Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Module 3: Terminology
front 1 Diaphoresis | back 1 excessive sweating usually due to a secondary condition - common causes include: menopause, hyperthyroidism, and types of medications |
front 2 Scoliosis | back 2 a deviation in the lateral curvature of the spine; curved spine |
front 3 Kyphosis | back 3 increase in the thoracic curvature of the spine; hunchback |
front 4 Epiphyses | back 4 the ends of long bones; made of cancellous bone |
front 5 lordosis | back 5 exaggerated curvature of the lumbar spine; sway back |
front 6 Osteoporosis | back 6 is the significant loss of bone mass and strength w/ an increased risk for fracture |
front 7 Flat bones | back 7 include the sternum; main function is to provide vital organ protection |
front 8 clonus | back 8 a rhythmic contraction of the muscle; occurs when the ankle is dorsiflexed or the wrist is extended |
front 9 Fasciculations | back 9 involuntary twitching of muscle fibers groups |
front 10 Contractures | back 10 are prolonged tightening of muscle groups |
front 11 effusion | back 11 the pathologic escape of body fluid; the college iron of excessive fluid within the capsule of a joint |
front 12 Tonus | back 12 state of readiness for muscles; produced by maintenance of some of the muscle fibers in a contracted state |
front 13 Spasticity | back 13 a muscle with greater-than-normal tone |
front 14 Atony | back 14 soft and flabby muscle tone |
front 15 Flaccidity | back 15 a muscle that is limp and without tone |
front 16 Bone Densitometry | back 16 used to detect bone density and can be used to assess the risk of fractures in osteoporosis |
front 17 Arthrography | back 17 used to detect acute or chronic tears of joint capsule or supporting ligaments |
front 18 Bone scans | back 18 used to detect metastatic and primary bone tumors, osteomyelitis, certain fractures, and aseptic necrosis |
front 19 Athroscopy | back 19 used to visualize a joint |
front 20 Telangiectasias | back 20 consist of red marks on the skin caused by the stretching of superficial blood vessels |
