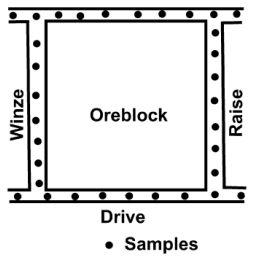
- used in single vein-type deposits
(e.g. gold-bearing quartz
veins)
- channel & chip sampling was
conducted at 3-6 ft
intervals along
the openings (drives, winzes, raises)
Tonnage (Old Style)
(area block)(thickness vein)(S.G.)
Delaunay Triangulation
Triangular Method
Tonnage (Triangular Method)
Volume=(area-triangle)(thickness)
Tonnage=(Volume)(S.G.)
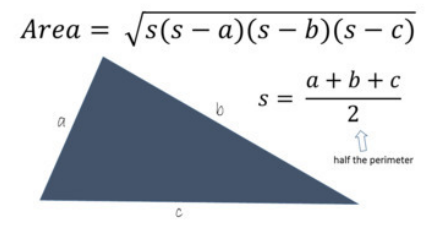
Area of Triangle
Square/Rectangle Method
for flat type/near surface
deposits (bauxite,laterite)
-
drill holes are at the centers
Polygonal Method
for flat type/near surface deposits
(bauxite,laterite)
-
perpendicular bisectors are drawn
between every drill hole; areas are
planimetered/calculated
Contour/Isopach/Isograde Method
- for flat type, low-dipping disseminated
deposits
Isolines
constructed by interpolation
between points of known
values
that assume a gradual
uninterrupted change from
one
point to another
Isopachs
thickness of contours
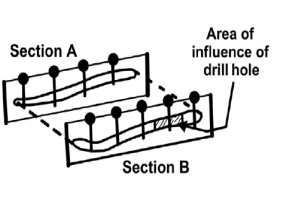
Cross-Section Method
estimates a block of ground that is
bounded between regularly spaced
sections
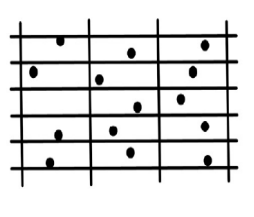
Random Stratified Grid (RSG) Method
regular grid of a suitable size and an
orientation is adjusted
on a set of drill
holes
- trial and error; until, at least
one
sample value falls per grid panel.
Longitudinal Vertical Section (LVS) Method
divided into subblocks
Regionalized variable” theory
spatial relationships
between sample values, thickness, or any
geological phenomena
showing intrinsic dispersion
theory of regionalized variables states that
t natural phenomena
are characterized by a distribution in space
of one or more variables
Geostatistics
for mapping of surfaces from limited sample data and
the
estimation of values at unsampled locations
Semivariance
Used to express the degree of relationship between the
points on
a surface
Kriging
Named after D.G. Krige
- an optimal spatial interpolation
technique that uses the
semivariogram in calculating estimates of
the surface at grid
nodes
Simple Kriging
- there is an assumption that the mean is both constant and known (making it the most restricted form of kriging
Ordinary Kriging
applicable to samples with constant, but unknown
mean (no
trend)
- most general and widely used