Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Skills IGCSE Geography Flashcards
front 1 Continuous data | back 1 Numerical data that can take any value within a given range, e.g. heights and weights. |
front 2 Discrete data | back 2 Numerical data that can only take certain values, e.g. shoe size |
front 3 Quantitative data | back 3 Results that can be expressed using numerical values. |
front 4 Qualitative data | back 4 Results that can’t be expressed as numbers, e.g. opinions |
front 5 What a histogram is. | back 5 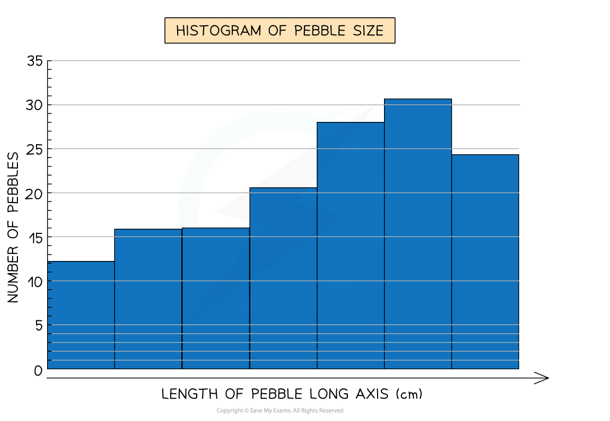 A bar chart is used to compare categorical data while histograms are used to analyse the distribution of data. |
front 6 Divided bar chart | back 6 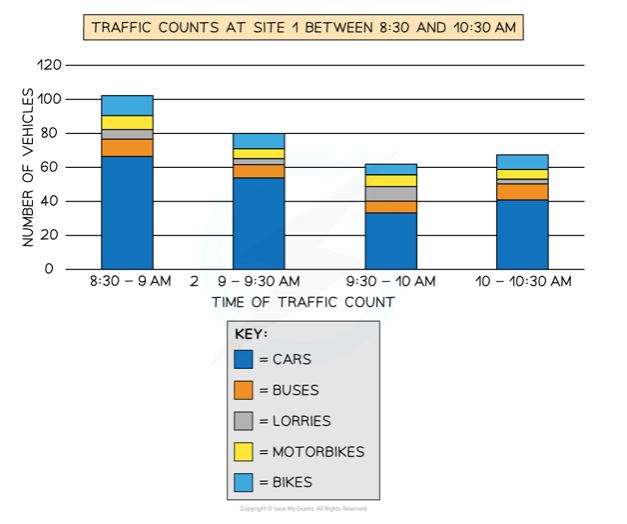 |
front 7 Rose diagram | back 7 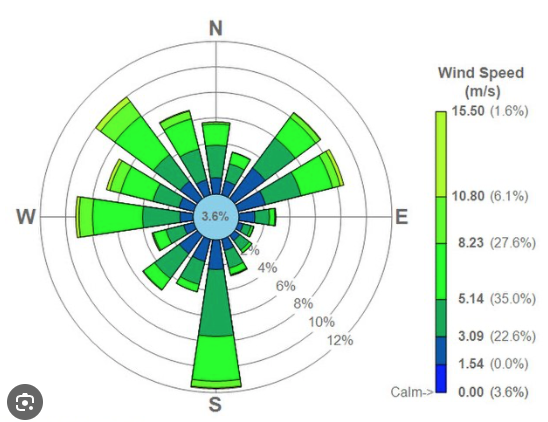 Diagram often used for wind, that shows how much at each direction and on what speed. |
