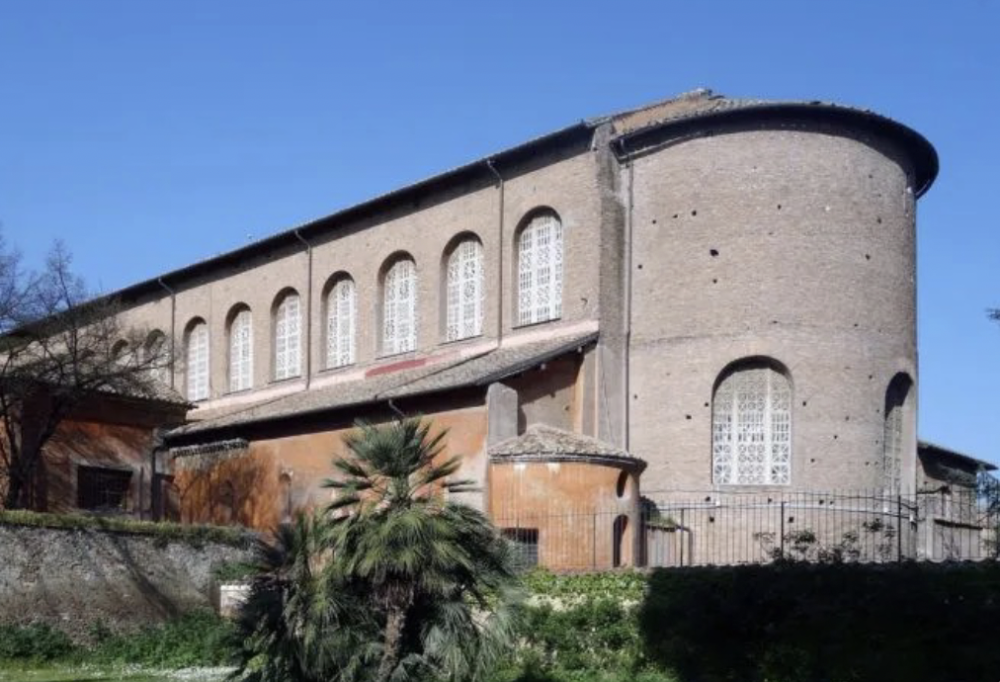  | back 70 Basilica of Santa Sabina (outside) 5th century (432 CE), Rome plain boring and weathers |
front 71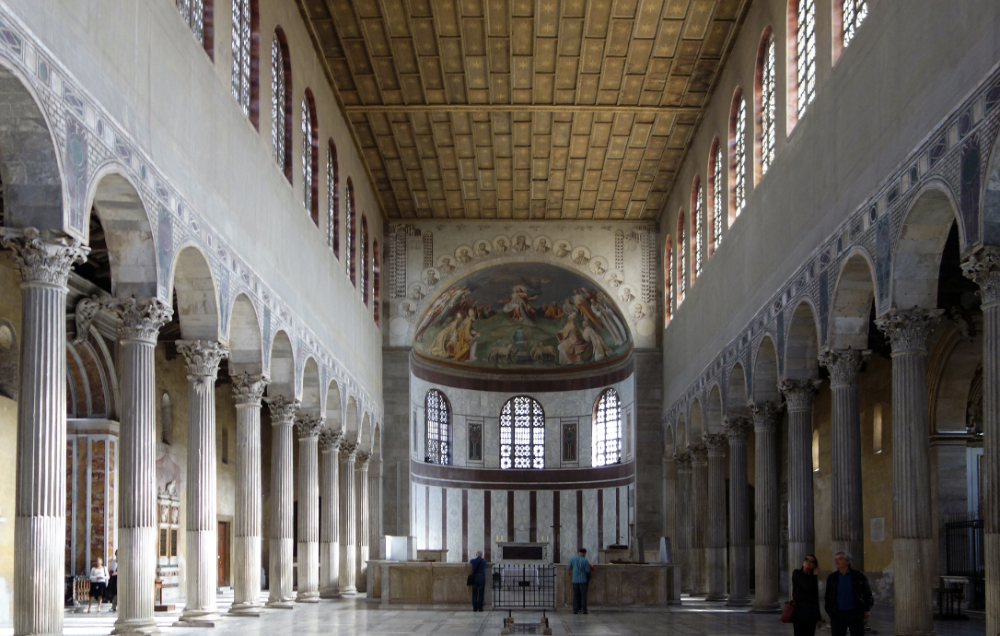  | back 71 Basilica of Santa Sabina (inside) 5th century (432 CE), Rome apse, side aisle and nave --> no transept! plain / empty original 5th century wooden ceiling spolia = wholesale reusing an object (parts of Roman buildings --> columns) clerestory windows = let large amounts of lights in --> feels like heaven |
front 72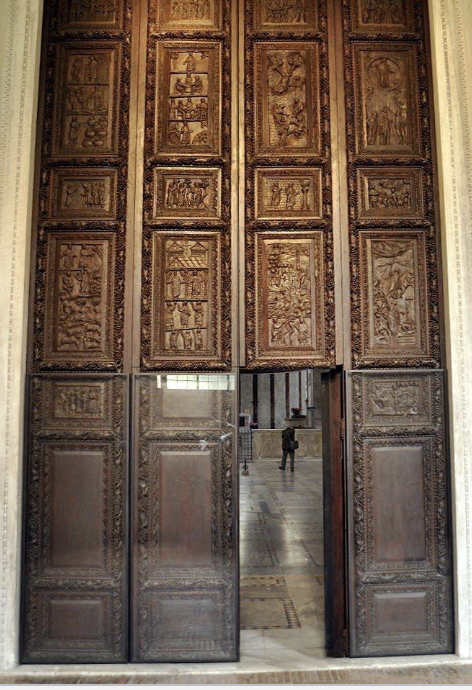  | back 72 Santa Sabina Doors 5th century (430-432 CE), cypress, Rome show stories form old and new testament bottom of doors (7 panels) are weathered from touch |
