Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ochem lab midterm
front 1 Distillation is the separation of multiple _____ components based on their different ______. As the mixture is heated and the first component ____, its _____ form travels through the distillation set-up and ______ into a different container. | back 1 liquid, boiling points. boils, vapor, condenses. |
front 2 To insert a thermometer into an adapter, use _____ to prepare the thermometer. Then, hold the thermometer _____ the adapter and _____ the thermometer into the adapter. | back 2 mineral oil, close to, slowly turn |
front 3 What are the concerns presented by overheating a distillation to a dry flask? | back 3 -> The empty glassware might heat quickly, igniting vapors from the distillation. -> The remaining solid residue might contain explosive peroxides. |
front 4 Before turning on the heat for a microscale distillation, what should you confirm about the set-up? | back 4 -> Secure connections at the joints -> Presence of boiling chip in the sample -> Existence of some opening in the set-up |
front 5 Where should the tip of the thermometer be placed in a microscale distillation set-up? | back 5 At or slightly below the side arm of the distillation head |
front 6 An azeotrope is a mixture that has _____ composition in the __________. Therefore, an azeotropic mixture _____ be separated by distillation. | back 6 the same, gas and liquid phases. cannot |
front 7 Suppose you are using distillation to separate cyclohexane and toulene. The boiling point of cyclohexane is ____ oC and the boiling point of toulene is ____ oC. Therefore, the liquid collected first should be ________. | back 7 81, 111, cyclohexane |
front 8 Lab#2 Most desired compound from one layer to another ____ Often involves a reaction in one of the layers _____ Leaves desired compound in its starting layer _____ Movies impurities from one layer to another ______ Leaves impurities in their starting layer _____ | back 8 1. Extraction 2. Extraction 3. Wash 4. Wash 5. Extraction |
front 9 Suppose you are performing an extraction procedure with a carboxylic acid, like benzoic or toluic acid. Which layer should contain the carboxylic acid in a two-layer mixture of water and an organic solvent, like diethyl ether? | back 9 The organic layer |
front 10 You then add a base to form the corresponding carboxylate. Which layer should contain the carboxylate in a two-layer mixture of water and organic solvent, like diethyl ether? | back 10 The aqueous layer |
front 11 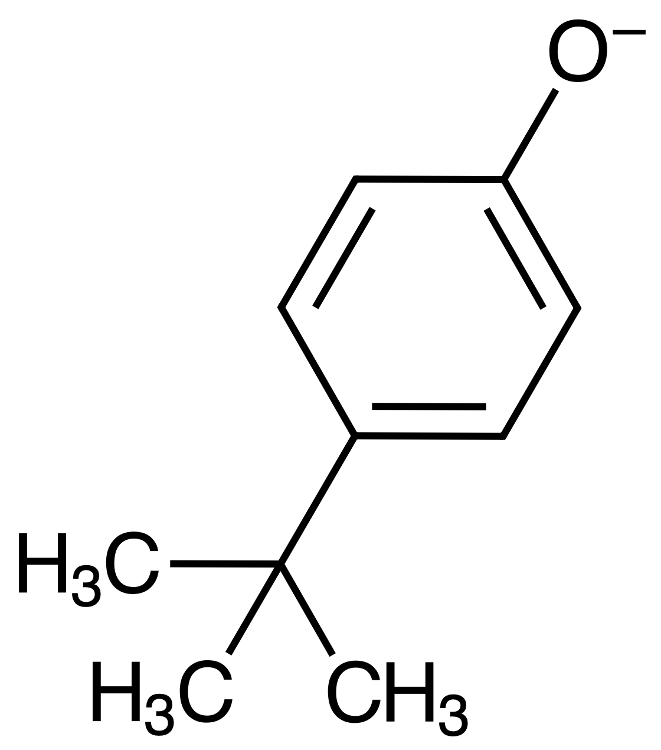 Suppose you are performing an acid/base extraction. After one of the steps, you have collected a NaOH extract containing phenolate. Next, you add HCl to the layer. What are the products of the HCl solution? | back 11 The acid can donate a proton to the phenolate, forming phenol. Chloride ion is left after the acid loses a proton. PhO- + HCl ----> PhOH + Cl- |
front 12 What is the purpose of a drying agent in the work up of an organic reaction? | back 12 To absorb small amounts of water in an organic solution |
front 13 When using acids and bases, note that these substances are ______. Make every effort to avoid contact with ___________. Be sure to wipe up any spills ________. | back 13 corrosive, the skin and lab surfaces, immediately |
front 14 Aniline involves an amine, which is a _____ functional group. When an aqueous acid solution is added to an organic solution including aniline, the aniline appears in the ______ layer in its ______ form. Then, a base is added to ________ the aniline. | back 14 basic, aqueous, protonated, reconstitute |
