Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Health Assessment Exam 1 Chapter 7-12
front 1 What is the difference between sensitivity and specificity What does it mean? | back 1 Sensitivity
Specificity
|
front 2 What are clues in patient history or clinical manifestations that may indicate eating disorder? | back 2 Clinical Manifestations
|
front 3 How do you take proper BP for most accuracy? | back 3
|
front 4 Recognize the S&S of depression? | back 4 personal history of a depressive episode, a family history of first-degree family members with depression, personal history of recent stressful life events or significant childhood adversity, chronic and/or disabling medical illness, and female gender S/S
|
front 5 Risk factors of suicide? | back 5
|
front 6 What is the relationship between substance abuse and depression/anxiety? | back 6 About 16 million adult Americans, or almost 7%, have major depression, often with coexisting anxiety disorders and substance abuse |
front 7 What is the difference between delirium and dementia? | back 7 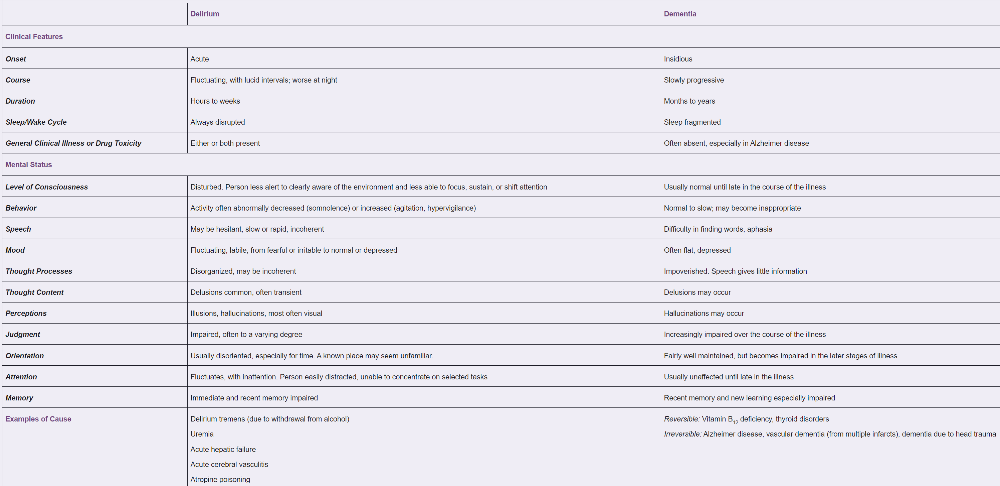 Delirium
Dementia
|
front 8 What are components of the MMSE? Why are they being assessed? | back 8
Score of 25 or higher is normal The Mini-Mental State Examination is the best-known screening test for dementia |
front 9 What is Beers criteria? What is the concern regarding anticholinergic medication in elderly? | back 9 Learn about drug–drug interactions and consult the 2019 AGS Beers Criteria, widely used by health care providers, educators, and policymakers. In addition to a list of hazardous drugs for older adults, this new criteria now include lists of select drugs that should be avoided or have their dose adjusted based on the individual’s kidney function and select drug–drug interactions documented to be associated with harms in older adults |
front 10 How to palpate lymph nodes? | back 10
|
front 11 Recognize normal neck anatomy? | back 11 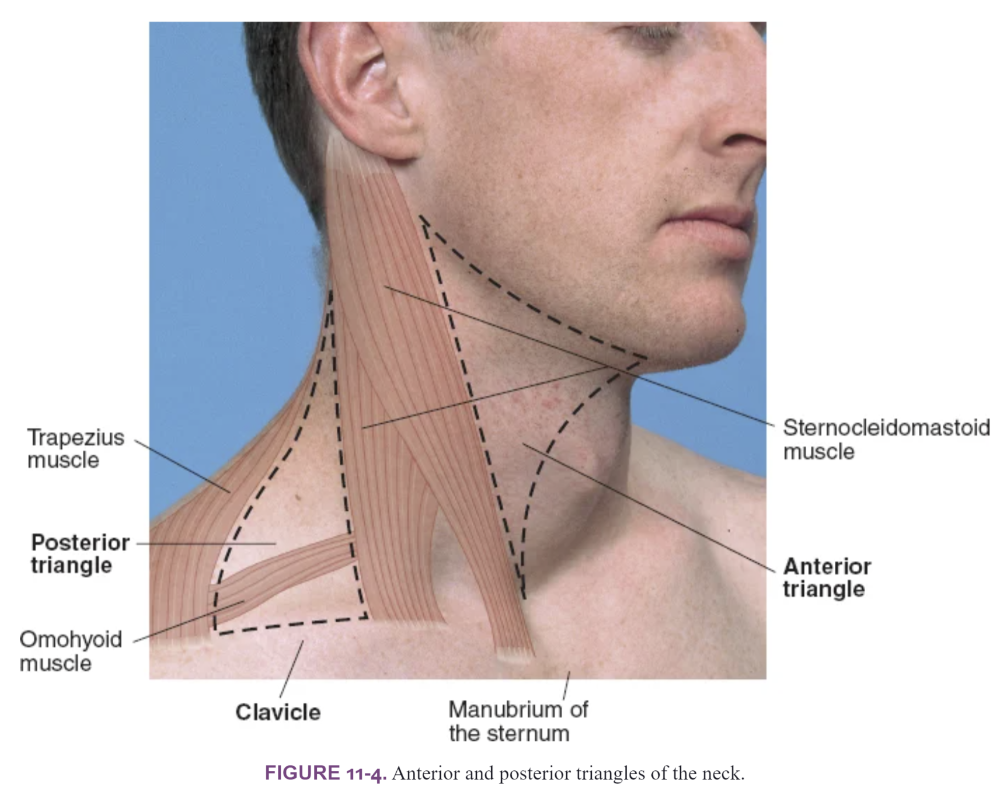