front 73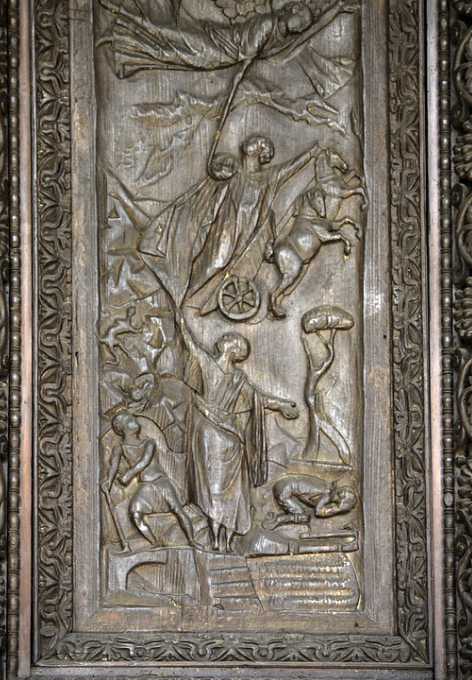  | back 73 Elijah ascends bodily into heaven like Mary and Jesus Sanat Sabina doors |
front 74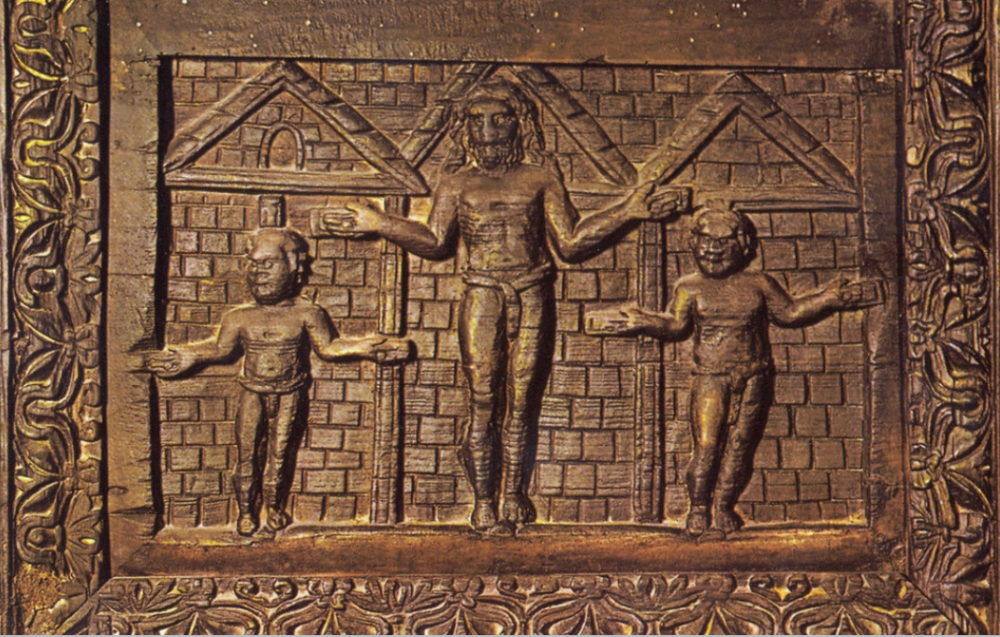  | back 74 earliest depiction of crucifixion Santa Sabina doors Jesus always beardless and a good shepherd in Dura Europa scary / hieratic scale bearded and long hair brick wall behind him --> carpentry? show it was in Rome? |
front 75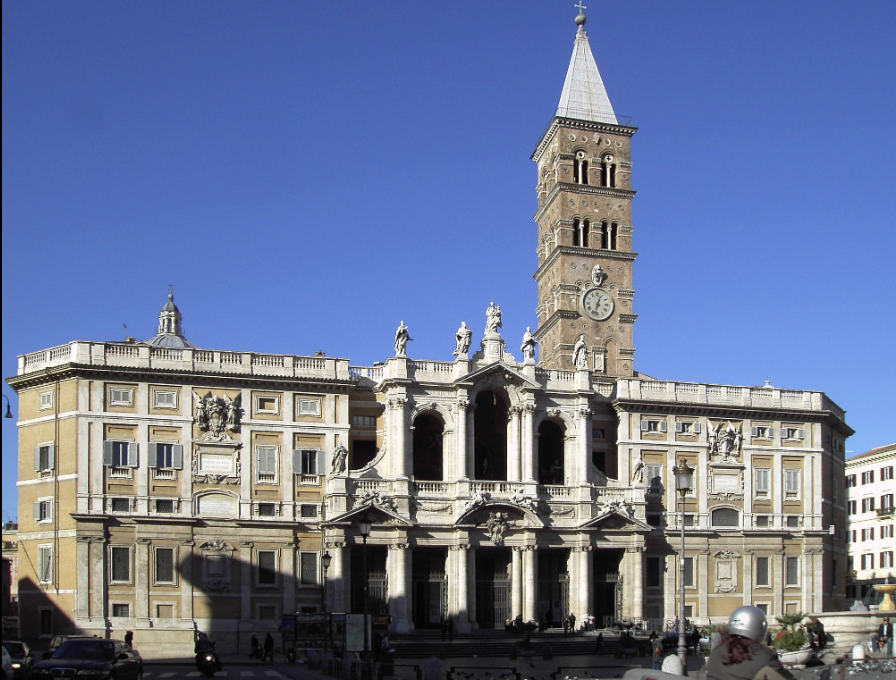  | back 75 Basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore (outside) 5th century (432-440 CE), Rome |
front 76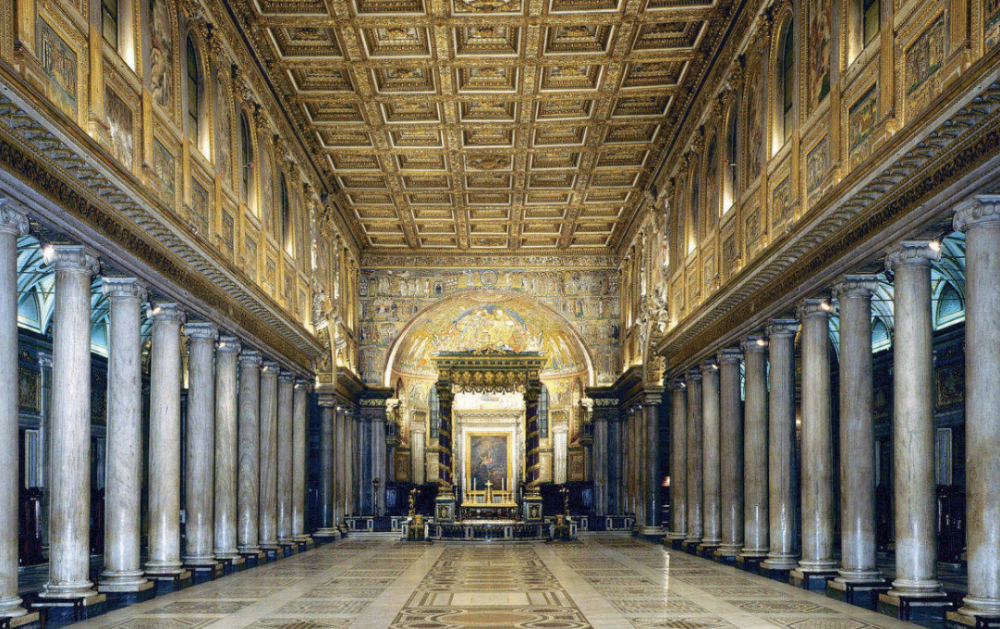  | back 76 Basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore (inside) 5th century (432-440 CE), Rome apse = extravagant --> triumphal arc mosaic |
