Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Histology(Ch1-5)
front 1 Where did Hematoxylin come from | back 1  From Logwood |
front 2 Is hematoxylin an acid or a base | back 2 Base |
front 3 What does Hematoxylin stain | back 3  RNA, DNA, Carbohydrates and cartilage, because they're acidic |
front 4 What does eosin stain | back 4 Most proteins and some extracellular fibers |
front 5 Is eosin an acid or a base | back 5 Negative Acid |
front 6 What color does Hematoxylin stain the Nucleus | back 6  Purplish blue |
front 7 What color does eosin stain | back 7 Red or pink |
front 8 What are the compounds in Masson's trichrome | back 8  Hematoxylin, acid fuchsin, methyl blue |
front 9 What color does Masson's trichrome stain Nuclei | back 9  Blue |
front 10 What color does Masson's trichrome stain connective tissue and basement layers | back 10 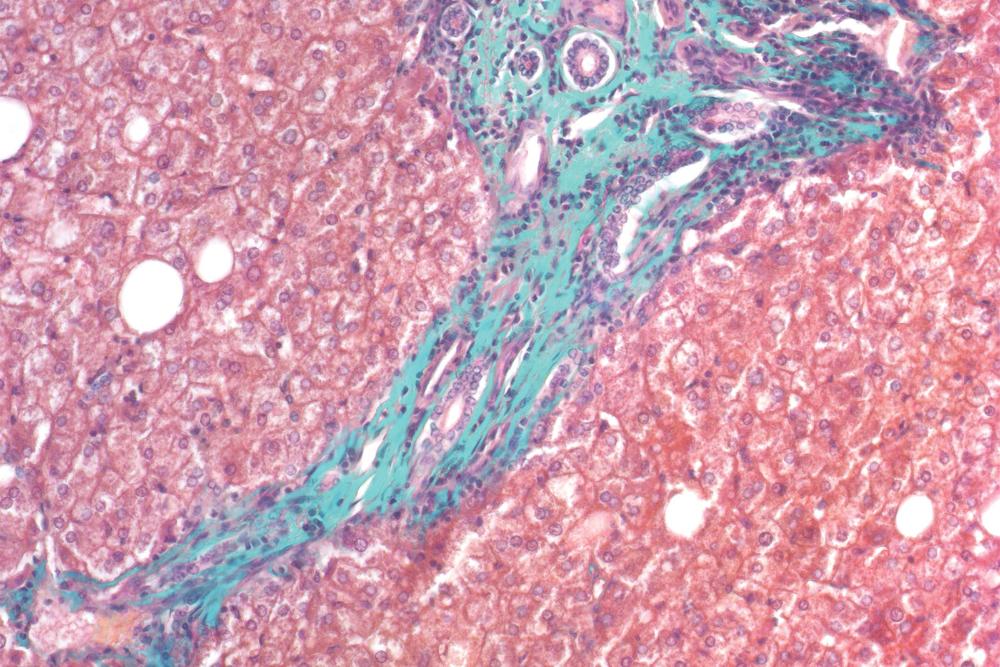 Green |
front 11 Whats Van Gieson stain used for? | back 11 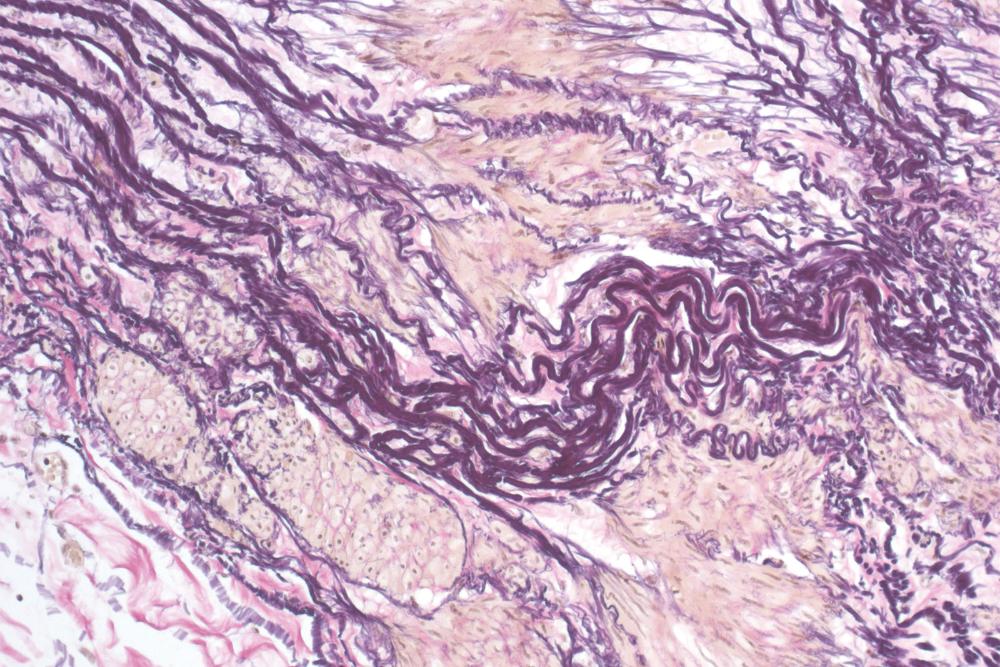 For connective tissue detection |
front 12 Whats Geimsa stains used for | back 12 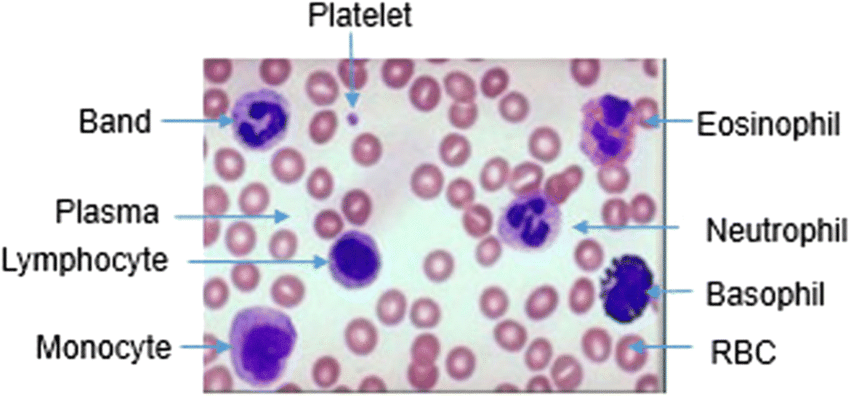 Detecting Erythrocytes in the bone marrow to see if they're sick, and also for blood smears (is a test used to see the shape, size and appearance of red blood cells) |
front 13 What color does giemsa stains stain red blood cells | back 13 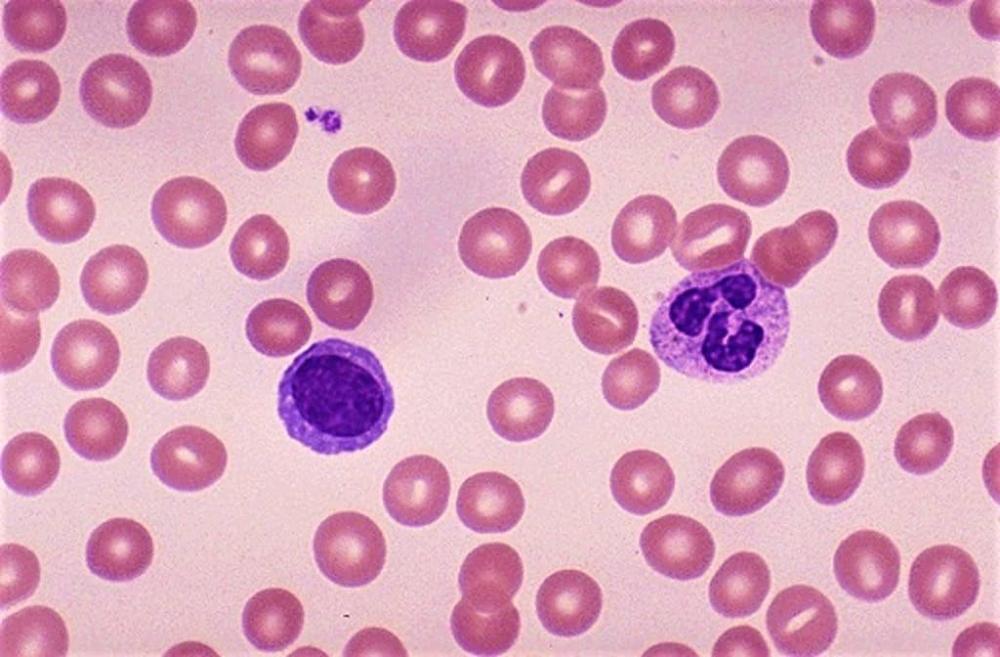 Pink |
front 14 What color does giemsa stains stain white blood cells | back 14  Dark purple/ blue |
front 15 What does silver stain used for | back 15 To stain nerves |
front 16 Whats Golgi-Cox used for | back 16 To stain nerves |