|
front 12 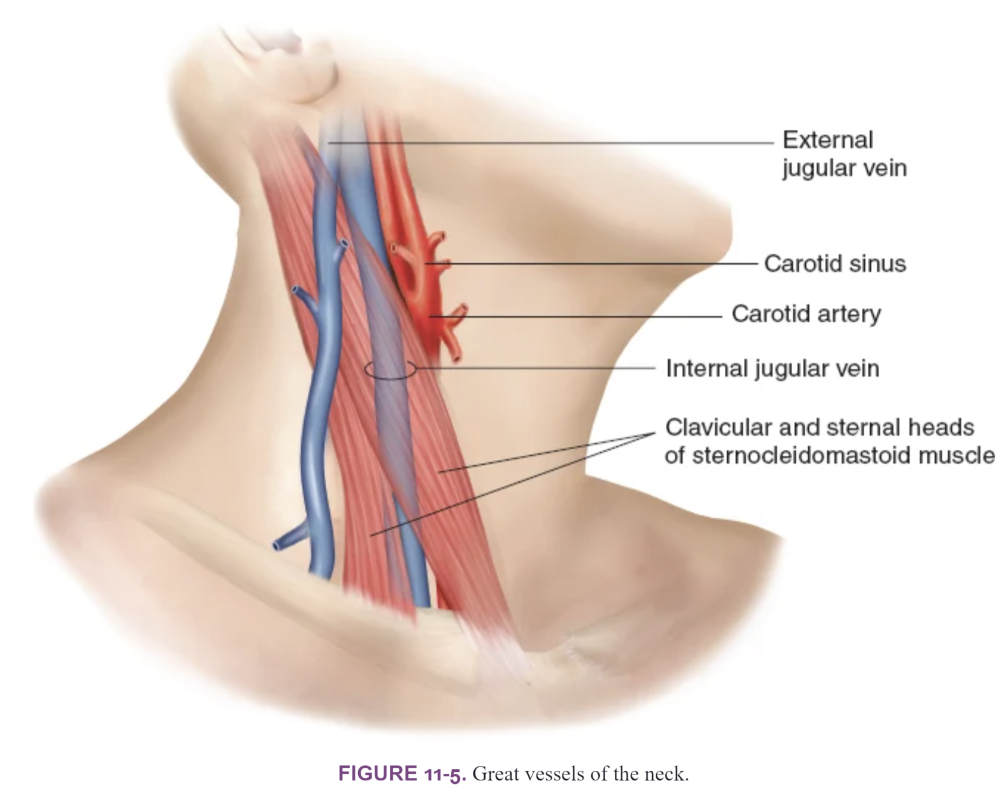 Great Vessels of the Neck
| back 12 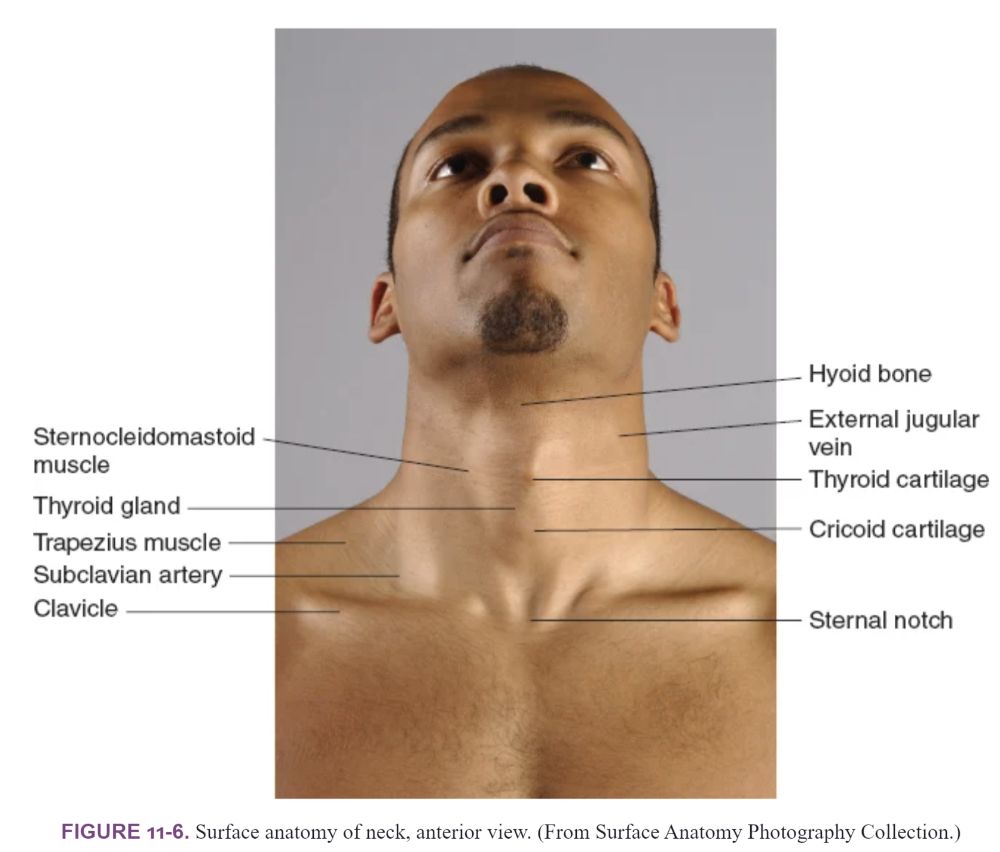 Midline structures of the neck
|
front 13 Midline structures of the neck | back 13 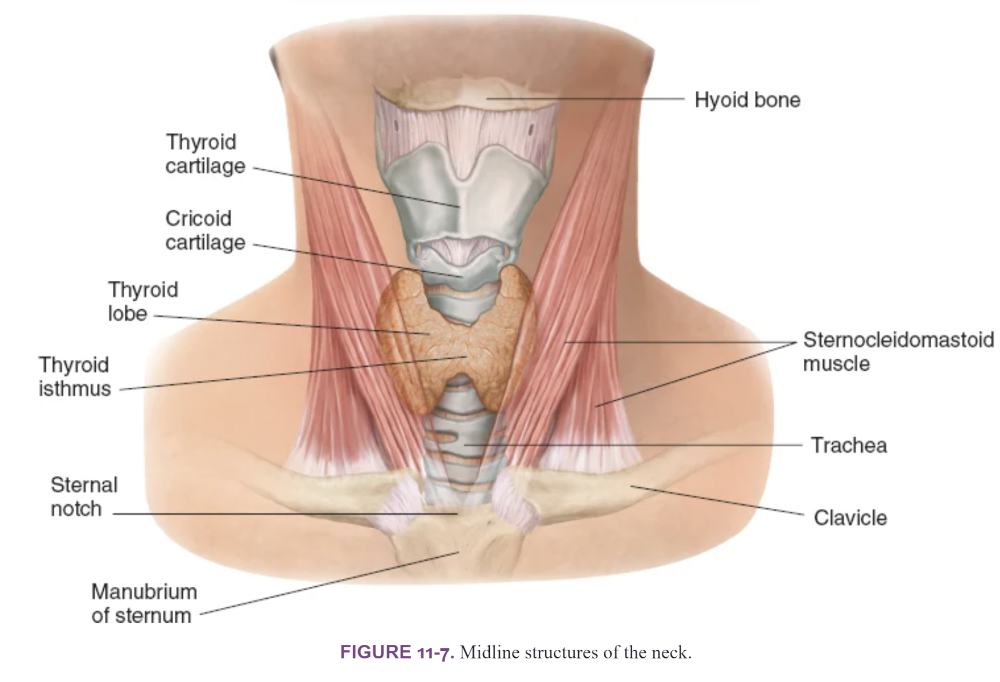 |
front 14 What is the best position for palpating the thyroid? | back 14
Posterior Approach
Anterior Approach
Thyroid gland is usually located above the suprasternal notch Note the size, shape, and consistency (soft, firm, or hard) of the gland and identify any nodules or tenderness |
front 15
| back 15
|
front 16
| back 16
|
front 17
| back 17  Strabismus
Dacryostenosis- blocked tear duct
Eye Turn in infants
|
front 18 What is Presbyopia? | back 18
|
front 19 What are the symptons of macular degeneration? | back 19
****think of the doctor from Virign River show*** |
front 20 What is clinical presentation of subconjunctival hemorrhage? | back 20
|