front 77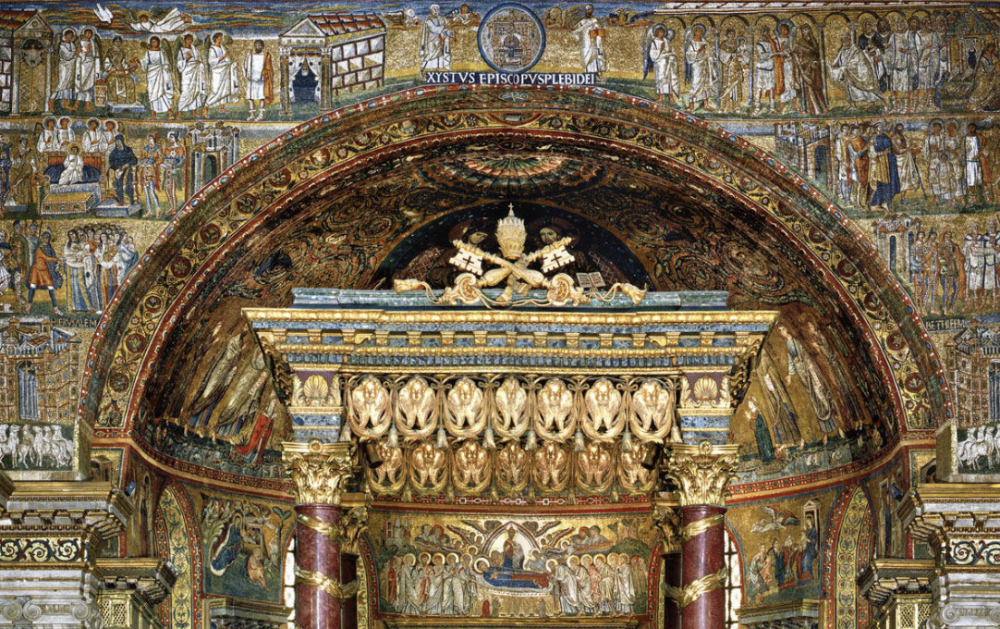  | back 77 Triumpha Arch Mosaics 5th century (432-440 CE), Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome similar to Arch of Titus in Rome that shows victory over Jesus Arch shows spiritual victory, not earthly viceroy --> victory of Christ over death |
front 78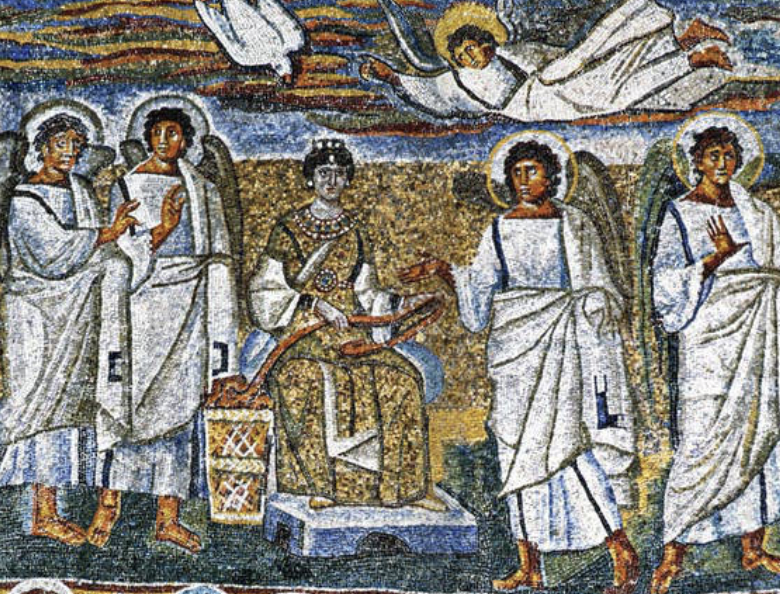  | back 78 Annunciation on Triumphal Arch Mosaic 5th century (432-440 CE), tesserae, Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome upper left of arch tesserae = individual squares in mosaic dove = holy spirit Mary dressed as Byzantine empress angels wearing togas --> upper-class roman wear togas |