front 17 What are the compounda in Golgi-Cox | back 17  Mercuric chloride, potassium chromate K2CrO4, potassium dichromate K2Cr2O7 |
front 18 Whats Cresyl violet used for | back 18 Detecting the endoplasmatic reticulum of the body of nerve cells(perikarya) |
front 19 What color does Cresyl Violet stain body of neurons? | back 19 Brown |
front 20 Name lipid stains | back 20  Nile Blue, Oil Red O and Sudan black |
front 21 How thick is sectioning if done with microtome | back 21  10-20 Microns |
front 22 What are low power Lenses | back 22  *1.6, *5 and *10 |
front 23 What are Hight low power Lenses | back 23  *20, *40, *63 and *100 |
front 24 What is the wave length range for halogen lamp(tungsten lamp) | back 24 starts at 300-400nm to 700-800nm |
front 25 What does the magnification of Light microscope depend on? | back 25 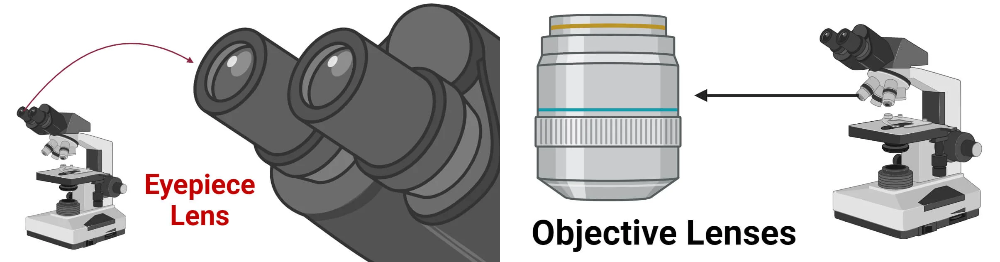 the Magnification of the eye piece and Objective lens, for example if you had a eyepiece in a light microscope that can magnify by x10 and then objective lens that can magnify by x10 then in total your light microscope can magnify by x100 |
front 26 Whats the best resolution obtainable from a light microscope | back 26 0.2 Microns or 200nm |
front 27 How big are cells in diameter | back 27 20-40 microns |
front 28 Whats the Wave length in a Electron microscope | back 28 0.004nm |
front 29 What does electro microscope use instead of lenses to focus the light | back 29  electromagnetic coils |
front 30 What is the Numerical aperture for electron microscope | back 30 0.012 |
front 31 What is the greatest magnification for electron microscope | back 31 x50,000 |
