Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
RESERVE ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES
front 1 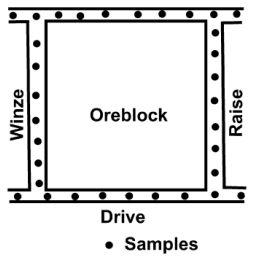 | back 1 - used in single vein-type deposits |
front 2 Tonnage (Old Style) | back 2 (area block)(thickness vein)(S.G.) |
front 3 Delaunay Triangulation | back 3 Triangular Method |
front 4 Tonnage (Triangular Method) | back 4 Volume=(area-triangle)(thickness) |
front 5 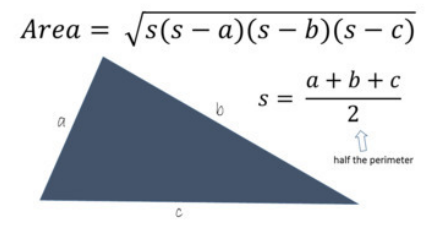 | back 5 Area of Triangle |
front 6 Square/Rectangle Method | back 6 for flat type/near surface |
front 7 Polygonal Method | back 7 for flat type/near surface deposits |
front 8 Contour/Isopach/Isograde Method | back 8 - for flat type, low-dipping disseminated |
front 9 Isolines | back 9 constructed by interpolation |
front 10 Isopachs | back 10 thickness of contours |
front 11 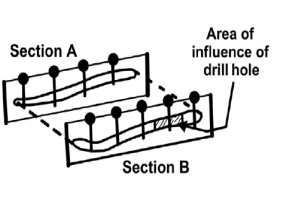 Cross-Section Method | back 11 estimates a block of ground that is |
front 12 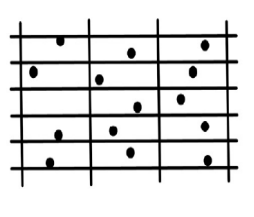 Random Stratified Grid (RSG) Method | back 12 regular grid of a suitable size and an |
front 13 Longitudinal Vertical Section (LVS) Method | back 13 divided into subblocks |
front 14 Regionalized variable” theory | back 14 spatial relationships |
front 15 theory of regionalized variables states that | back 15 t natural phenomena |
front 16 Geostatistics | back 16 for mapping of surfaces from limited sample data and
the |
front 17 Semivariance | back 17 Used to express the degree of relationship between the |
front 18 Kriging | back 18 Named after D.G. Krige |
front 19 Simple Kriging | back 19 - there is an assumption that the mean is both constant and known (making it the most restricted form of kriging |
front 20 Ordinary Kriging | back 20 applicable to samples with constant, but unknown |