front 21 Be able to differentiate between the presentation of chalazion, hordeolum, blepharitis What is Chalazion? What is Hordeolum? | back 21 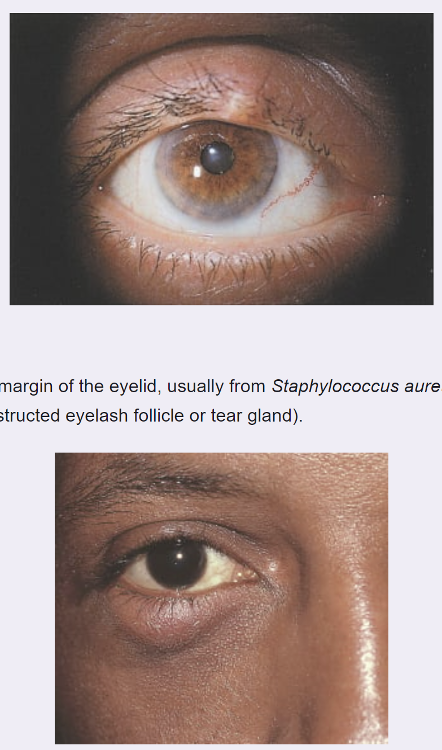 Hordeolum- Stye
Chalazion
|
front 22 What is presentation of blepharitis? | back 22 Blepharitis
Typical complaints are:
On examination, may see the following:
|
front 23 What is the clinical presentation of: Acute Bacterial conjunctivitis? | back 23 Bacterial
|
front 24 What is the clinical presentation of: Viral conjunctivitis? | back 24
|
front 25 What is the clinical presentation of: Allergic conjunctivitis? | back 25
|
front 26 What is the evaluation of conjunctivitis | back 26
|
front 27 What are RED FLAGS: Indicating serious eye issues | back 27 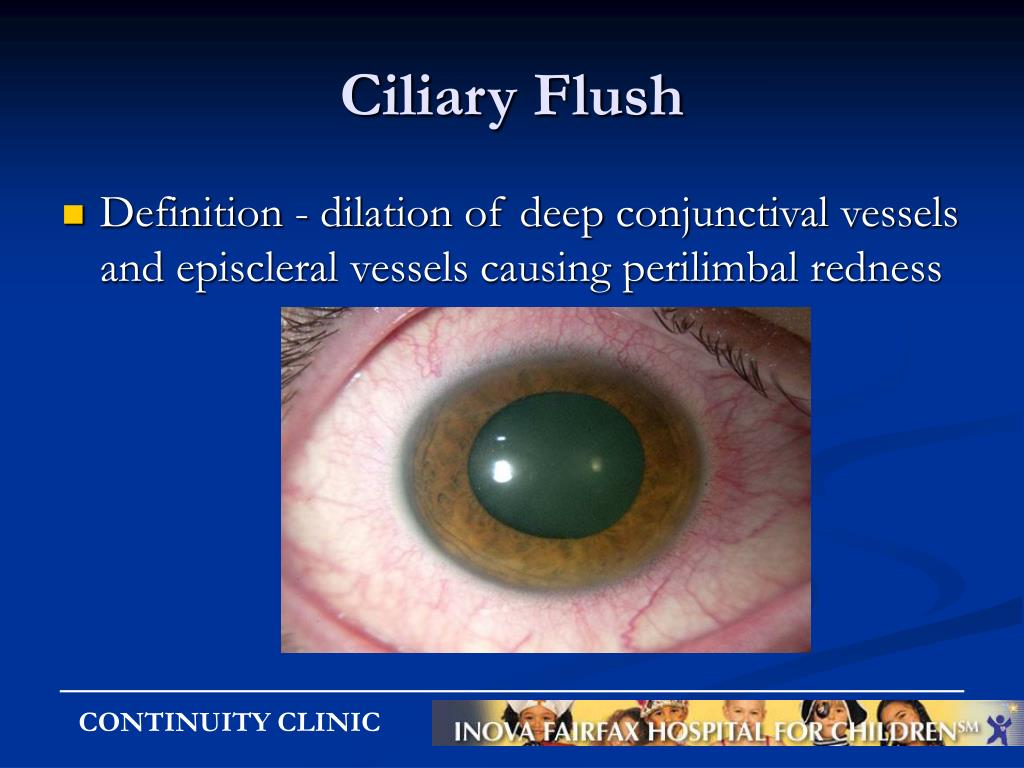 Important to distinguish conjunctivitis from other more serious conditions causing red eye (iritis, keratitis, acute angle closure glaucoma, foreign body). In conjunctivitis:
Red flag or warning signs that indicate a more serious ophthalmic
problem than
|
front 28 What is papilledema and what does it signify? | back 28
