Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy and physiology Exam 1
front 1 Using the anatomical terminology presented in this video, how would you describe the location of a bruise on the front right lower leg? a) posterior, proximal to hip b) anterior, proximal to knee c)anterior, distal to knee d)posterior, distal to hip | back 1 c)anterior, distal to knee |
front 2 What directional term would be used to indicate sunburn on a patient’s back? a)distal b)posterior c)proximal d)anterior | back 2 b)posterior |
front 3 level of organization of the human body | back 3 1,Chemical level 2.Cellular level 3.Tissue level 4.Organ level 5.Organ system level 6.Organismal level |
front 4 Whats the order of the homeostasis | back 4 1, Stimulus 2. receptors 3. input 4, Control Center 5. Output 6. Effectors 7.Response |
front 5 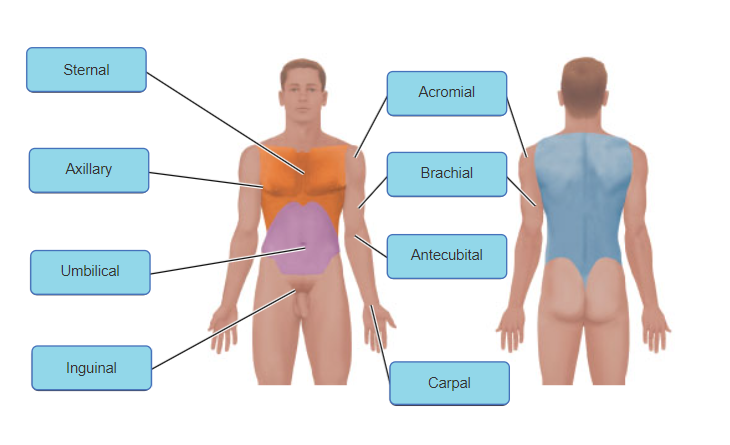 | back 5 no data |
front 6 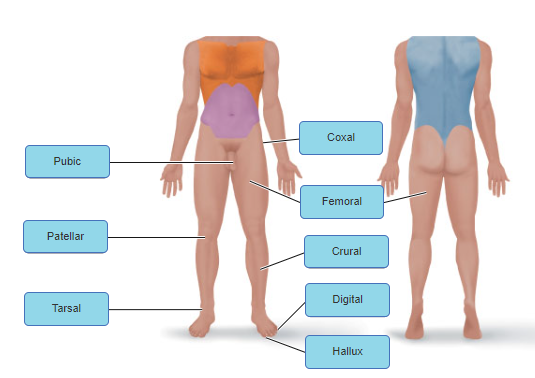 | back 6 no data |
front 7 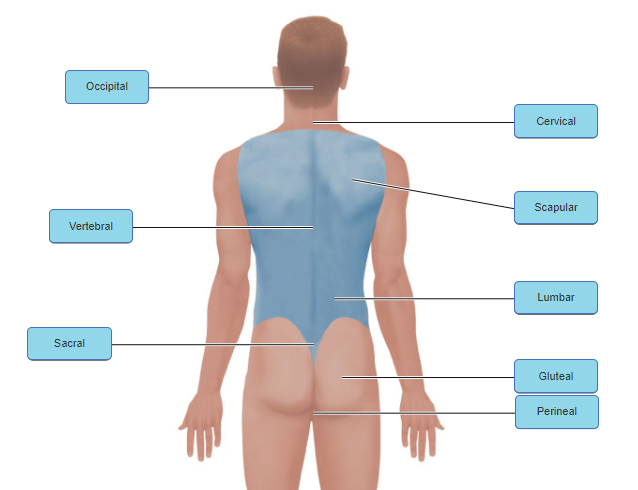 | back 7 no data |
front 8 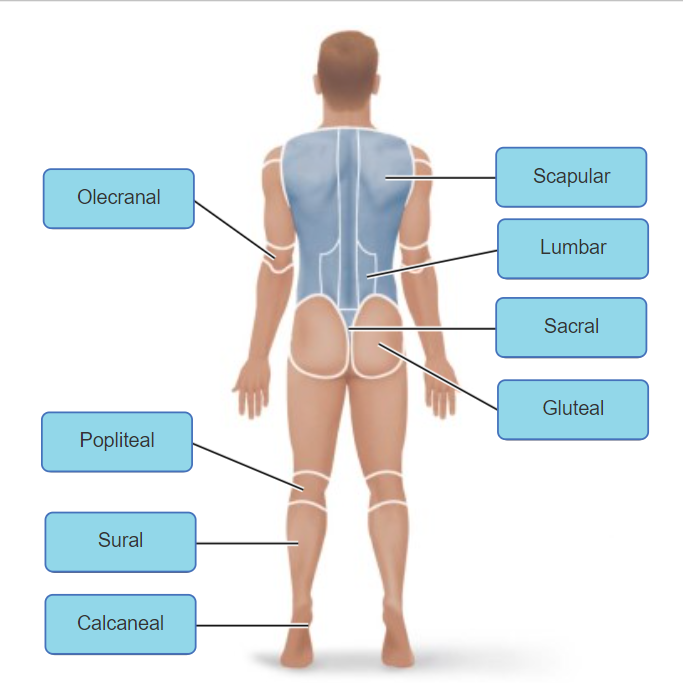 | back 8 no data |
front 9 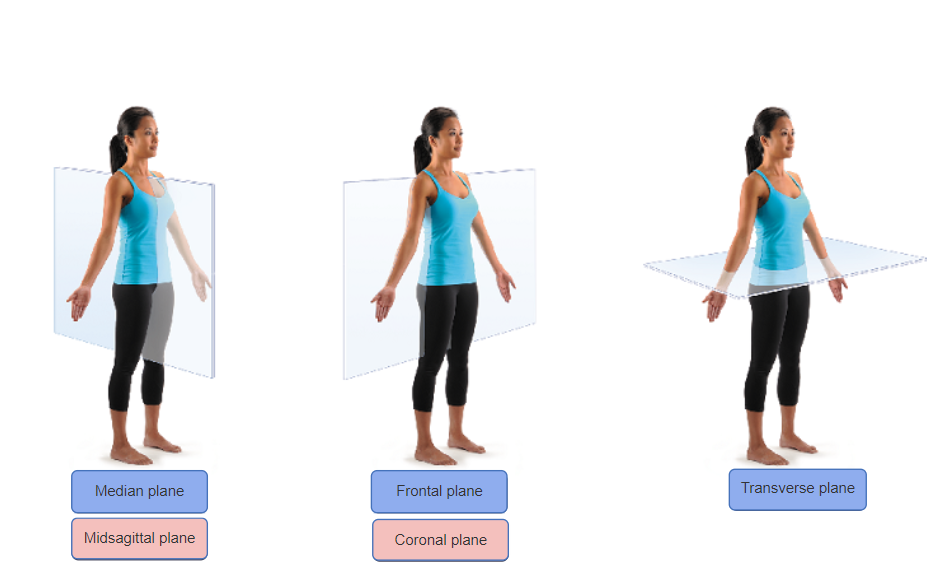 | back 9 no data |
front 10 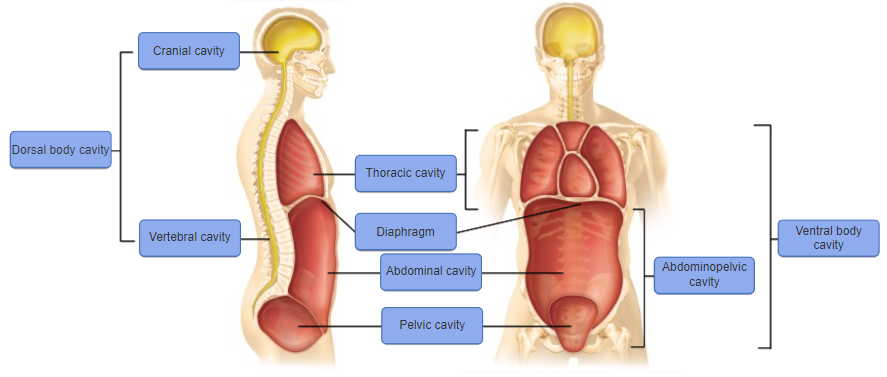 What is the role of the serous membranes covering some organs? a)to prevent friction between the organ and body cavity wall b)to provide passage of nutrients for the organ tissues c)to serve as extra tissue for blood flow to the organ d) to provide a protective outer covering for the organ | back 10 a)to prevent friction between the organ and body cavity wall |
front 11 What is the function of serous fluid? a)It prevents the organs from drying out when in contact with air. b)It aids in the repair of damaged organs. c)It helps the stomach and other organs maintain neutral buoyancy within body cavities, even during fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, or when gases, such as oxygen or methane, are present in varying ratios. d)It enables organs, such as the heart and the stomach, to slide across cavity walls and each other without friction. | back 11 d)It enables organs, such as the heart and the stomach, to slide across cavity walls and each other without friction. |
front 12 Which of the following organs is least likely to be damaged in an automobile accident? a)stomach b)intestines c)urinary bladder d)liver | back 12 c)urinary bladder |
front 13 medi- | back 13 The prefix means middle. |
front 14 micro- | back 14 The prefix micro- means abnormally small. |
front 15 hypo- | back 15 The prefix means under, beneath, or less than normal. |
front 16 trans- | back 16 The prefix means across, beyond, or through. |
front 17 phys- | back 17 The prefix means nature or physical. |
front 18 A body section that is cut across the body horizontally is | back 18 transverse section. |
front 19 The study of the cells in gastric pits is an example of | back 19 microscopic anatomy |
front 20 is the study of the nature of the body and how it functions. | back 20 Physiology |
front 21 The area where the heart is located is the ________ which lies between the two lungs. | back 21 mediastinum, |