front 15 Identify the solution used for each described purpose. Reconstitute aniline from aqueous layer ____ Reconstitute benzoic acid out out of the aqueous layer ______ Extract benzoic acid into the aqueous layer ____ Extract reconstituted 3-nitroaniline out of the aqueous layer ____ Extract aniline into the aqueous layer _____ | back 15 1. 6 M NaOH 2. 6 M HCl 3. Dichloromethane 4. 5% NaOH solution 5. Dichloromethane 6. 5% HCl solution |
front 16 What hazards are associated with napthalene? | back 16 -> Naphthalene is flammable -> Naphthalene produces nauseating vapors -> Naphthalene is toxic |
front 17 Lab #3 Before adding a sample or solvent to a separatory funnel, what should you have in place? | back 17 -> A stopcock in the closed position -> A funnel in the top of the separatory funnel -> A flask under the separatory funnel |
front 18 After mixing solutions in a separatory funnel, the stopper should be _____ and the liquid should be ________ and the layers allowed to separate. When you get close to the interface between the layers, _______ the funnel and _______ until the first layer is collected. _______ to collect the second layer. | back 18 removed, drained through the stopcock get eye level with, slow the draining switch to a new flask |
front 19 After an organic reaction involving an aqueous solution, the organic solution might be washed with a saturated sodium chloride aqueous solution, known as brine. What is the purpose of the brine wash? | back 19 To reduce the amount of water in the organic solution. |
front 20 What is the visual indicator that enough of a drying agent, such as anhydrous MgSO4 or CaCl2, has been added to properly dry an organic solution? | back 20 The drying agent will move freely like a powder around the solution. |
front 21 After drying an organic solution, what methods can be used to remove the drying agent from the solution? | back 21 -> Decanting -> Vacuum or gravity filtration |
front 22 If crystal growth does not start on its own after the solution in the flask returns to room temperature, identify the best ways to promote this process. | back 22 -> Add a bit of solid as a seed crystal. -> Scratch the bottom of the flask gently with a stirring rod. |
front 23 What is the best course of action if solid material remains in the flask after the heating step of a recrystallization? | back 23 Filter the hot mixture. |
front 24 In general, when hydrocarbons like oil are added to water, the two liquids ______ because hydrocarbons are _____ and water is ______. | back 24 do not mix, non-polar, polar. |
front 25 Identify the characteristics of a good recrystallization solvent. | back 25 -> Dissolves a sample well at high temperatures -> Does not dissolve a sample well at low temperatures |
front 26 Identify the best support for a separatory funnel. | back 26 Iron ring clamped to a ring stand. |
front 27 When using a separatory funnel, you should burp the funnel. What does the therm burping mean? | back 27 Opening the stopcock when the flask is inverted during mixing. |
front 28 When drying an organic solution, start by transferring the solution to ________ or a test tube, depending on the amount. Then, add ________ of the drying agent and ______ to determine if you added enough drying agent. Continue _______ until the solution is dry. | back 28 an Erlenmeyer flask pea-sized amount, swirl the flask adding small amounts |
front 29 Identify the best drying agent or process for each described purpose.