front 79  | back 79 4 Evangelists on Triumphal Arch Mosaic 5th century (432-440 CE), tesserae, Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome in order form left to right: Luke, Matthew, Mark, John Peter on left --> goes west to spread Christianity (white hair) Paul on right --> goes east to spread Christianity (bald and behaeaded) Mary - chair, Jesus = cross |
front 80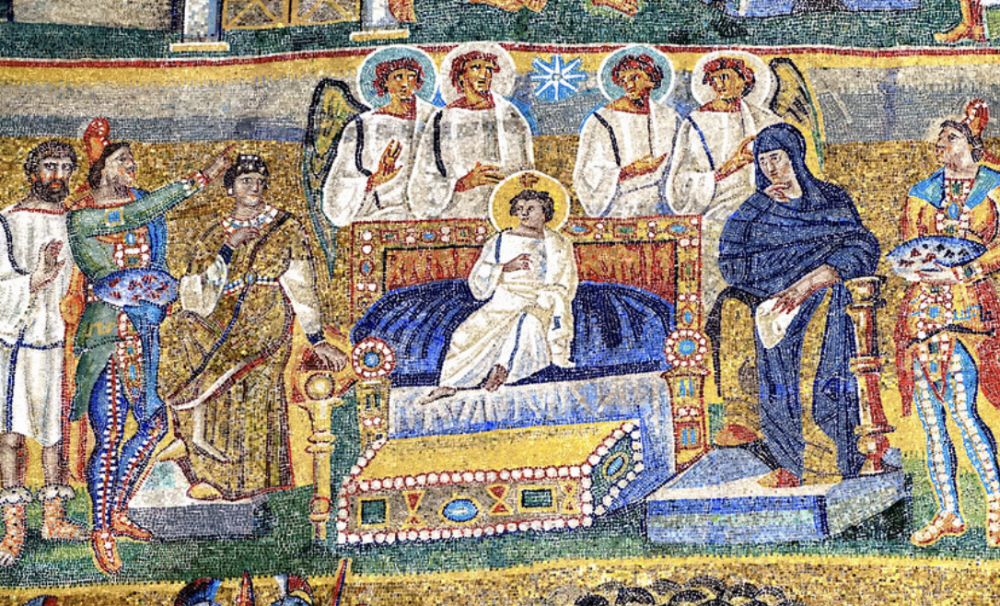  | back 80 Epiphany on Triumphal Arch Mosaic 5th century (432-440 CE), tesserae, Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome Magi dressed like clowns --> eastern clothes Mary is both in yellow and blue (regular person on Eartha nd empress in heaven) embalming spices --> Jesus is gin to die |
