Sampling
obtaining objective, reliable information on a population
Sample collection
a mechanical function and depends on:
• sampling method,
•
site accessibility,
• geology,
• objectives of the project,
and
• requirements for statistical analysis.
Sampling pattern
determined by the nature and geometry of mineralization
(i.e.
size, shape, orientation, and distribution)
Sample spacing
determined by the coefficient of variability (ratio of
std. dev
to the mean) or in other words, the degree
of
homogeneity/heterogeneity of mineralization
sample collection
the taking of representative
fractions
sample preparation
processing of the samples
collected through reduction in size
and quantity
Sample testing
sample analysis
Grab Sampling
Quick approximation
- Randomly picked
Percussion Drilling
churn drill
suitable for soft and medium formation
-
relatively short holes (10-50 m)
Auger Drilling (Rotary)
low cost, speed and mobility
soft and loose
ground
inaccurate due to wall collapse & contamination
Hand-operated augers
3 m with 10-15cm hole diameter
Mechanically driven augers
up to >30 m or more depending
on subsoil
Percussive Cum Rotary
Jackhammers, wagon drills
air-driven drills with depth of
drilling limited to 6 m
for development of tunnels, advance
mining faces and
breaking big boulders in road and other
construction areas.
Diamond Drilling (Rotary)
extensively used for mineral exploration, dam sites +
other
foundation test works, mine development face, drainage
of
mine workings, mine vent., oil structure investigations &
oilgas wells
drill rods
usually 10 feet (3.05 m) long through which water is
pumped to
cool the bit + flush the rock cuttings
Diamond core bit
a cylindrical
hollow tube made of special alloys with a crown at
one end
Drilling mud
– (bentonite, barite)
prevents damage of drilling
tools,
serves as lubricant
Core barrel
attached between the lower end of the drill rods
and the reamer
shell. It holds the core inside while drilling and
brought to the surface.
Single tube
best core recovery condition or non-coring bits in
blast hole drilling
Double tube
average core recovery, where the inner and outer
tubes are
connected and rotate simultaneously
“Triple tube
complex core barrels and expensive type used in
broken, friable
and sheared formations
Wire Line Drilling
saves considerable time and energy.
withdrawing the core and inner tube assembly (core barrel) from
the hole without pulling out the hollow drill rods by a separate
hoisting unit fixed at a different pulley.
Continuous Core Drilling
refers to circulating air down to the bit head outside the drill rods
and returning it up through inside the bit,
core barrel and drill rods.
RC Drillingv
- commonly used for open pit excavation of iron ore,
bauxite,
limestone, rock phosphate, and coal seams.
- 10-15
cm large diameter vertical blast holes at high speed and
low cost
core samples
from diamond drills or from the casing drills
dry cuttings
from air-flushed diamond, rotary, auger or
percussion drilling, and
wet cuttings
or sludge from churn drills, diamond
drill, or wet rotary or
percussion drilling
Soil Sampling/Talus Debris
Usually in scanty outcrops
- Soil samples are collected on a
relatively closely spaced
rectangular/square grid pattern at
specified intervals
float samples
- for analyzing whether it would be useful in
the detection of
concealed mineralization with a thin cover
Pitting/Pit Sampling
Commonly during initial stage of surface
geochemical
exploration
- Excavating 1x1 m2 pits in
rectangular or square grid
patterns covering the entire target
area w/ varying depths
depending on extent of weathering and
nature of rocks
Trenching/Trench Sampling
10m and 3-5m deep
Trenches are often cut across
the orebody after
the
probable configuration of
mineralization is
outlined
either by pitting or by
rock/soil sampling
tack/Dump Sampling
center, then 4 more from
halfway to the corners
collection of representative
broken material generated
by
pitting, trenching, mine
production etc.
Muck Sampling
few handheld spade or mechanized shovels full of
mineralized
fragments and fines collected from the mine
face or stope draw points

Alluvial Placer
Usually less-consolidated materials
(weathered) but
stratified
- Scooping by hand spade or by auger
drills
Channel Sampling
For uniformly distributed mineralization (veins,
stringers,
disseminations)
- cutting of channels across
mineralized body in fresh surface
exposures/underground mine
workings ( face, walls and
roof)
Chip Sampling
For hard, dense irregularly distributed/disseminated mineralization
- chipping off same-sized fragments of about 1x1 to 2x2 cm size
covering the entire surface exposure, underground
mine face, wall
and roof in a regular grid interval (25x25 cm)
Car & Sampling
Handful of the broken ore
material picked up randomly
every
5th/10th… moving car
transported by mine-car
from
underground operations,
dumpers/trucks

Cross-Belt & Falling stream Sampling
Bulk Sampling
normally of large volume (100 -1000
tonnes) representing all the
distinctive
characteristics of the orebody
- From different parts of stockpile of trial
pit (surface),
trial crosscuts
(underground) and ROM of regular
production
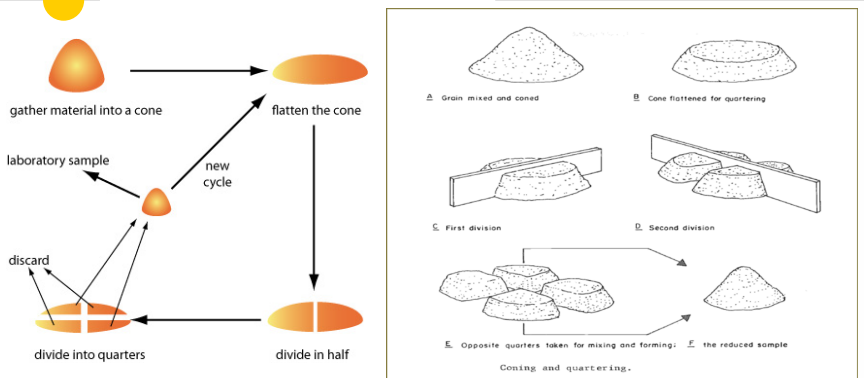
Coning & Quartering
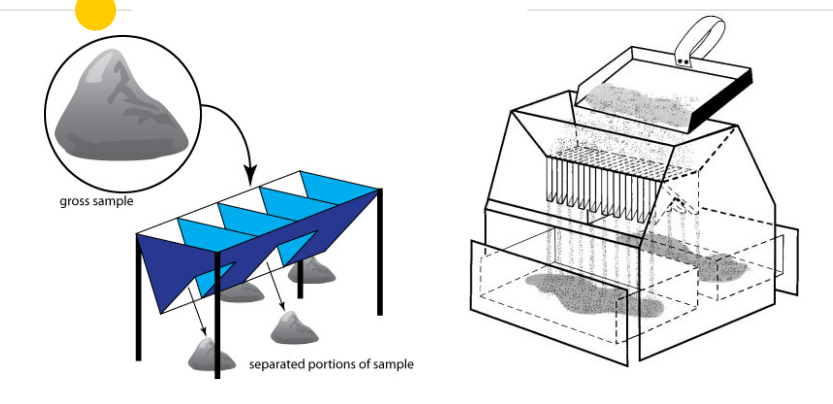
Riffle Splitter
) Surface Exploration
- Pitting, Trenching, Stack and Placer sampling
Surface and Underground
Diamond drill core, RC drill cuttings, Sludge, Channel and Chip sampling
Quick Estimation of ROM (run-of-mine) grade
Grab, Muck, Car, Bulk sampling
Thick (uniform)
Chip or Grab Sampling
Medium (uniform)
Chip + Channel Sampling
Too thin (in layers
Chip sampling
Very Large
Large number of chip samples
Gold, rare metals
Bulk Sampling
Banded
Channel Sampling