Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Intro to DNA History, Structure and Replication
front 1 nucleotide | back 1  the monomer of a nucleic acid (DNA, RNA) |
front 2 Sugar in DNA | back 2 deoxyribose |
front 3 Nitrogenous Bases in DNA | back 3 adenine (A) thymine (T) guanine (G) cytosine (C) |
front 4 Purines | back 4 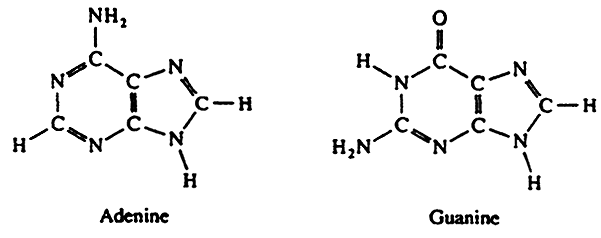 double ringed nitrogenous bases includes adenine and guanine |
front 5 pyrimidines | back 5 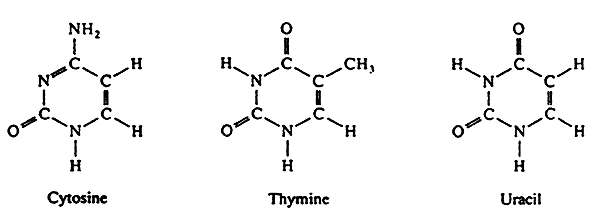 single ring nitrogenous bases includes cytosine and thymine |
front 6 hydrogen bonds | back 6 what holds the two strands of DNA together A-T=2 G-C=3 |
front 7 What are the sides of the DNA made of? | back 7 Sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate |
front 8 What are the rungs of the DNA model made of? | back 8 complementary base pairs A-T, G-C |
front 9 Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? | back 9 in the nucleus |
front 10 Francis Griffith | back 10 scientist who studied streptococcus pneumoniae found the "transforming principle" |
front 11 Avery, MacLeod, McCarty | back 11 proved DNA was the genetic material using streptococcus pneumoniae and various enzymes to isolate carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. We identifying what the "transforming principle" was. |
front 12 Hershey & Chase | back 12 The scientists who finally settled the debate that DNA, not protein was the genetic material. Used a bacteriophage virus, bacteria and radioactive isotopes. |
front 13 Erwin Chargaff | back 13 Chargaff's Rules The amount of A equals the amount of T The amount of G equals the amount of C |
front 14 Friedrich Miescher | back 14 First scientist to isolate (extract) DNA |
front 15 Franklin and Wilkins | back 15 took X-Ray crystallography pictures of the DNA identified DNA was a helix |
front 16 Watson and Crick | back 16 the scientists who identified the structure of DNA, the double helix. |
front 17 When does DNA replication take place? | back 17 prior to a cell dividing |
front 18 Why is DNA replication semi-conservative? | back 18 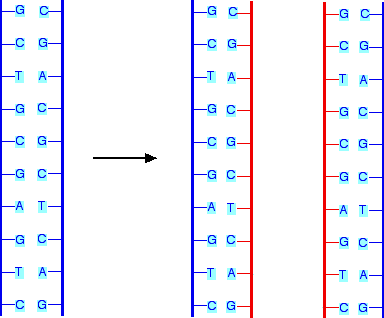 It saves half of the original strand and uses it as a template to make the other half new and complementary. End up with two identical copies. |
front 19 DNA Helicase | back 19 the enzyme that unwinds and unzips the DNA for replication |
front 20 DNA Polymerase | back 20 the enzyme that adds new complementary nucleotides to the template strand. |
front 21 SSB | back 21 single stranded binding proteins hold the original 2 DNA strands apart |
front 22 RNA primase | back 22 provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin copying the DNA |
front 23 DNA ligase | back 23 the enzyme that seals the Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand |
front 24 leading strand | back 24 the original DNA strand that is copied continuously |
front 25 lagging strand | back 25 the original DNA strand that is copied in pieces, Okazaki fragment. |
front 26 mutation | back 26 a change in the DNA |
front 27 mutagen | back 27 anything that causes a mutation |