front 22 Parents bring a toddler to the emergency department after she tripped and fell on the sidewalk. You note a submental laceration. As you evaluate this girl, you are most concerned about trauma to which other anatomic region? a)Occipital b)Otic c)Orbital d)Oral | back 22 d)Oral |
front 23 You have been asked to teach the principles of CPR to a group of teens training to be lifeguards. You use a diagram of the thoracic cavity to help you explain how chest compressions can maintain circulation. Which view of the chest would best illustrate this point? a)Sagittal b)Frontal c)Transverse d)Oblique | back 23 a)Sagittal |
front 24 Choose the anatomical topic and definition that is NOT correctly matched. a)Cytology: study of the structures in a particular region. b)Embryology: study of the changes in an individual from conception to birth. c)Microscopic anatomy: study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. d)Gross anatomy: study of structures visible to the eye. | back 24 a)Cytology: study of the structures in a particular region. |
front 25 Which of the following represents the correct order in which the components interact in a homeostatic control system? a)the variable, the receptor, and the set point b)the receptor, the control center, and the effector c)the effector, the stimulus, and the receptor d)the receptor, the stimulus, and the effector | back 25 b)the receptor, the control center, and the effector |
front 26 The knee is proximal to the thigh. True False | back 26 False |
front 27 A coronal section divides an organ into superior and inferior portions. True False | back 27 False |
front 28 The dorsal body cavity is divided into which of the following subdivisions? a)the vertebral/spinal and cranial cavities b)the thoracic, pleural, and abdominopelvic cavities c)the vertebral/spinal and thoracic cavities d)the vertebral/spinal, cranial, and pleural cavities | back 28 a)the vertebral/spinal and cranial cavities |
front 29 Which of the following best defines anatomy? a) It is the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships with one another. b)It is the study of tissues. c)It is the study of how the body parts work and carry out their life-sustaining activities. d)It is the study of all chemical reactions that occur within body cells. | back 29 a) It is the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships with one another. |
front 30 Which subdivision of anatomy would include the study of individual cells? a)gross anatomy b)systemic anatomy c)microscopic anatomy d)developmental anatomy | back 30 c)microscopic anatomy |
front 31 Which of the following statements most accurately describes the complementarity of anatomy and physiology? a) Anatomy can be described only by the underlying physiology. b) Anatomy describes the form of the body, which is more concrete than physiology because we can see anatomical structure. c) Physiology is more concrete than anatomy, because it describes structures that can be seen. d) Functions occur because of the anatomy that exists within the body. | back 31 d) Functions occur because of the anatomy that exists within the body. |
front 32 Brachial | back 32 Arm. |