front 21 Ecchymosis | back 21 aka bruises |
front 22 purpura | back 22 consist of pinpoint hemorrhages into the skin |
front 23 Urticariais | back 23 aka wheals or hives |
front 24 Cherry angiomas | back 24 appear as bright red "moles"; common in the elderly, usually benign |
front 25 solar lentigo | back 25 aka "liver spots" |
front 26 Seborrheickeratoses | back 26 described as crusty brown "stuck on" patches |
front 27 Xanthelasma | back 27 appears as yellowish, waxy deposits on the upper eyelids |
front 28 Macules | back 28 is a flat, non palpable skin color change |
front 29 papule | back 29 is an elevated, solid, palpable mass |
front 30 vesicle | back 30 circumscribed, elevated, palpable mass containing serous fluid |
front 31 pustule | back 31 a puss-filled vescicle |
front 32 Addison's disease | back 32 patient will exhibit a bronze discoloration to their skin due to increased melanin production |
front 33 Nodule | back 33 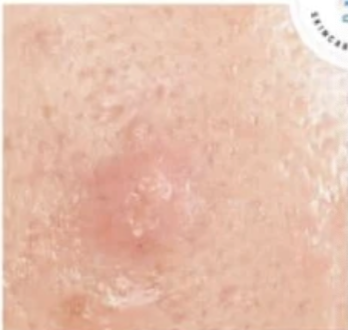 - a growth of abnormal tissue; can develop just below the skin, develop in deeper skin tissues, or internal organs - a solid skin lesion more than 1 cm and usually involve deeper layers of skin |
front 34 wheal (weal) | back 34 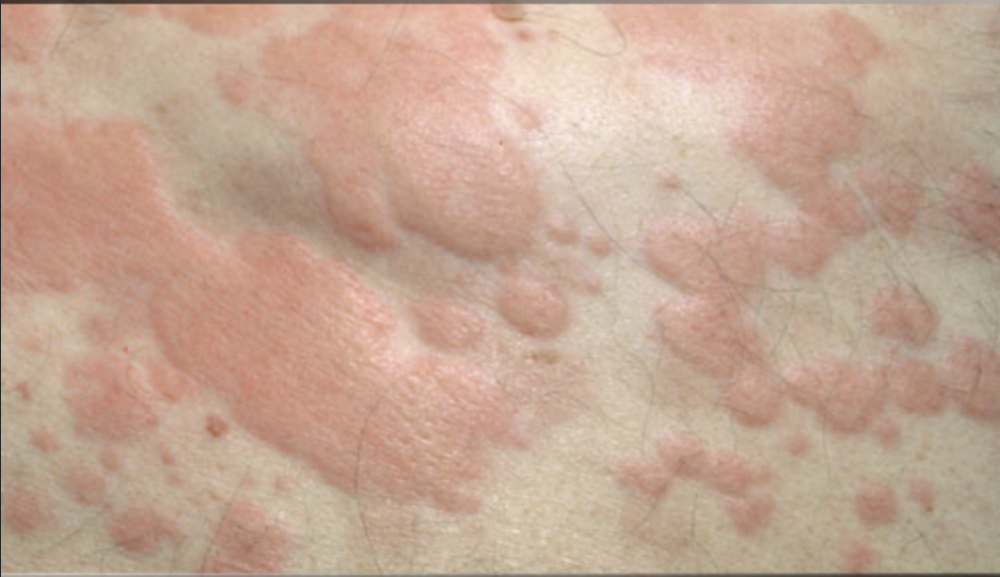 aka hives; superficial skin-colored or pale skin sweeping, usually surrounded by erythema |
front 35 vesicle | back 35 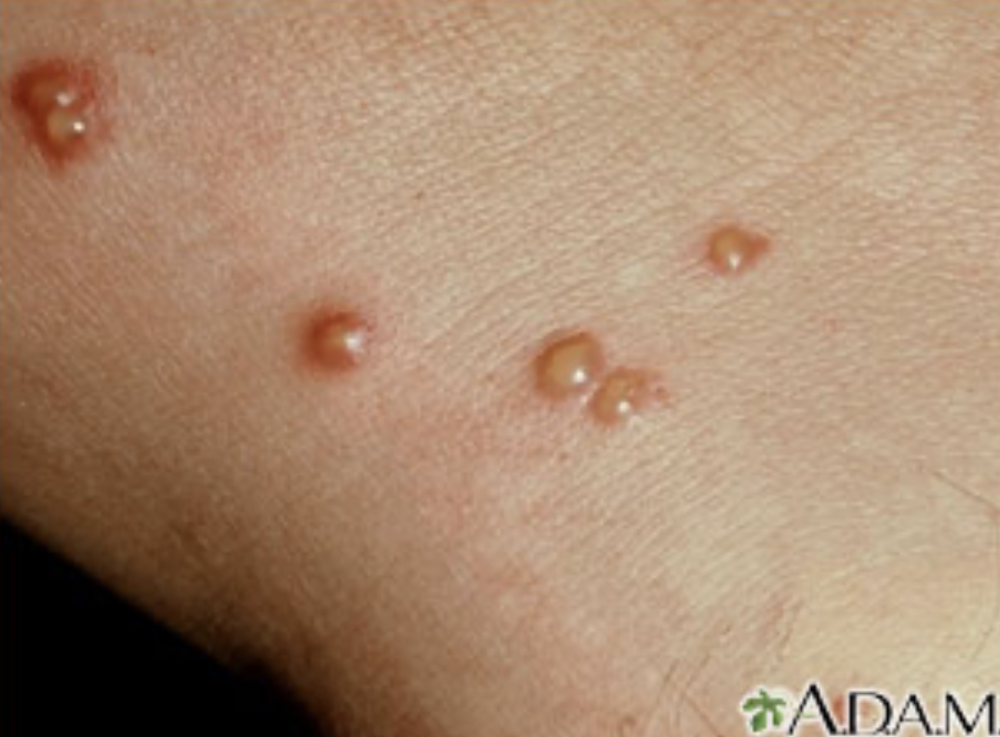 - break easily and release fluid onto the skin - is small, no more than 5 millimeters wide (if larger its called a bulla) aka blister |
front 36 Skin lesion | back 36 any area of skin that's abnormal from the skin around it; are very common and often the result of damage to the skin (ex: injury) - very general (literally all others term fit under this umbrella term) |
front 37 excoriation disorder | back 37 aka skin picking disorder or dermatillomania main sign = can't stop picking skin |
front 38 keloid | back 38 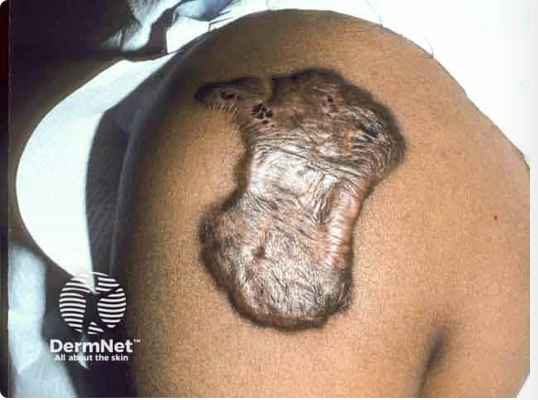 type of scar; is a smooth, hard growth that occurs as a result of excessive scar formation |