front 8 Triangular graph | back 8 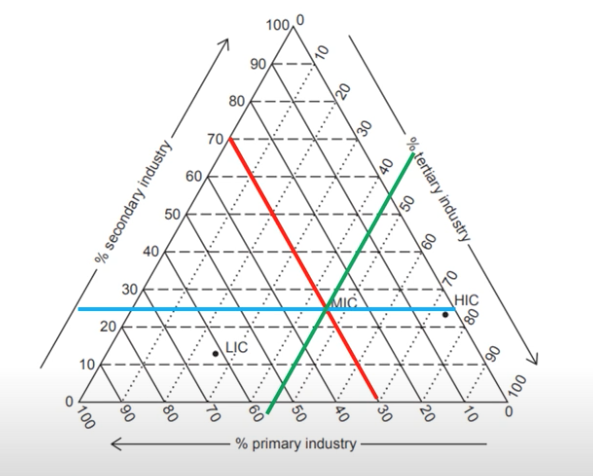 Have axes on three sides all of which go from 0-100 which show percentages, data which is divided into 3. Draw a line from each side on its percent and where they meet is the point. |
front 9 Scatter graph | back 9 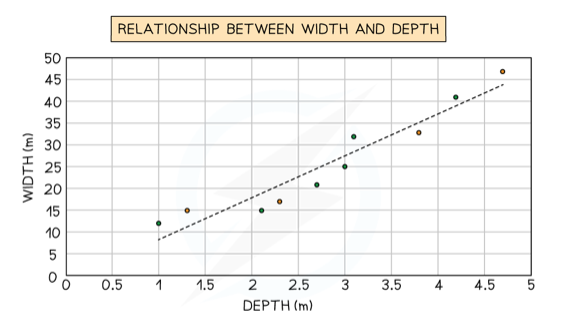 Used to show the relationship between two variables, the best fit line can be added to show the relations. |
front 10 Choropleth map | back 10 Maps which are shaded according to a pre-arranged key with each shade representing a range of value. |
front 11 Proportional symbols map | back 11 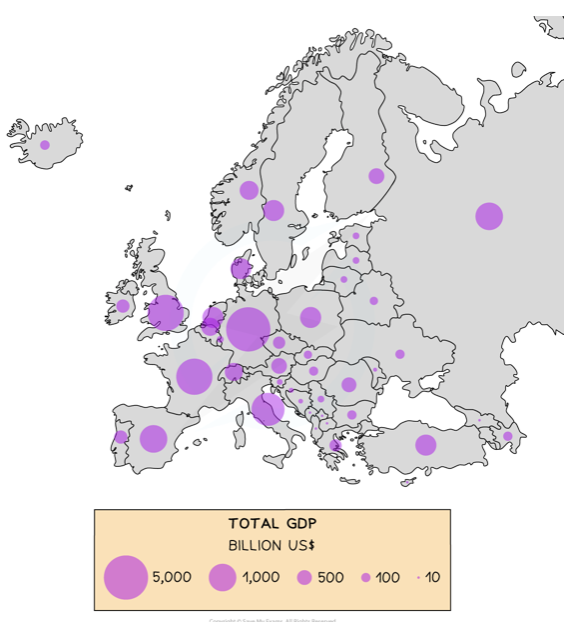 The symbols on the map are drawn in proportion to the variable represented, can be circles but also other shapes. |
front 12 Pictograms | back 12 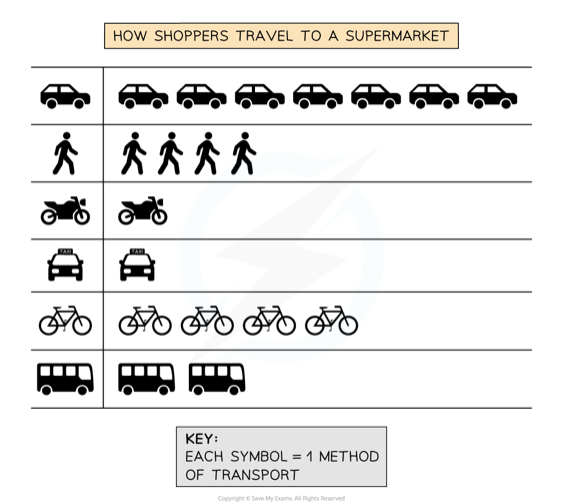 These are a way of displaying data using symbols or diagrams on a graph. |