front 81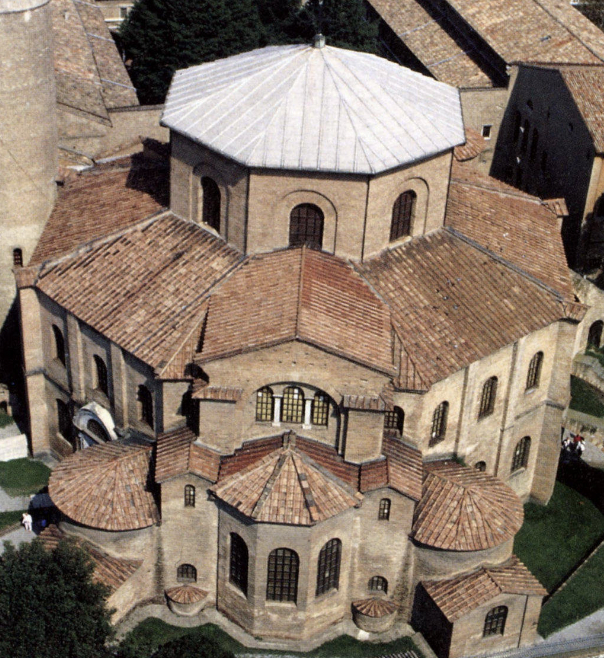  | back 81 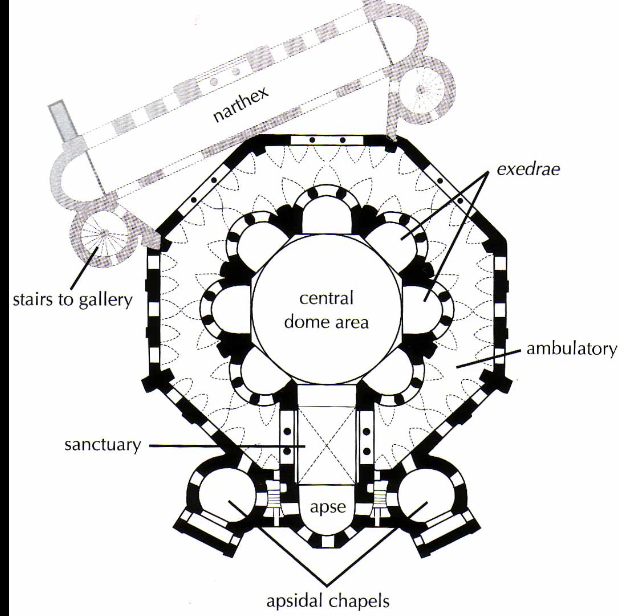 Church of San Vitale (outside) 548 CE, Ravenna Italy centrally planned --> similar to grave of holy figures (circular buildings mark graves) apse in the front narthex = entrance hall ambulatory = able to walk around --> in a circle not decorated outside |
front 82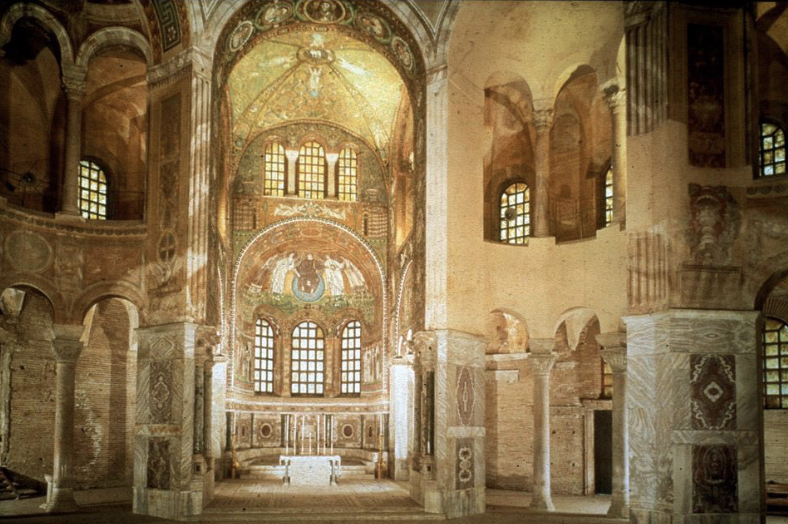  | back 82 Church of San Vitale (inside) 548 CE, marble, Ravenna Italy very decorated butterfly looking thing is able resentment 6th century alabaster windows --> gold and glowing on the inside |
front 83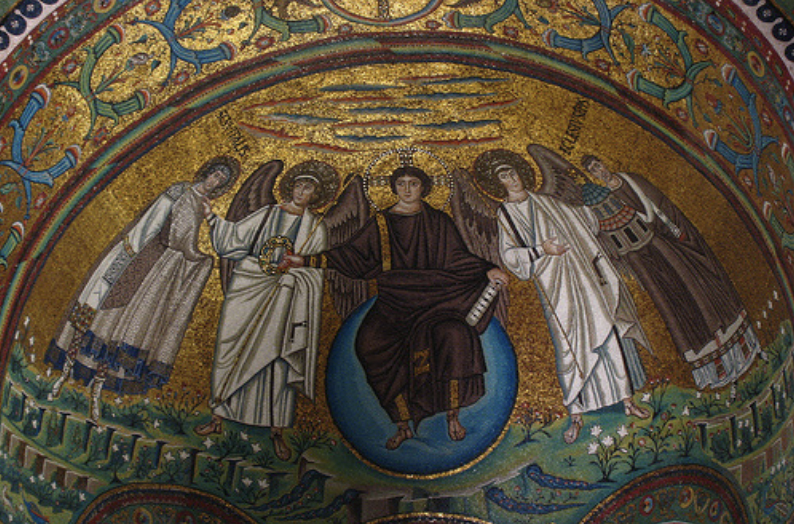  | back 83 Apse Mosaic 548 CE, Church of Santa Sabina in Ravenna Italy Jesus with cruciform halo --> sitting on earth to show he knows everything about it angels dressed in togas to represent language of Rome --> Jesus purple toga far right = local bishop --> donated land for local church |