|
front 29 What are eye findings in Thyroid disease? | back 29
HypoT
HyperT
|
front 30 Eye findings for hyperlipidemia disorders What are findings that indicate hyperlipemia? | back 30 Xanthelasma
|
front 31 Presentation of a pterygium What are clinical findings of pterygium? | back 31 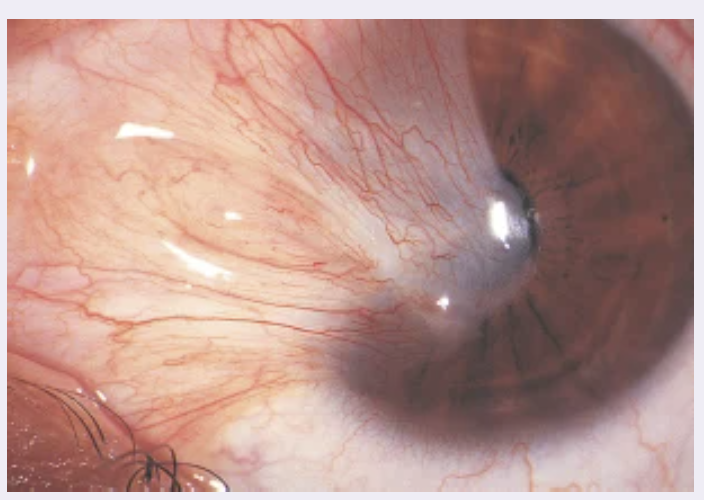
|
front 32 Presentation of presentation of a pinguecula What are clinical findings of pinguecula? | back 32 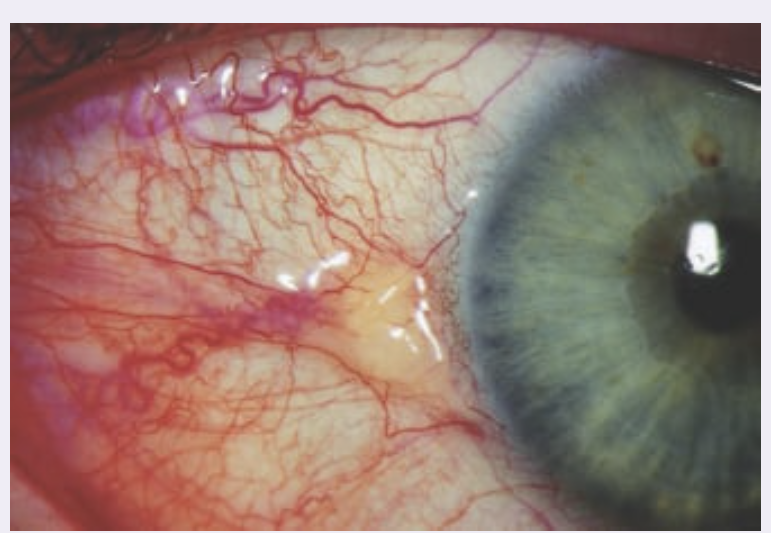
|
front 33 What are normal findings when checking for PERRLA | back 33 Pupils Equal, Round, Reactive to Light and Accommodation
|
front 34 What are clinical presentations of otitis externa? | back 34
Predisposing factors
Common pathogens
|
front 35 What is the presentation of otitis media with effusion? | back 35
Otoscopic findings
|
front 36 What is otitis media? What are clinical presentations of otitis media infection? | back 36
|