front 33 Gluteal | back 33 Buttock. |
front 34 Cephalic | back 34 Head. |
front 35 Patellar | back 35 Knee (anterior aspect). |
front 36 Thoracic | back 36 Chest. |
front 37 The anatomical position is characterized by all of the following EXCEPT ________. a) body erect b)arms at sides c)palms turned posteriorly d) thumbs pointed laterally | back 37 c) palms turned posteriorly |
front 38 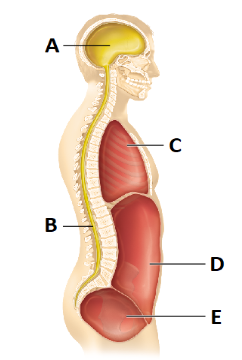 Which of the following is a correct pairing of a body cavity with its contents? a) The cavity at D contains the urinary bladder. b) The cavity at C contains the lungs. c) The cavity at E contains most of the digestive organs. d) The cavity at D contains the reproductive organs | back 38 b) The cavity at C contains the lungs. |
front 39 In which body cavities are the lungs located? a) pleural, dorsal, and abdominal b) pleural, ventral, and thoracic c) pericardial, ventral, and thoracic d) mediastinal, thoracic, and ventral | back 39 b) pleural, ventral, and thoracic |
front 40 Choose the following statement that is NOT completely correct regarding serous membranes. a)Serous membranes secrete a watery lubricating fluid. b) Visceral pericardium covers the outer surface of the heart, and parietal pericardium lines the internal walls of the heart. c) Serosa are very thin, double-layered structures. d) Serous membranes are divided into parietal and visceral membranes with a virtual space between the two. | back 40 b) Visceral pericardium covers the outer surface of the heart, and parietal pericardium lines the internal walls of the heart. |
front 41 Which of these is NOT part of the dorsal cavity? a) thoracic cavity b)spinal cord c) cranial cavity d) vertebral cavity | back 41 a) thoracic cavity |
front 42 The dorsal body cavity is the site of which of the following? a) liver b) intestines c) lungs d) brain | back 42 d) brain |
front 43 Which of the following statements is correct? a) The sternum is posterior to the spine. b) The heart is dorsal to the sternum. c) The heart is posterior to the spine. d) The sternum is dorsal to the spine. | back 43 b) The heart is dorsal to the sternum. |
front 44 Which of the following is the best explanation for why cells are considered the smallest units of living things. a) Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye and are considered microscopic. b) Cells are highly ordered and complex. c) Cells are the simplest structure to fit all of the characteristics necessary to be considered alive. d) Cells have the ability to reproduce identical copies of themselves in a process called mitosis. | back 44 c) Cells are the simplest structure to fit all of the characteristics necessary to be considered alive. |
front 45 Which life process generates the raw materials and energy needed to sustain all other life processes? a)responsiveness b)reproduction c) metabolism d) movement | back 45 c) metabolism |
front 46 Which of the following regional anatomy terms matches the anatomical description "anterior and most distal?" a) femoral b) popliteal c) crural d) metatarsal | back 46 d) metatarsal |
