Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
o chem exam 1
front 1 How to find formal charge: | back 1 Formal charge= Group#-lines-dots |
front 2 a central atom is | back 2 the one that you have less of |
front 3 the most electronegative element is | back 3 fluorine |
front 4 Electronegativity increases from | back 4 left to right |
front 5 waves can combine: | back 5 constructively (more stable) and destructively (smaller w/ change of sign) |
front 6 Low energy= | back 6 more stable |
front 7 MOT only applies to | back 7 covalent bonding |
front 8 How to find hybridization: | back 8 x+1 = # of sigma bonds + # of lone pairs |
front 9 Lewis acid: | back 9 accepts electrons (deficient) |
front 10 Lewis base: | back 10 donates electrons (electron rich) |
front 11 Bronsted Lowry acid: | back 11 has a labile H+ |
front 12 Bronsted Lowry base: | back 12 removes a labile H+ |
front 13 a lewis base is a | back 13 bronsted lowry base |
front 14 strong acids are | back 14 completely ionized by water |
front 15 conjugate base of a strong acid is | back 15 weak |
front 16 conjugate acid of a strong base is | back 16 weak |
front 17 strong acids have large values of | back 17 Ka |
front 18 weak acids have low values of | back 18 ka |
front 19 pka= | back 19 -log Ka |
front 20 strong acids have _____ pka values | back 20 low |
front 21 weak acids have _______ pka values | back 21 high |
front 22 acid-base reactions proceed in the direction that yield a | back 22 weak acid and a weak base (favored) |
front 23 acid-base reactions occur if the ______ > ______ | back 23 pKa base, pKa acid |
front 24 The conjugate base of a strong acids is a ________ base The conjugate base of a weak acid is a ________ base | back 24 weak, strong |
front 25 The larger the Ka value, the __________ the acid The larger the pKa value the _________ the acid | back 25 stronger, weaker |
front 26 Acidity ____________ within a given row Acidity ____________ within a given column | back 26 increases, increases |
front 27 any features that stabilizes a conjugate base make the acid ____________ | back 27 stronger |
front 28 What are two ways a conjugate base can be stabilized | back 28 resonance, and inductive effect |
front 29 acid-base reactions will always proceed in the directions of (reactant or products) that yield the _______________ and the ____________ | back 29 weaker acid, weaker base |
front 30 acid base reactions proceed towards products as long as the pKa of the base is __________________________ | back 30 higher than the pka of the acid |
front 31 2sp3 with no lone pairs is | back 31 tetrahedral |
front 32 2sp3 with 1 lone pairs is | back 32 trigonal pyramidal |
front 33 2sp3 with 2 lone pairs | back 33 bent |
front 34 2sp2 is | back 34 trigonal planar |
front 35 2sp | back 35 linear |
front 36 hybridization applies to atoms from the | back 36 2nd row |
front 37 increasing order of energy | back 37 sigma<pi<pi*<sigma* |
front 38 relative energy | back 38 sp<sp2<sp3 |
front 39 relative electronegativity | back 39 sp>sp2>sp3 (sp close to nucleus) |
front 40 which orbitals are arranged in order of increasing energy? | back 40 sp < sp2 <sp3 |
front 41 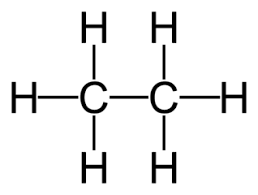 how many sigma 1s-2sp3 bonds are there in ethane? | back 41 6 |
front 42 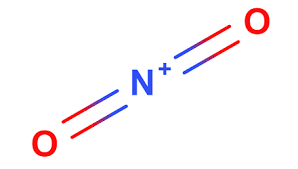 What are the hybridization and formal charge around the central atom in the nitronium ion (NO2+) | back 42 Hybridization: 2sp Charge +1 |
front 43 when the 1s orbitals of two hydrogen atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule, how are the electrons distributed in order to form the resulting molecular orbitals? | back 43 2 electrons in the bonding molecular orbital |
front 44 overlap of p-orbital lobes of opposite signs results in the formation of | back 44 an anti bonding (pi) orbital |
front 45 which molecule would be expected to be linear | back 45 HCN |
front 46 assuming that hybridization takes place, which orbitals form the O-O sigma bond in O2 | back 46 2sp2 |
front 47 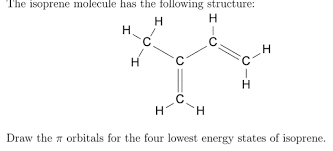 how many 2sp2-1s bonds are there in the following molecule | back 47 5 |
front 48 In ammonia (NH3) the hybridization of the nitrogen atom and the geometry are expected to be | back 48 hybridization: 2sp3 Geometry: trigonal pyramidal |
front 49 anything that stabilizes the conj. base makes the acid _______ | back 49 stronger |