How to find formal charge:
Formal charge= Group#-lines-dots
a central atom is
the one that you have less of
the most electronegative element is
fluorine
Electronegativity increases from
left to right
waves can combine:
constructively (more stable) and destructively (smaller w/ change of sign)
Low energy=
more stable
MOT only applies to
covalent bonding
How to find hybridization:
x+1 = # of sigma bonds + # of lone pairs
Lewis acid:
accepts electrons (deficient)
Lewis base:
donates electrons (electron rich)
Bronsted Lowry acid:
has a labile H+
Bronsted Lowry base:
removes a labile H+
a lewis base is a
bronsted lowry base
strong acids are
completely ionized by water
conjugate base of a strong acid is
weak
conjugate acid of a strong base is
weak
strong acids have large values of
Ka
weak acids have low values of
ka
pka=
-log Ka
strong acids have _____ pka values
low
weak acids have _______ pka values
high
acid-base reactions proceed in the direction that yield a
weak acid and a weak base (favored)
acid-base reactions occur if the ______ > ______
pKa base, pKa acid
The conjugate base of a strong acids is a ________ base
The conjugate base of a weak acid is a ________ base
weak, strong
The larger the Ka value, the __________ the acid
The larger the pKa value the _________ the acid
stronger, weaker
Acidity ____________ within a given row
Acidity ____________ within a given column
increases, increases
any features that stabilizes a conjugate base make the acid ____________
stronger
What are two ways a conjugate base can be stabilized
resonance, and inductive effect
acid-base reactions will always proceed in the directions of (reactant or products) that yield the _______________ and the ____________
weaker acid, weaker base
acid base reactions proceed towards products as long as the pKa of the base is __________________________
higher than the pka of the acid
2sp3 with no lone pairs is
tetrahedral
2sp3 with 1 lone pairs is
trigonal pyramidal
2sp3 with 2 lone pairs
bent
2sp2 is
trigonal planar
2sp
linear
hybridization applies to atoms from the
2nd row
increasing order of energy
sigma<pi<pi*<sigma*
relative energy
sp<sp2<sp3
relative electronegativity
sp>sp2>sp3 (sp close to nucleus)
which orbitals are arranged in order of increasing energy?
sp < sp2 <sp3
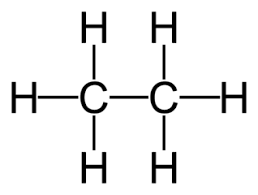
how many sigma 1s-2sp3 bonds are there in ethane?
6
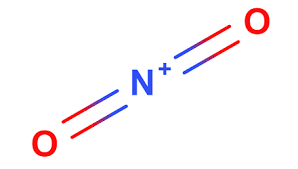
What are the hybridization and formal charge around the central atom in the nitronium ion (NO2+)
Hybridization: 2sp Charge +1
when the 1s orbitals of two hydrogen atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule, how are the electrons distributed in order to form the resulting molecular orbitals?
2 electrons in the bonding molecular orbital
overlap of p-orbital lobes of opposite signs results in the formation of
an anti bonding (pi) orbital
which molecule would be expected to be linear
HCN
assuming that hybridization takes place, which orbitals form the O-O sigma bond in O2
2sp2
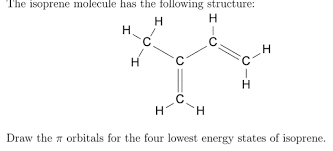
how many 2sp2-1s bonds are there in the following molecule
5
In ammonia (NH3) the hybridization of the nitrogen atom and the geometry are expected to be
hybridization: 2sp3
Geometry: trigonal pyramidal
anything that stabilizes the conj. base makes the acid _______
stronger