front 47 You are asked to take a person's heart rate at the popliteal pulse point. You will look for this pulse ________. a) on the palmar side of the hand b) on the posterior side of the knee c) at the posterior side of the wrist d) in the distal end of the lower leg | back 47 b) on the posterior side of the knee |
front 48 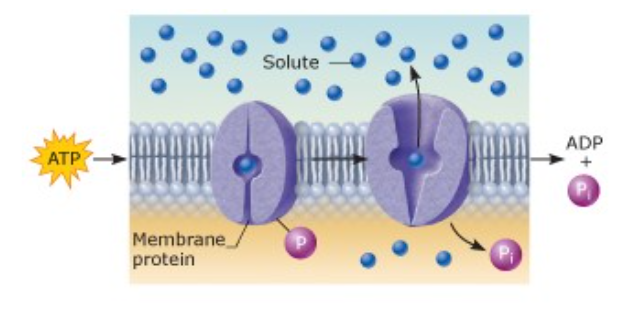 | back 48 Transport work |
front 49 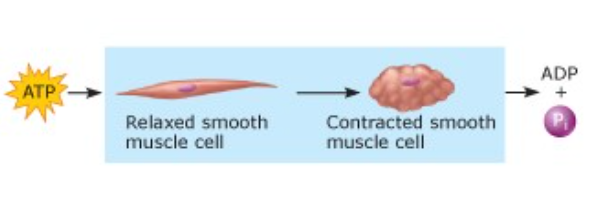 | back 49 Mechanical work |
front 50 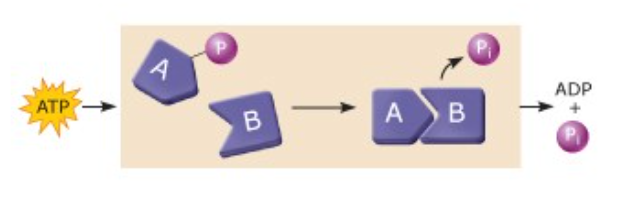 | back 50 Chemical work |
front 51 In a solution, the solute is the substance present in the greatest amount. True False | back 51 False |
front 52 All salts are ionic compounds, but not all ionic compounds are salts. True False | back 52 True |
front 53 The pH scale __________. a) is based on the salinity of a solution b) is based on the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution c)is linear d) ranges from 1 to 7 | back 53 b) is based on the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution |
front 54 What is the classification of a solution of NaOH with a pH of 8.3? a) acidic solution b) neutral solution c)buffered solution d) alkaline solution | back 54 d) alkaline solution |
front 55 The prefix co- | back 55 means with, together, or shared. |
front 56 The prefix an- | back 56 means not, without, or upward. |
front 57 The prefix hydr- | back 57 means water, hydrogen, or accumulation of fluid. |
front 58 The prefix poly- | back 58 means many, several, or polymer. |
front 59 The prefix ex- | back 59 means out of or away from. |
front 60 The process of building up large molecules from small components is a(n) | back 60 anabolic process. |
front 61 A lipid with four sites lacking hydrogen saturation is a | back 61 polyunsaturated lipid. |
front 62 A bond in which valence electrons are shared is called | back 62 covalent. |
front 63 If energy is released when a molecule is broken apart, it is a(n) | back 63 exergonic reaction. |
front 64 ____________ is the process of breaking large molecules into smaller ones by adding water. | back 64 Hydrolysis |
front 65 The husband of a patient who is critically ill asks, "Why do they keep checking my wife's pH? Isn't knowing her oxygen level enough?" What is the best response? a) "We want to make sure that she isn't running out of buffers to keep her pH just right." b) "Yes, her oxygen levels are what's most important, but the lab always sends up all those numbers as a set." c)"Many of her body's systems only work properly when her pH is within a narrow range, so we monitor it carefully." d) "As long as her oxygen levels are good, her pH really isn't that important." | back 65 c)"Many of her body's systems only work properly when her pH is within a narrow range, so we monitor it carefully." |
front 66 Which four elements comprise approximately 96% of our body weight? a) carbon, oxygen, iron, and potassium b) carbon, oxygen, potassium, and sodium. c) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and potassium. d) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. | back 66 d) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. |