Removal of visible pockets of water from an organic solvent ______ Storage of solvents or other materials in a desiccator _____ | back 29 Anhydrous calcium chloride Brine wash Drierite |
front 30 Lab#4 After a recrystallization, a pure substance will ideally appear as a network of _______. If this is not the case, it may be worthwhile to reheat the flask and allow the contents to cool more ______. | back 30 large crystals, slowly |
front 31 In order to dissolve a chemical sample in a recrystallization solvent, add the room- temperature solvent _________ in a Erlenmeyer flask on a hot plate. Turn on the heat, starting at ___________. Using a _____, add additional solvent from a second container on the heat source. Swirl the sample flask after each addition, and try to add __________ in order to dissolve the solid. | back 31 just until it covers the sample a low setting and increasing gradually pipet as little solvent as possible |
front 32 What property is the basis of the purification technique recrystallization? | back 32 Solubility |
front 33 After a mixture has been poured through filter paper, the ______ component remains on top while the _____ flows through. To collect the solid, spread the filer paper _______ and allow the solvent to ______. | back 33 solid, liquid, on a watch glass, evaporate. |
front 34 After assembling a gravity filtration apparatus, begin the separation of the mixture by _____ it into the filter paper. Pour the entire contents of the mixture into the filter paper, ______ the solid in the filter paper if needed to speed up filtration. After all the liquid has drained through the filter paper, finish by rinsing the solid with ______. | back 34 decanting, stirring, solvent. |
front 35 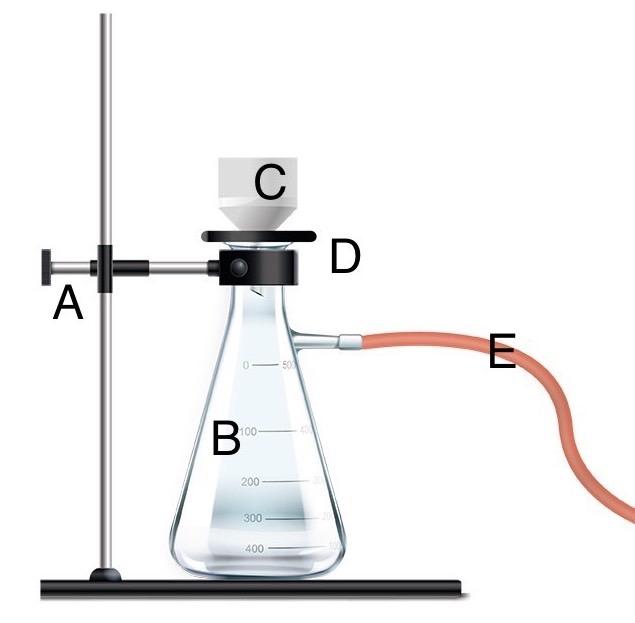 Using letters on the imagine, identify each component of the vacuum filtration set up. | back 35 A - Clamp B - Side-arm flask C - Buchner funnel D - Adapter E - Vacuum tubing |
front 36 You can separate a mixture of sand and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate using filtraton. What difference in properties enables the separation of the two solids by filtration? | back 36 The hydrate is soluble in water but the sand is not. |
front 37 Sulfuric acid, H2SO4, is an important industrial chemical, typically synthesized in a multi-step process. What is the percent yield if a batch of H2SO4 has a theoretical yield of 3.6 kg, and 2.7 kg are obtained at the end of the process? | back 37 75% percent yield = actual yield / theoretical yield x 100% |
front 38 Why might activated carbon be added to a sample during the recrystallization process? | back 38 To absorb impurities causing the recrystallization solution to have an incorrect color. |
front 39 When using vacuum filtration to separate a dissolved solid from an undissolved solid, what techniques should you use to ensure a a quantitative separation? | back 39 -> Dry the solid on the filter paper after the separation -> Wet the filter paper before pouring the mixture into the filter funnel. |
front 40 Lab#5 At the melting point, the solid form of a substance _________ the liquid form of the substance. | back 40 is in equilibrium with |
front 41 1. Experimental melting point is close to literature value____ 2. Experimental melting point is below literature value_____ 3. Wide melting point range_____ 4. Narrow melting point range______ | back 41 1 & 4 : Pure sample of a single compound 2 & 3 : Impure sample of multiple compounds. |
front 42 To prepare a sample in a capillary tube for a melting point determination, gently tap the tube into the sample with _____ end of the tube down. Continue tapping until the sample is ________ . Then, with the _____ end of the tube down, tap the sample down slowly or ____________ to move the sample down faster. Finally, make sure that you can see _________ in the magnifier when placed in the melting point apparatus before turning on the heat. | back 42 open couple of millimeters high closed, drop the tube into a longer tube some or all of the solid |
front 43 Why should you use a finely ground solid when determining the melting point of a sample? | back 43 -> Air pockets in a coarse sample could disrupt heat distribution. -> Uniform, small particles heat more consistently throughout the sample. |
front 44 What characteristics should a good sample for melting point determination have? | back 44 -> Solid phase -> Thoroughly dry -> Small particles |
front 45 What is the recommended order of measurements to report the most accurate melting point possible? Use quick heating to estimate the melting point _____ Use slow heating to carefully observe melting _____ Use slow heating to confirm the careful measurement ____ | back 45 First step Second step Third step |
front 46 When performing a melting point determination, how should you report your findings? | back 46 As a rang from the temperature when melting starts to the temperature when it ends. |
front 47 When melting mixtures of compounds, what is the eutectic composition? | back 47 The mixture composition with the lowest melting point. |