front 84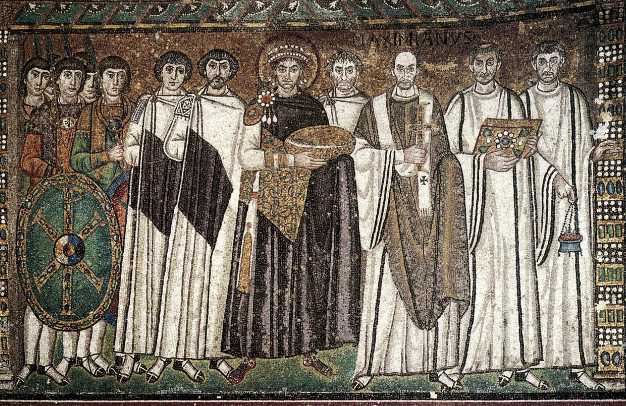  | back 84 Justinian Apse Mosaic 548 CE, north wall of Church of Santa Sabine in Ravenna Italy Justinian in center with halo --> red shows to symbolize authority on his right is clergy --> cross, book, incense on his left is military --> shows he is supported by church and state participating in the euchatist need = bishop who was in Ravenna when it was built shield has Cairo (p with x) |
front 85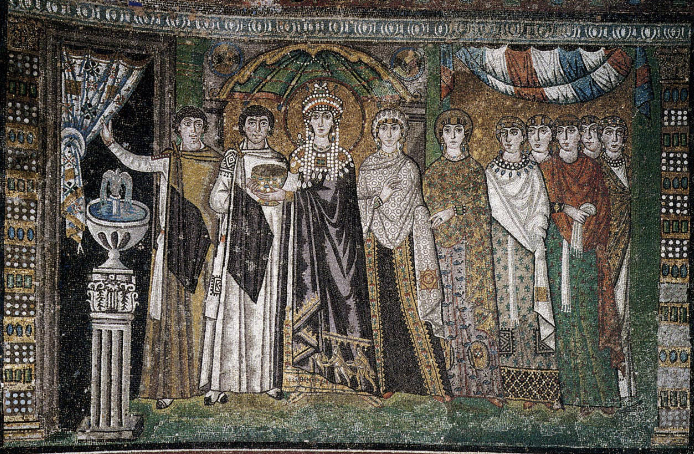  | back 85 Theodora Apse Mosaic 548 CE, south wall of Church of Santa Sabine in Ravenna Italy only Theodora painting we have supposed by ladies in witing fountain = baptismal