Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
genetics midterm definitions
front 1 What are zea mays? | back 1 corn |
front 2 What is a bacterial colony? | back 2 A group of bacteria that came from a single bacteria. (Then they would be genetically similar) |
front 3 What is the pattern of inheritance? | back 3 where certain traits were dominant and recessive, with dominant traits masking the effects of recessive genes. (created by gregor mendel) |
front 4 What is the parental generation? | back 4 consist of two true bred specimen so that their alleles are known and will be homozygous |
front 5 What was the first filial generation? | back 5 Offspring of the P generation, consisting of 100% heterozygous individuals, thus containing both alleles from parents and 100% exhibiting the dominant traits |
front 6 What was the second filial generation? | back 6 Offspring of F1 generation, will have an even amount of homozygous and heterozygous individuals but 75% will exhibit the dominant trait |
front 7 What are punnett squares? | back 7 A tool that allows us to predict the outcomes of certain crosses. Alleles from both parents being crossed are represented and combined to create a new set of alleles. |
front 8 What are dihybrid crosses? | back 8 allow us to predict the chances of two alleles being inherited simultaneously. |
front 9 What is probability? | back 9 The likelihood of something happening or being the case |
front 10 What is binomial expansion? | back 10 Allows us calculate probability without having to think of
every |
front 11 What is the chi-squared test? | back 11 Allows us to calculate deviations from observed and greater than (.05) 5% is insignificant less than (.05) 5% is significant |
front 12 What is degree's of freedom? | back 12 the number of categories being measured (in this case phenotypes) minus one |
front 13 What are genetically modified organisms(GMOs)? List examples | back 13 Any animal, plant, or microbe that has had their DNA altered using genetic engineering. We are around GMOs everyday, some can be helpful, some can be harmful. Wild carrots, chickens, hybrid dogs (doodles), E. coli k-12 |
front 14 Single gene testing? | back 14 Looking at singular genes |
front 15 What are genetic testing panels? | back 15 Looking at multiple genes |
front 16 What is genetic testing? | back 16 Any test that is capable of identifying changes to DNA |
front 17 What is a pedigree? | back 17 Shows relationships between individuals as well as
affected |
front 18 What is a proband? | back 18 The individual who serves as the starting point for genetic study for a family. |
front 19 What is a consultand? | back 19 The patient seeking information |
front 20 What is a carcinogen? | back 20 Any chemical capable of inducing cancer |
front 21 What is cancer? | back 21 A disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. (Can happen in any type of cells) |
front 22 What are benign tumors? | back 22 non-cancerous cells that don't harm us |
front 23 What are malignant tumors? | back 23 Cancerous and spread through metastasis |
front 24 What is Hereditary Colon Cancer(HNPCC)? | back 24 A type of cancer that is caused by 4 types of mutated genes. MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 |
front 25 What is lynch syndrome? | back 25 Also known as HNPCC and is a type of inheritable cancer |
front 26 What is gel electrophoresis? | back 26 Method of separating DNA, RNA, or even proteins by size and charge |
front 27 What are restriction enzymes? | back 27 proteins produced by bacteria that cuts DNA at specific sites. (Restriction endonucleases) |
front 28 What are palindromic sequences? | back 28 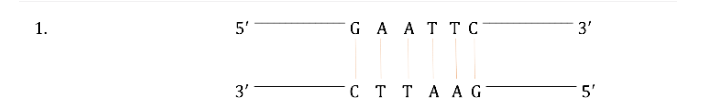 nucleic acid sequence in a double-stranded DNA or RNA molecule where both strands are identical |
front 29 What is the serial dilution formula? | back 29 C1V1=C2V2 |
front 30 What is the cell cycle? | back 30 The cell cycle is a process of growth and division for cells |
front 31 What is mitosis? | back 31 Creates two daughter cells from a single parent cell. also means thread for its threadlike appearance. |
front 32 What is meiosis and what does it create at the end? | back 32 Reduces the number of chromosomes from 2n to n in a cell to create gametes (reproductive cells) The end goal is four daughter cells with a variety of chromosomes to allow for genetic diversity in offspring |
front 33 What is crossing over and when does it occur? | back 33 Occurs during prophase I and allows for genetic diversity in the world and is the reason why you are not 100% like your parents or siblings |
front 34 What is the chiasmata? | back 34 Where the homologous chromosomes cross over and genetic material is exchanged |
front 35 What is autosomes? | back 35 non-sex related chromosomes |
front 36 What is Topoisomerase? | back 36 alleviates any tension that is created by the unwinding of the double helix of DNA |
front 37 What is Endonucleases? | back 37 It looks for specific areas in the DNA to cut. It is capable of making double strand breaks |
front 38 What is Exonucleases? | back 38 It removes the areas that the endonucleases cut through |
front 39 What is DNA Ligase? | back 39 It seals breaks in the DNA, allowing for the integration of the new DNA onto the existing strand |