front 67 Water is an important molecule because it __________. a) can form hydrogen bonds b) has a low heat capacity c) is non-polar d) is a poor solvent since few things dissolve in it | back 67 a) can form hydrogen bonds |
front 68 ATP is an unstable, high-energy molecule that provides body cells with a form of energy that is immediately usable. True False | back 68 True |
front 69 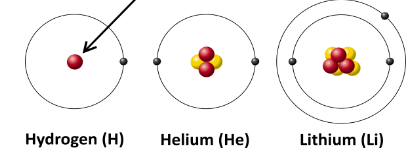 Which particle is indicated by the arrow? b) proton c) electron d) neutron | back 69 b) proton |
front 70  The three atoms shown represent three unique __________. b)elements c) molecules d) cells | back 70 b)elements |
front 71 Negatively charged subatomic particle. | back 71 Electron |
front 72 Neutral subatomic particle. | back 72 Neutron |
front 73 Smallest particle of an element that retains its properties. | back 73 Atom |
front 74 Positively charged subatomic particle. | back 74 Proton |
front 75 Subatomic particle having an AMU (Atomic Mass Unit) of zero. | back 75 Electron |
front 76 Which of the following is not a compound? a) water b)carbon dioxide c) oxygen gas d) methane (natural gas) | back 76 c) oxygen gas |
front 77 Which of the following statements is FALSE? a) The pH of blood is slightly basic. b) The more hydrogen ions in a solution, the more acidic the solution. c) When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases. d) When acids and bases are mixed, they react with each other to form water and a salt. | back 77 c) When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases. |
front 78 A charged particle is generally called an ion or electrolyte. True False | back 78 True |
front 79 The lower the pH, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration. True False | back 79 True |
front 80 Which of the following does NOT describe uses for the ATP molecule? a) mechanical work b) transport down their concentration gradient c)chemical work d) pigment structure | back 80 d) pigment structure |
front 81 How many phosphates would ADP have attached to it? a)one b)threen c)one d) two | back 81 d) two |
front 82 water is a | back 82 compound |
front 83 saline is a | back 83 solution |
front 84 Dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide ) is a | back 84 compound |
front 85 Blood is a | back 85 Suspension |
front 86 Which of the following is not a fundamental subatomic particle that forms elements? a) neutrons b) electrons c) nucleus d)protons | back 86 c) nucleus |
front 87 Which of the following is NOT a subatomic particle? a) neutron b) proton c) electron d) molecule | back 87 d) molecule |
front 88 The four elements that make up about 96% of body weight are ________. a) nitrogen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium b) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, calcium c) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen d) sodium, potassium, hydrogen, oxygen | back 88 c) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen |
front 89 What does CH4 mean? a) There is one carbon and four hydrogen atoms. b) This was involved in a redox reaction. c) There are four carbon and four hydrogen atoms. d) This is an inorganic molecule. | back 89 a) There is one carbon and four hydrogen atoms. |