font holding chalice --> participating in the eucharist Theodora grows up poor and on a bear farm? hem of dress = magi looks like Mary dressed as a byzantine empress |
front 86 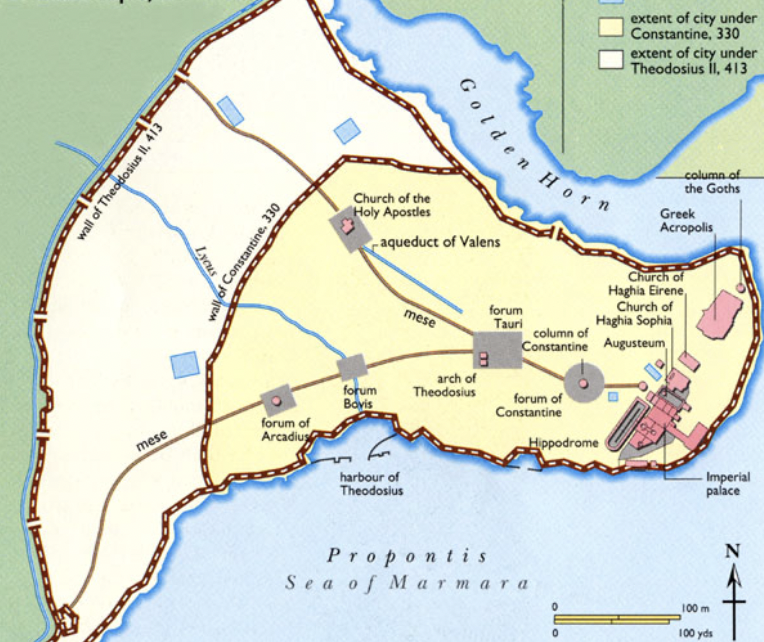 | back 86 Justinian moves Roman capital to Constantinople Justinian always here, never in Ravenna Hagia Sophia is burned down --> Justinian rebuilds it in spite of civilians |
front 87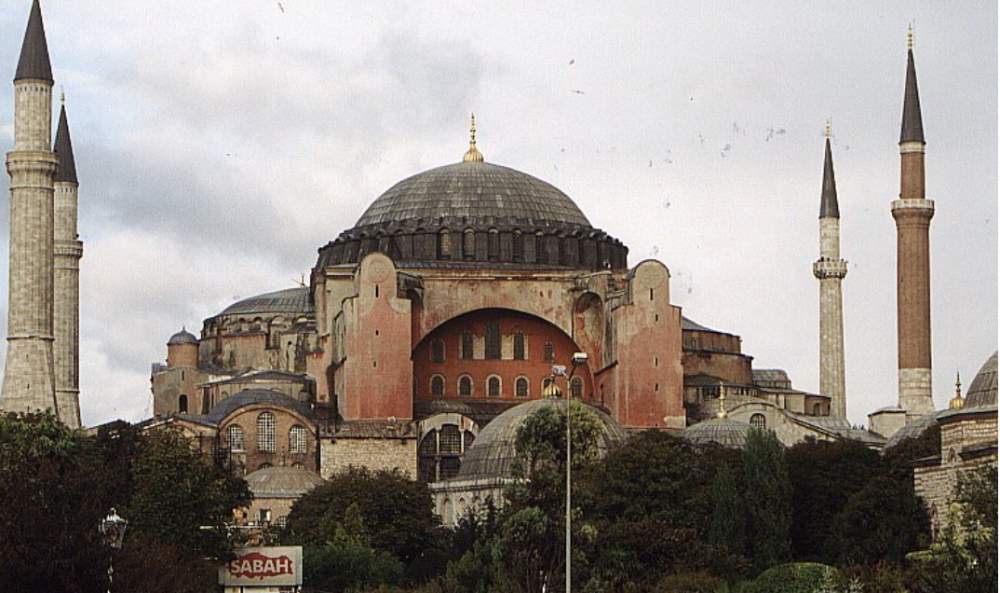  | back 87 Church of Hagia Sophia (outside) (532-537 CE), istanbul Turkey basilica style church |
front 88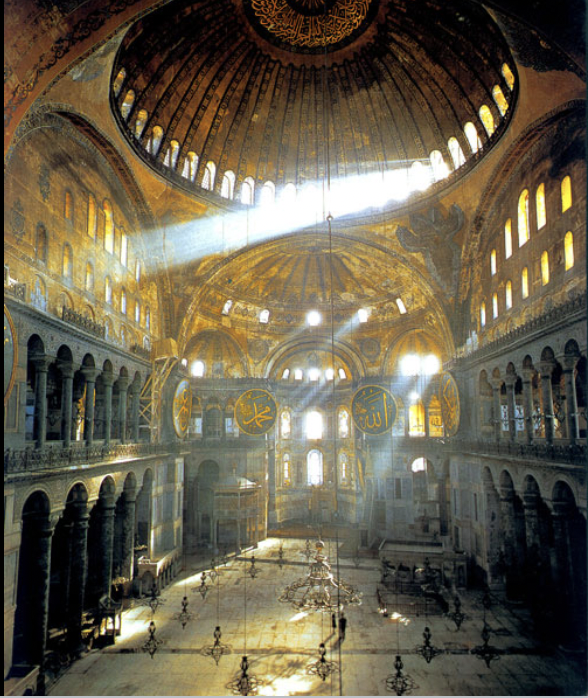  | back 88 Church of Hagia Sophia (inside) (532-537 CE), istanbul Turkey 3rd story windows --> light = presence of God massive (186 ft high) gold = think you are