front 32 How thick are the prepared sections for Electron microscope | back 32 60-100nm |
front 33 How thick is the plasmatic membrane | back 33 8-10nm |
front 34 How much is the diameter of the Nucleus | back 34 10 Microns |
front 35 What is the function of the Nucleolus | back 35 Making Ribosomes |
front 36 How much of cell volume do endoplasmic reticulum constitute | back 36 10% |
front 37 What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum | back 37
|
front 38 How many membranes does the Smooth ER have | back 38 it has the same structure as the plasmatic membrane, a single lipid bilayer membrane |
front 39 How wide are the lumens of Rough ER | back 39 20-30nm |
front 40 How wide are the lumens of Smooth ER | back 40 30-60nm |
front 41 What is Cisternae | back 41 its the first 3-7 discs of the Golgi apparatus, the discs that receive, modify, transform and pack proteins |
front 42 What is the trans face of Golgi apparatus | back 42 its the face that transports the proteins to the plasmatic membrane |
front 43 What is the function of secreting vesicles | back 43 to get molecules to the plasmatic membrane |
front 44 What is the function of Endosomes | back 44 they bring molecules from outside the cell inward, then to the lysosomes so that it can break it down |
front 45 What is the function of Macropinosomes | back 45 they bring large amounts of fluid into the cell |
front 46 What is the function of endosomes that do Phagocytosis | back 46 they kill bacteria |
front 47 What is the function of Peroxisomes | back 47 they degrade fatty acids by adding an oxygen, then convert them to cholesterol |