front 39 exudate | back 39 is any fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound |
front 40 pallor | back 40 - is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock, stress, stimulant use, or anemia - check lips, lining of eyes, palms of hands, inside of mouth, and surface of tongue is pallor is suspected on patients with darker skin |
front 41 petechiae | back 41 are round freckle-like spots that appear on the skin; occur due to bleeding from the capillaries that attached arteries to the veins - may look like a rash and are red, brown, or purple |
front 42 cyanosis | back 42 bluish tone to the skin, lips, or nails; occurs when the blood lacks oxygen |
front 43 nosocomial | back 43 a hospital-acquired infection |
front 44 purulent | back 44 consisting of, containing, or discharging pus |
front 45 serous | back 45 any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent; of a benign nature |
front 46 jaundice | back 46 condition where the skin, sclera, and mucous membranes (inside of nose and mouth) turn yellow |
front 47 pustule | back 47 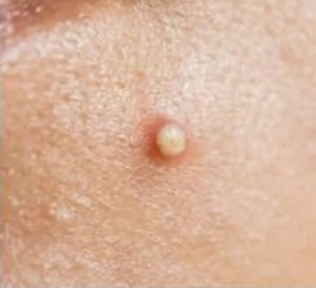 a small blister or pimple on the skin containing pus (<1 cm) |
front 48 turgor | back 48 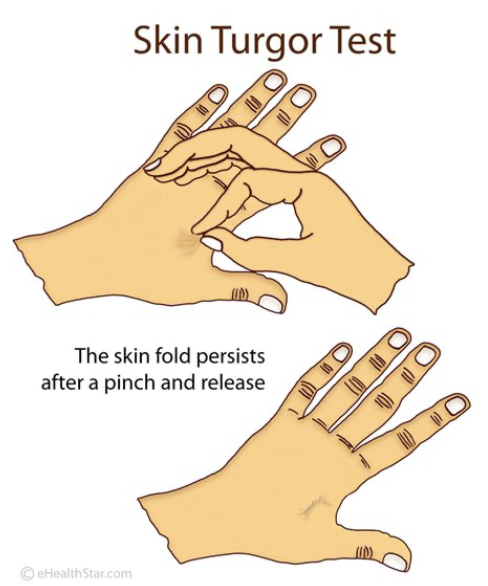 the state of turgidity and resulting rigidity of cells or tissues, typically due to the absorption of fluid - can be sign of hydration |
front 49 serosanguineous | back 49 means contains or relates to both blood and the liquid part of blood (serum) |
front 50 fissure | back 50 is small tear in the skin |
front 51 edema | back 51 is swelling caused by too much fluid trapped in the body's tissues; can affect any part of the body but is most likely to show up in the legs and feet |
front 52 sanguineous | back 52 fluid that resembles or contains blood |
front 53 ulcer | back 53 are injuries to the skin and tissue below the skin that are due to pressure on the skin for a long time; usually found over a bony prominence |
