Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Sampling
front 1 Sampling | back 1 obtaining objective, reliable information on a population |
front 2 Sample collection | back 2 a mechanical function and depends on: |
front 3 Sampling pattern | back 3 determined by the nature and geometry of mineralization
(i.e. |
front 4 Sample spacing | back 4 determined by the coefficient of variability (ratio of |
front 5 sample collection | back 5 the taking of representative |
front 6 sample preparation | back 6 processing of the samples |
front 7 Sample testing | back 7 sample analysis |
front 8 Grab Sampling | back 8 Quick approximation |
front 9 Percussion Drilling | back 9 churn drill |
front 10 Auger Drilling (Rotary) | back 10 low cost, speed and mobility |
front 11 Hand-operated augers | back 11 3 m with 10-15cm hole diameter |
front 12 Mechanically driven augers | back 12 up to >30 m or more depending |
front 13 Percussive Cum Rotary | back 13 Jackhammers, wagon drills |
front 14 Diamond Drilling (Rotary) | back 14 extensively used for mineral exploration, dam sites +
other |
front 15 drill rods | back 15 usually 10 feet (3.05 m) long through which water is |
front 16 Diamond core bit | back 16 a cylindrical |
front 17 Drilling mud | back 17 – (bentonite, barite) |
front 18 Core barrel | back 18 attached between the lower end of the drill rods |
front 19 Single tube | back 19 best core recovery condition or non-coring bits in |
front 20 Double tube | back 20 average core recovery, where the inner and outer |
front 21 “Triple tube | back 21 complex core barrels and expensive type used in |
front 22 Wire Line Drilling | back 22 saves considerable time and energy. |
front 23 Continuous Core Drilling | back 23 refers to circulating air down to the bit head outside the drill rods
and returning it up through inside the bit, |
front 24 RC Drillingv | back 24 - commonly used for open pit excavation of iron ore,
bauxite, |
front 25 core samples | back 25 from diamond drills or from the casing drills |
front 26 dry cuttings | back 26 from air-flushed diamond, rotary, auger or |
front 27 wet cuttings | back 27 or sludge from churn drills, diamond |
front 28 Soil Sampling/Talus Debris | back 28 Usually in scanty outcrops |
front 29 float samples | back 29 - for analyzing whether it would be useful in |
front 30 Pitting/Pit Sampling | back 30 Commonly during initial stage of surface
geochemical |
front 31 Trenching/Trench Sampling | back 31 10m and 3-5m deep |
front 32 tack/Dump Sampling | back 32 center, then 4 more from |
front 33  Muck Sampling | back 33 few handheld spade or mechanized shovels full of |
front 34  Alluvial Placer | back 34 Usually less-consolidated materials |
front 35 Channel Sampling | back 35 For uniformly distributed mineralization (veins,
stringers, |
front 36 Chip Sampling | back 36 For hard, dense irregularly distributed/disseminated mineralization |
front 37 Car & Sampling | back 37 Handful of the broken ore |
front 38  | back 38 Cross-Belt & Falling stream Sampling |
front 39 Bulk Sampling | back 39 normally of large volume (100 -1000 |
front 40 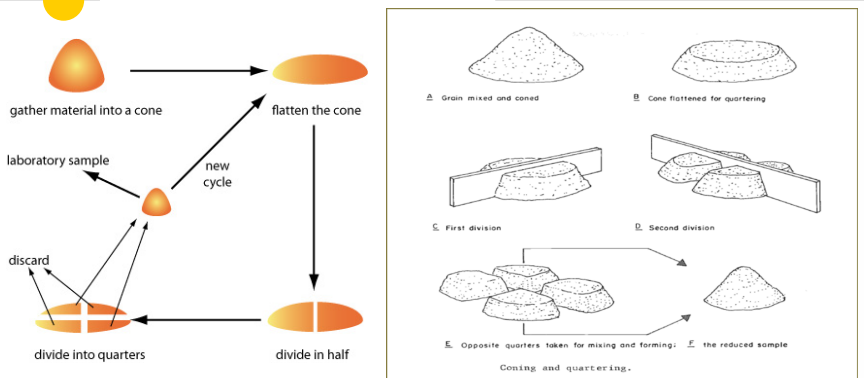 | back 40 Coning & Quartering |
front 41 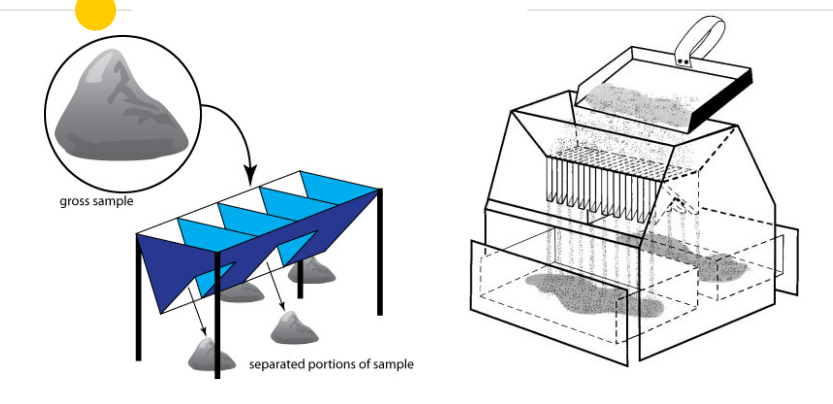 | back 41 Riffle Splitter |
front 42 ) Surface Exploration | back 42 - Pitting, Trenching, Stack and Placer sampling |
front 43 Surface and Underground | back 43 Diamond drill core, RC drill cuttings, Sludge, Channel and Chip sampling |
front 44 Quick Estimation of ROM (run-of-mine) grade | back 44 Grab, Muck, Car, Bulk sampling |
front 45 Thick (uniform) | back 45 Chip or Grab Sampling |
front 46 Medium (uniform) | back 46 Chip + Channel Sampling |
front 47 Too thin (in layers | back 47 Chip sampling |
front 48 Very Large | back 48 Large number of chip samples |
front 49 Gold, rare metals | back 49 Bulk Sampling |
front 50 Banded | back 50 Channel Sampling |