front 48 Where are Peroxisomes common/abundant | back 48  liver and kidney |
front 49 How big are vesicles | back 49 50-200nm |
front 50 What is Christae | back 50 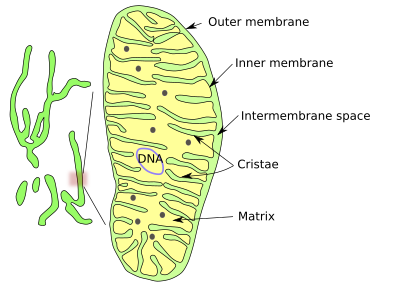 they're the folds of the inner membrane of mitochondria that folds inward, the folds are empty intermediate space |
front 51 What is the function of Actin filaments | back 51 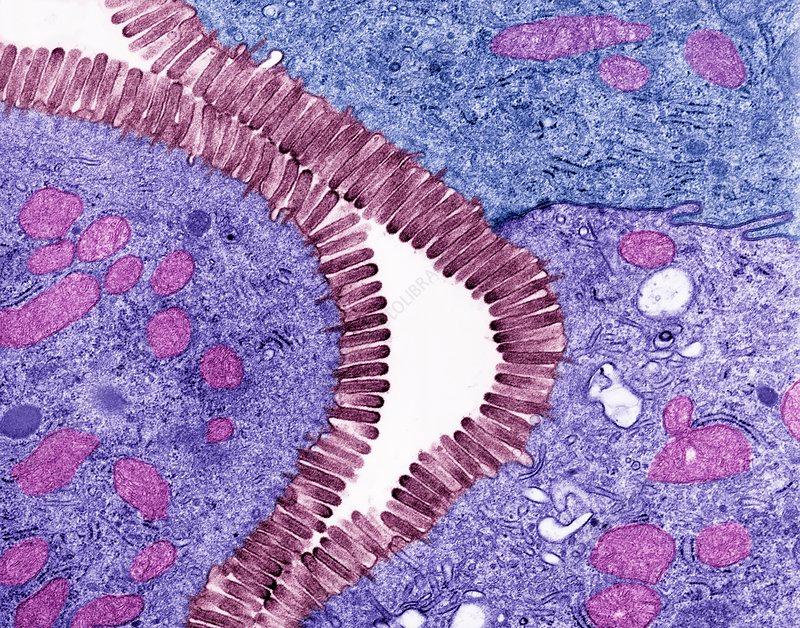
|
front 52 How thick are actin filaments | back 52 7nm |
front 53 What is the function of Intermediate filaments | back 53 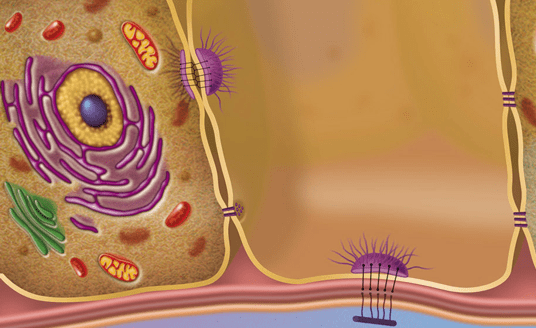 they make it easier for cells to stick to each other by desmosomes and hemidesmosomes |
front 54 What is the function of Microtubules | back 54
|
front 55 What makes Microtubules | back 55 Centrosomes |
front 56 How big are Intermediate filaments | back 56 10nm |
front 57 How big are Microtubules | back 57 25nm |
front 58 What are the things you do in tissue processing for electron microscope that you don't do in light Microscopy | back 58 1)The fixative isn't formality It's rather glutaraldehyde 2)Post fixation(another fixation after glutaraldehyde) by osmic acid 3)We put the tissue in propylene oxide that allows us to impregnate it later with resin instead of wax 4) Machine For sectioning is Ultramicrotome That has a glass Or diamond knife 5)Stains are heavy salt Metals like Osmium, uranyl acetate And lead To increase. The contrast Because they dispersed |
front 59 Why do we post-fixate with osmic acid in tissue processing for electron microscopy | back 59 glutaraldehyde results in cross-linking proteins that reserves protein structure while osmic acid preserves lipids |