front 90 What is the primary energy-transferring molecule in cells? a) Carbohydrates b) ATP c) RNA d) DNA | back 90 b) ATP |
front 91 An acid with a pH of 6 has ________ hydrogen ions than pure water. a) 100-fold fewer b) 100-fold more c) 10-fold fewer d) 10-fold more | back 91 d) 10-fold more |
front 92 Which response provides the best explanation as to why ionic compounds easily dissociate in water? a) The polarity of water allows it to easily dissociate most covalently bound compounds. b) The polarity of water easily breaks the charges between the oppositely charged ions in the compound. c) Nonpolar organic molecules such as fats and waxes dissolve well in water. d) As a polar molecule, water cannot easily dissociate inorganic compounds. | back 92 b) The polarity of water easily breaks the charges between the oppositely charged ions in the compound. |
front 93 Which of the following is the main component of the cell membrane? a)carbohydrates b) water c) phospholipids d)cholesterol | back 93 c) phospholipids |
front 94 Which of the following is a characteristic of the cell membrane? a) not permeable b) fully permeable c) semipermeable d) impermeable | back 94 c) semipermeable |
front 95 Which of the following is not a major function of proteins in the cell membrane? a) forming the entire glycocalyx b) acting as receptors c)forming channels d) anchoring cells to other structures | back 95 a) forming the entire glycocalyx |
front 96 What part of a cell membrane is usually in contact with the interstitial fluid? a) fatty acid tails b) cholesterol c) phosphate heads of phospholipids d) hydrophobic molecules | back 96 c) phosphate heads of phospholipids |
front 97 Which of the following best explains diffusion? a) movement of molecules from where there are fewer of them to where there are more b) exchange of nonpolar molecules for polar molecules c) movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration d) movement of molecules farther away from equilibrium | back 97 c) movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
front 98 Which of the following is most likely to move through the cell membrane by facilitated diffusion? a) CO2 b) small lipids c) O2 d) Na+ | back 98 d) Na+ |
front 99 What is the basic difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion across a cell membrane? a) In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein in the membrane. b) In simple diffusion, molecules move down the concentration gradient but in facilitated diffusion molecules move up the concentration gradient. c) Simple diffusion requires molecules to move through special doorways in the cell membrane. d) Simple diffusion is passive but facilitated diffusion is an active process that uses energy. | back 99 a) In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein in the membrane. |
front 100 Which of the following is least likely to increase the rate of diffusion? a) high temperature b) higher concentration of molecules c) small molecule size d)small concentration gradient | back 100 d)small concentration gradient |