front 40 What is sex linkage? | back 40 Some genes are located on sex chromosomes, meaning
some |
front 41 What are the male and female chromosmes? | back 41 male - XY female - XX |
front 42 What are some examples of sex linked traits? | back 42 Red-green color blindness, Hemophilia, Male pattern baldness, fragile X syndrome |
front 43 What is phylum Ascomycota? | back 43 Most diverse fungal phylum |
front 44 What is the ascus? | back 44 The defining feature is a microscopic sexual structure. Ascospores are formed there |
front 45 What is Plasmogamy? | back 45 The fusion of two hyphae together |
front 46 What is the Dikaryotic stage? | back 46 Cells have two haploid nuclei |
front 47 What is the karyogamy stage? | back 47 Nuclei fuse together and create one diploid nucleus |
front 48 What happens in meiosis in ascomycetes? | back 48 Results in four cells haploid ascospores |
front 49 What happens in mitosis in ascomycetes? | back 49 Cells divide to form eight ascospores in an ascus |
front 50 What happens in the dispersal stage? | back 50 Mature ascus release the ascospores to start a new mycelium |
front 51 What is sordoria fimicola? | back 51  It is a microscopic ascomycete thats life cycle is usually 1 to 2 weeks |
front 52 What is gene linkage? | back 52 The tendency of genes that are located close to each other
on |
front 53 What is genetic mapping? | back 53 When 2 traits are regularly inherited together and we can determined that those genes are close together on a chromosome. |
front 54 What is the recombination frequency? | back 54 Calculating the frequency of recombination events between genes. total recombination's/total offspring's) x 100 |
front 55 What is the central dogma of biology? | back 55 Theory that describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Proteins |
front 56 What is transcription? | back 56 Making a copy of RNA from a genes DNA sequence. Also produces mRNA from segments of DNA to produce proteins |
front 57 What is translation? | back 57 The strand of mRNA is decoded to produce a particular sequence of amino acids (proteins) |
front 58 What are peptide chains? | back 58 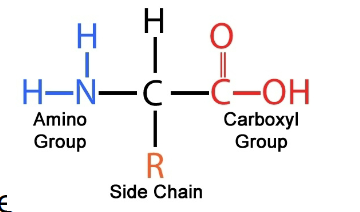 chains of amino acids that have the same basic structure. (amino acid, carboxy group, and a side chain) |
front 59 What is protein structure? | back 59 Caused by the interaction of amino acids in the linear |
front 60 What is the primary protein structure? | back 60 The linear sequence of amino acids. A straight chain often called a polypeptide |
front 61 What is the secondary protein structure? | back 61 Folding patterns caused by hydrogen bonds between the polypeptide backbone. Formation of alpha helices and beta sheets |
front 62 What is the tertiary protein structure? | back 62 Interactions between amino acid side chains causes a 3D structure to begin forming. These can be ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, Van der Waals interactions, and disulfide bonds |
front 63 What is the quaternary protein structure? | back 63 Multiple polypeptides arrange to create a protein complex |
front 64 What is sickle cell anemia? | back 64 A codominant genetic disorder caused by a single
nucleotide |
front 65 What is codominance? | back 65
If an individual is
heterozygous one allele does not mask the |
front 66 What happens in chromosome 11? | back 66 The sixth nucleotide in the sequence changes from adenine (A) |
front 67 What are centrosomes? | back 67 where the tubules or spindle comes from |
front 68 What are sister chromatids? | back 68 Identical copies of a chromosome formed by DNA replication |
front 69 What is a centromere? | back 69 The part where sister chromatids are joined together |
front 70 What is cohesin? | back 70 Cohesin forms rings that hold the sister chromatids together in prophase |
front 71 What is condensin? | back 71 Condensin forms rings that coil the chromosomes into
highly |
front 72 What are kinetochores? | back 72 A complex of proteins positioned at the centromere. microtubules attach to the kinetochores to connect to the chromosomes. |
front 73 What are interpolar microtubules? | back 73 They extend from the spindle pole across the equator, almost to the opposite spindle pole |
front 74 What are astral microtubules? | back 74 They extend from the spindle pole to the cell membrane |
front 75 What is anaphase a? | back 75 The kinetochore microtubules shorten and draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles. |
front 76 What is anaphase b? | back 76 The astral microtubules that are anchored to the cell membrane pull
the poles further apart and the interpolar microtubules slide past
each other, exerting additional pull |
front 77 What is the cleavage furrow? | back 77 The cell membrane pinches in at the cell equator. The position of the
furrow depends on the position of the astral and |
front 78 What are sex chromosomes? | back 78 They determine whether an individual is male or female. XY and XX |
front 79 What is a zygote? | back 79 Egg and sperm join to make this and they develop into an offspring |
front 80 What is recombination? | back 80 Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange stretches of DNA which makes new allele combinations |
front 81 true or false. Unlinked genes, whether on the same or different chromosomes, are inherited separately 50% of the time. | back 81 true |