front 37 What is Cholesteatoma presentation? | back 37 Middle ear disorders Abnormal collection of skin cells deep inside your ear Complication of AOM |
front 38 What is Epistaxis? Common causes and management? | back 38
|
front 39 What is rhinitis medicamentosa? How do you avoid it? | back 39
|
front 40 What is the Weber test ? How and why do you perform it? | back 40
How to perform the test:
Results
|
front 41 What is the Rinne Test? How and Why do you perform it? | back 41 Compare air conduction (AC) and bone conduction (BC) How do you perform it?
Results
|
front 42 Difference in Conductive and Sensorineural loss? | back 42 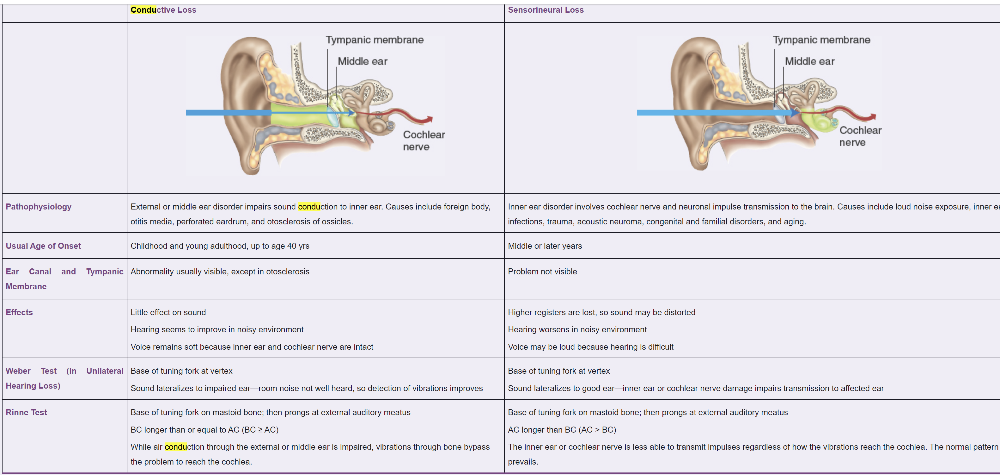
|
front 43 Presentation of acute bacterial sinusitus | back 43
Objective signs include:
|
front 44 Expected lab findings in mononucleosis? | back 44 Labs: Elevated LFTs, lymphocytosis |
front 45 What is clinical presentation of viral pharyngitis? | back 45
|
front 46 What is clinical presentation of strep throat? | back 46
|
front 47 What are guideline recommendations for oral health? | back 47
|