front 101 Which of the following is not required for osmosis to occur? a) water b) cellular energy c) concentration gradient d) selectively permeable membrane | back 101 b) cellular energy |
front 102 Which of the following solutions contains the most solute? a) isotonic b) hypotonic c) equilibrium d) hypertonic | back 102 d) hypertonic |
front 103 In general, to maintain homeostasis the relationship between our intracellular and extracellular fluids should be which of the following? a) intracellular and extracellular should both be hypertonic b) intracellular should be hypotonic to extracellular c) isotonic to each other d) intracellular should be hypertonic to extracellular | back 103 c) isotonic to each other |
front 104 If a person is severely dehydrated, their extracellular fluids will become hypertonic to the intracellular fluid. What do you predict will happen to the person’s cells? a) Extracellular fluids do not impact cell size, because cells contain intracellular fluid b) The cells will lose water and shrink. c) The cells will rupture. d) The cells will swell. | back 104 b) .The cells will lose water and shrink. |
front 105 Active process includes ? | back 105 - Primary active transport - Secondary active transport - Endocytosis - Exocytosis |
front 106 Passive Process include ? | back 106 - Simple diffusion - Facilitated Diffusion - oSmosi |
front 107 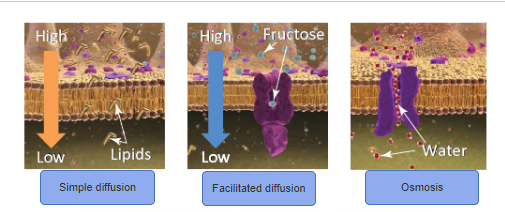 | back 107 no data |
front 108 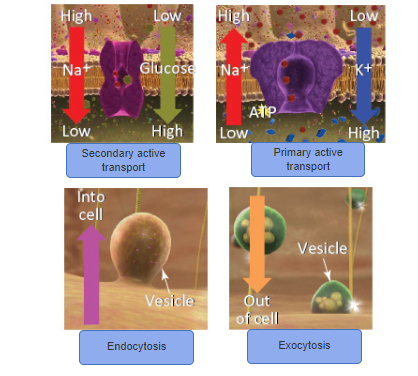 | back 108 no data |
front 109 Which of the following is characteristic of cilia? a) They increase the surface area of absorptive cells in the kidneys and intestines. b) They are substantially longer than flagella, and are less common than flagella in humans. c) They are used for cellular adhesion. d) They are whiplike, motile cellular extensions that occur in large numbers on the exposed surfaces of certain cells. | back 109 d) They are whiplike, motile cellular extensions that occur in large numbers on the exposed surfaces of certain cells. |
front 110 What is a membrane potential? a) the types of integral membrane proteins associated with a particular cell membrane b) cooperation between cells involving membrane interactions c) a voltage or electrical charge across the plasma membrane d) the possibility of a membrane based cell activity | back 110 c) a voltage or electrical charge across the plasma membrane |
front 111 Drinking alcohol can cause dehydration, which makes the blood hypertonic. Which option best describes the consequences of this hypertonic blood? a) Hypertonic blood draws water out of the interstitial fluid, which makes the interstitial fluid hypertonic. This, in turn, draws water out of the cells. b) Hypertonic blood forces water into the interstitial fluid, which makes the interstitial fluid hypotonic. This, in turn, makes the interstitial fluid lose water to the cells. c) Hypertonic blood draws water out of the interstitial fluid, which makes the interstitial fluid hypotonic. This, in turn, makes the interstitial fluid lose water to the cells. d) Hypertonic blood will lose water to the interstitial fluid, which makes the interstitial fluid hypertonic. This, in turn, causes water to move into the cells. | back 111 a) Hypertonic blood draws water out of the interstitial fluid, which makes the interstitial fluid hypertonic. This, in turn, draws water out of the cells. |