front 54 erythema | back 54 superficial Redding of the skin, usually in patches, as a result of injury or irrational causing dilation of the blood capillaries |
front 55 crepitus | back 55 grating/cracking sound or sensation act a point of motion; usually a sign of a fracture |
front 56 supination | back 56 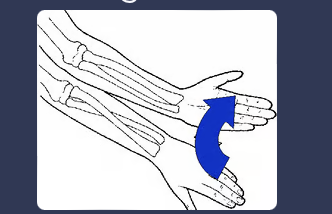 rotation of the forearm and hand so that the palm faces forward or upward |
front 57 abduction | back 57 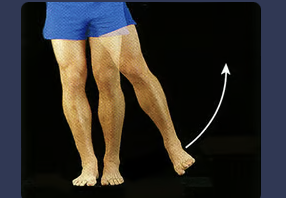 movement of a body part away from the main axis |
front 58 pronation | back 58 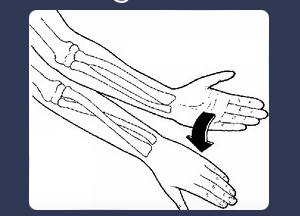 rotation of the hand and forearm so that the palm faces backwards or downwards |
front 59 adduction | back 59 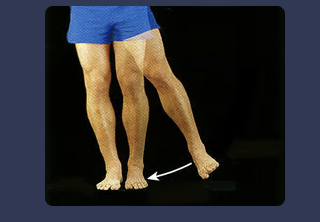 movement of a body part toward the main axis |
front 60 hemiparesis | back 60 is one-sided muscle weakness |
front 61 inversion | back 61 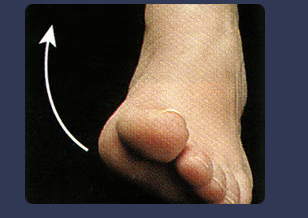 the condition of being turned inward; refers to the medial rotation of the foot frequently leading to a sprained ankle |
front 62 circumduction | back 62 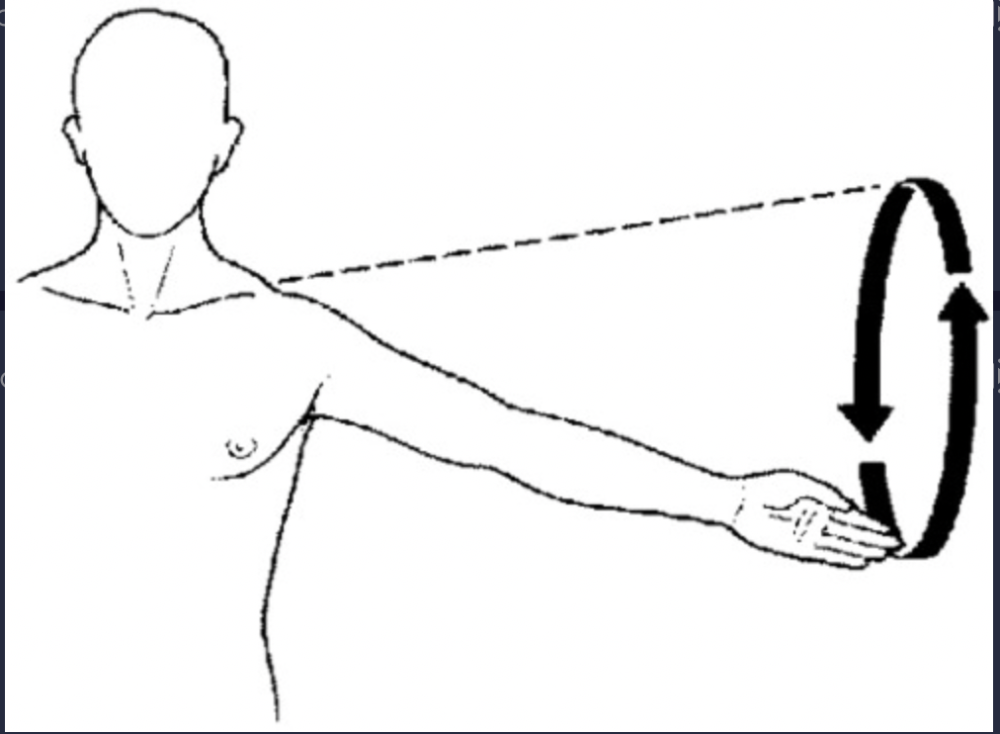 circular movement of a body segment, such as a limb |
front 63 hemiplegia | back 63 paralysis of one side of the body (either the right or left side of the body); can be temporary or permanent |
front 64 flexion | back 64 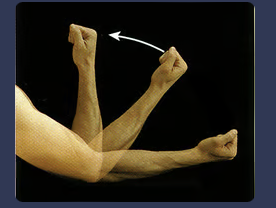 movement that decreases the angle of a joint |
front 65 eversion | back 65 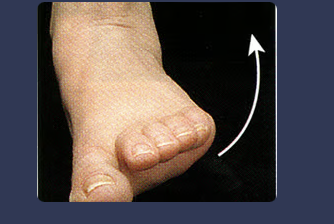 lateral rotation of the foot; the act of turning inside out |
front 66 paralysis | back 66 the loss of the ability to move (and sometimes feel anything) in part or most of the body |
front 67 cachexic/cachexia | back 67 aka wasting syndrome; is a condition that causes significant weight loss or muscle loss - often affects people w/ sever chronic disease like advanced cancer and heart disease |
front 68 extension | back 68  a type of movement that increases the angle of a joint in a sagittal plane (ex: straightening the knee) |