Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 2 General Biology
front 1 An element is defined as a substance that: | back 1 cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical reactions. |
front 2 Which of the following elements is NOT responsible for a significant portion of the mass of living organisms? | back 2 S. |
front 3 An atom has six protons and eight neutrons. Its atomic mass is __ atomic mass units. | back 3 fourteen. |
front 4 The difference between a stable isotope and a radioisotope is that: | back 4 the radioisotope emits radiation. |
front 5 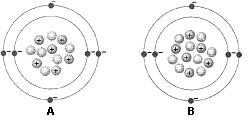 Figure 2-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). The atomic mass of the atom identified as A in Figure 2-1 is: | back 5 12. |
front 6 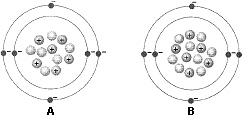 Figure 2-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). Figure 2-1 represents: | back 6 two isotopes of the same element. |
front 7  Figure 2-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). The difference between the two atoms in Figure 2-1 is: | back 7 the number of neutrons. |
front 8 Isotopes differ from each other with respect to the number of: | back 8 neutrons only. |
front 9 Radioisotopes are used in all of the following scientific applications except: | back 9 measuring the pH of the blood. |
front 10 The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the: | back 10 number of valence electrons. |
front 11 Which of the following statements is FALSE? | back 11 The 2nd energy level contains a maximum of 10 electrons. |
front 12 Chlorine has seven electrons in its valence shell. The number of electrons it must gain to complete its valence shell is: | back 12 1. |
front 13 Any chemical interaction between atoms: | back 13 involves only valence electrons. |
front 14 The representation H-O-H is known as: | back 14 a structural formula. |
front 15 The molecular mass of C6H12O6 is 180 amu. 0.25 moles of this substance contain: | back 15 45 g. |
front 16 How many molecules are present in one mole of C6H12O6? | back 16 6.02 x 1023 molecules. |
front 17 In a chemical reaction, the product is: | back 17 generally written on the right side and is the substance generated by the reaction. |
front 18 When a chemical reaction is at dynamic equilibrium: | back 18 the forward and reverse reactions are proceeding at equal rates. |
front 19 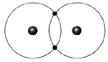 Figure 2-2 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). Figure 2-2 represents: | back 19 molecular hydrogen. |
front 20 Figure 2-2 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). The type of bond illustrated in Figure 2-2 is: | back 20 a single covalent bond. |
front 21 Which covalent bond involves only 2 electrons: | back 21 single. |
front 22 A covalent bond: | back 22 may be polar or nonpolar depending on the atoms involved. |
front 23 In a water molecule, because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared electrons are more commonly found around the __ nucleus more often than the __ nucleus. | back 23 oxygen; hydrogen. |
front 24 The covalent bond between a hydrogen atom and the oxygen atom in water is formed when: | back 24 hydrogen and oxygen share an electron pair. |
front 25 Covalently bonded atoms with similar electronegativities are: | back 25 nonpolar. |
front 26 An atom becomes a cation if: | back 26 it loses one or more electron. |
front 27 The difference between an electrically neutral atom and an ion is that: | back 27 an ion has an unequal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an equal number. |
front 28 In the formation of common table salt, sodium and chlorine interact because: | back 28 sodium donates one electron to chlorine. |
front 29 Table salt dissolves easily in water because: | back 29 the partial positive charge of the hydrogens in the water molecule can associate with the negative charge of the chloride ion, and the partial negative charge of the oxygen of the water molecule can associate with the positive charge of the sodium atom. |
front 30 The process whereby water molecules surround ions during the process of dissolving is called: | back 30 hydration. |
front 31 Which of the following statements concerning van der Waals interactions is FALSE: | back 31 they are very strong. |
front 32 Which component becomes oxidized in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3 | back 32 iron. |
front 33 Which component is the oxidizing agent in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3 | back 33 oxygen. |
front 34 The cohesiveness between water molecules is due largely to: | back 34 hydrogen bonds. |
front 35 A stalk of celery is placed in a solution of blue colored dye. After one hour, the leaves have blue fluid in their veins. Which property of water is being demonstrated? | back 35 adhesion and cohesion. |
front 36  Which characteristic of water molecules directly contributes to the remarkable “water walking" success of the aquatic insects pictured in the accompanying figure? | back 36 hydrogen bonds. |
front 37 Which of the following statements is not correct? | back 37 Water heats up and cools down very quickly. |
front 38 It takes 1 calorie of heat to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius at sea level. This is referred to as the __ of water. | back 38 specific heat. |
front 39 Evaporative cooling is a process whereby __ moving __ molecules vaporize, thus __ large amounts of heat. | back 39 fast; water; removing. |
front 40 At what temperature is water most dense? | back 40 4 degrees Celsius. |
front 41 This characteristic of a molecule determines the ability of hydrogen bonds to form between it and hydrogen: | back 41 an atom with a partial negative charge. |
front 42 Which characteristic of water makes the existence of pH possible? | back 42 ionization. |
front 43 A pH of 4 is __ times more __ than a pH of 7. | back 43 1000; acidic. |
front 44 What is the OH- concentration of a solution having a pH of 2? | back 44 1 x 10-12. |
front 45 When a small amount of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of Na2HPO4, the pH of the solution does not change markedly. The pH also does not change drastically when a small amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to this same solution. Based on these observations, the compound Na2HPO4 is: | back 45 acting as a buffer. |
front 46 A salt is a compound in which the hydrogen ion of __ is replaced by some other cation. | back 46 an acid. |
front 47 A solution having a pH of 6 would: | back 47 be slightly acidic. |
front 48 Identify the chemical(s) that act(s) as a buffer in human blood: | back 48 bicarbonate. |
front 49 Identify the hydrogen ion concentration that represents the lowest pH from the following list: | back 49 1 x 10-3. |
front 50 Which of the following has a pH closest to that of human blood? | back 50 sea water. |