front 112 The prefix cyto- means | back 112 cell. |
front 113 The prefix endo- means | back 113 inside, taking in, or within. |
front 114 The prefix nucle- means | back 114 nucleus or nuclear. |
front 115 The prefix anti- means | back 115 against or opposite. |
front 116 The prefix glyco- means | back 116 sugar. |
front 117 The prefix auto- means | back 117 self or self-acting. |
front 118 is the process of bringing substances into a cell. | back 118 Endocytosis |
front 119 The process during which a cell eats itself is referred to as | back 119 autophagy. |
front 120 A molecule made primarily of amino acids with carbohydrate side chains would be described as a | back 120 glycoprotein. |
front 121 Small structures in the nucleus of cells responsible for producing ribosomal subunits are called | back 121 nucleoli. |
front 122 The sequence on tRNA that is opposite to the codon on mRNA is the | back 122 anticodon. |
front 123 The structural framework of a cell is the | back 123 cytoskeleton |
front 124 Two genetic diseases, Hunter and Hurler syndromes, are caused by an inability of cells to break down and recycle mucopolysaccharides, which are substances found in the extracellular areas of the body. Which organelle is responsible for performing this function in normal cells? a) Endoplasmic reticulum b) Mitochondria c) Lysosomes d) Golgi apparatus | back 124 c) Lysosomes |
front 125 You are explaining the causes of smoker's cough to a client, including altered function of the cilia in the lining of large respiratory passages. Which of these is true? a) Toxins in cigarette smoke irritate nerves under the cilia, causing a cough. b) Smoking damages the cilia, rendering them unable to sweep mucus out of the respiratory passages, resulting in coughing. c) Cigarette smoke causes an overgrowth of cilia, leading to cough. d) Smoking causes the cilia to produce more mucus, resulting in coughing. | back 125 b) Smoking damages the cilia, rendering them unable to sweep mucus out of the respiratory passages, resulting in coughing. |
front 126 On your first pediatrics rotation you meet a young boy diagnosed with a mitochondrial disorder. Which of these would most likely be symptoms of his disorder? a) Digestive problems b) All of the choices are correct. c) Seizures d) Muscle weakness | back 126 b) All of the choices are correct. |
front 127 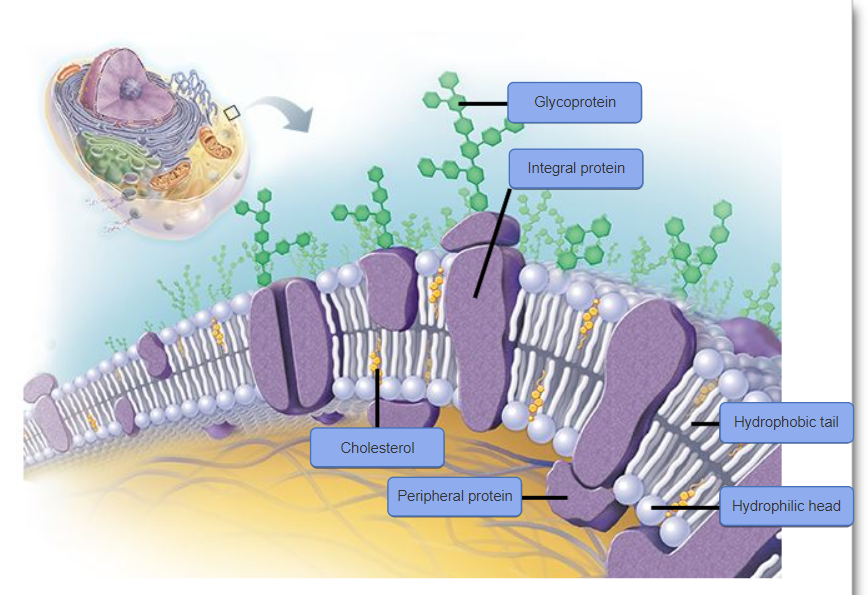 | back 127 no data |
front 128 Which component of the plasma membrane might allow the body to recognize cells as “self” (its own) or “non-self” (foreign)? a)Cholesterol b) Phospholipid c) Protein d) Carbohydrate | back 128 d) Carbohydrate |
front 129 In this course, you will learn about hormones and their effects on cells. Certain hormones bind to receptors at the plasma membrane to “deliver” their message to the cell. What function of the plasma membrane is this? a) Cell-to-cell recognition b) Physical barrier c) Communication d) Selectively permeable | back 129 c) Communication |