in realm of heaven roman arch is strongest form in architecture --> build pillars curving up equally on both sides and then connect them |
front 89 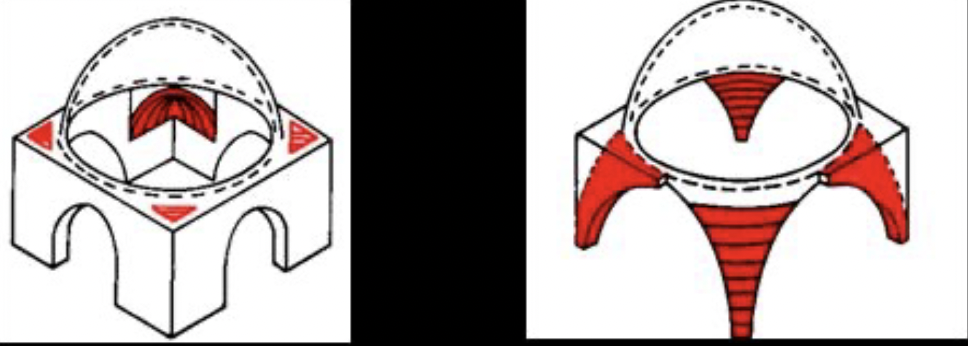 | back 89 left = squint --> square base the dome sits on right = pendentive --> downward sloping to send the force down |
front 90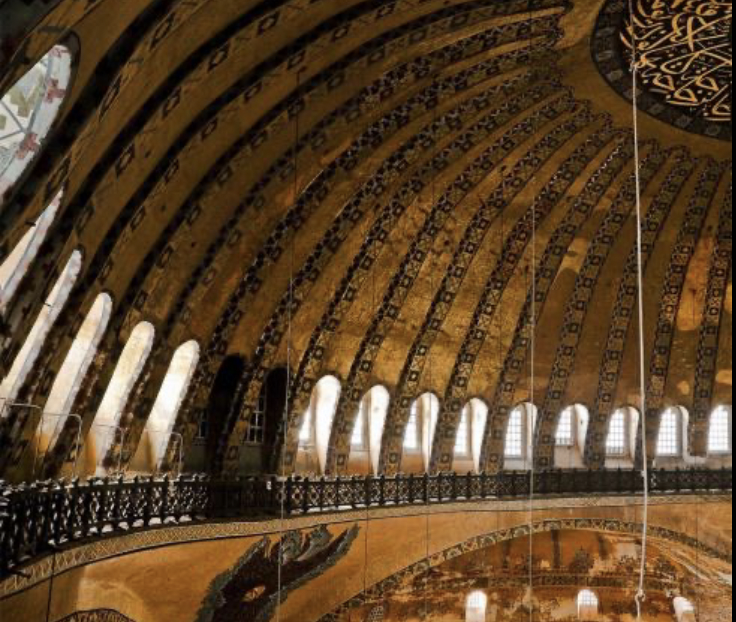  | back 90 dome of Hagia Sophia Chruch dome collapsed in 538 that was built by Isidore and rebuilt in 562 dome angle is moved upward and ribs added to help transfer to squelch and force pressure down --> holes in the dome make the dome weaker changed to a mask --> covered preexsiiitng mosaics like Mary and Jesus in the apse (only faces are covered, i.e. wings from seraphim's are kept) |