nucleotide

the monomer of a nucleic acid (DNA, RNA)
Sugar in DNA
deoxyribose
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
adenine (A)
thymine (T)
guanine (G)
cytosine (C)
Purines
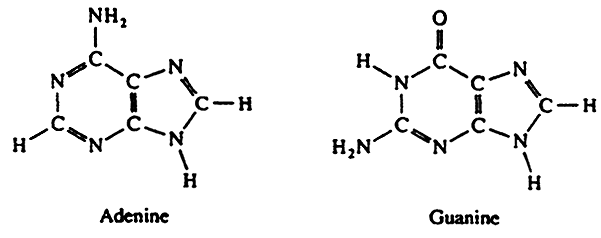
double ringed nitrogenous bases
includes adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
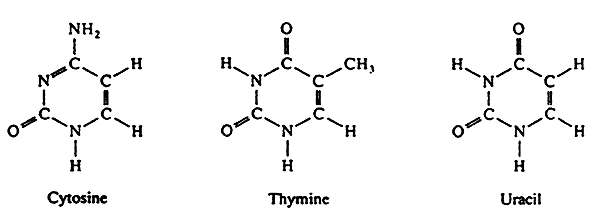
single ring nitrogenous bases
includes cytosine and thymine
hydrogen bonds
what holds the two strands of DNA together
A-T=2
G-C=3
What are the sides of the DNA made of?
Sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate
What are the rungs of the DNA model made of?
complementary base pairs
A-T, G-C
Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell?
in the nucleus
Francis Griffith
scientist who studied streptococcus pneumoniae
found the "transforming principle"
Avery, MacLeod, McCarty
proved DNA was the genetic material using streptococcus pneumoniae and various enzymes to isolate carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. We identifying what the "transforming principle" was.
Hershey & Chase
The scientists who finally settled the debate that DNA, not protein was the genetic material. Used a bacteriophage virus, bacteria and radioactive isotopes.
Erwin Chargaff
Chargaff's Rules
The amount of A equals the amount of T
The amount of G equals the amount of C
Friedrich Miescher
First scientist to isolate (extract) DNA
Franklin and Wilkins
took X-Ray crystallography pictures of the DNA
identified DNA was a helix
Watson and Crick
the scientists who identified the structure of DNA, the double helix.
When does DNA replication take place?
prior to a cell dividing
Why is DNA replication semi-conservative?
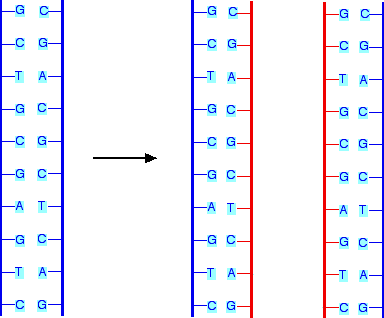
It saves half of the original strand and uses it as a template to make the other half new and complementary. End up with two identical copies.
DNA Helicase
the enzyme that unwinds and unzips the DNA for replication
DNA Polymerase
the enzyme that adds new complementary nucleotides to the template strand.
SSB
single stranded binding proteins
hold the original 2 DNA strands apart
RNA primase
provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin copying the DNA
DNA ligase
the enzyme that seals the Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand
leading strand
the original DNA strand that is copied continuously
lagging strand
the original DNA strand that is copied in pieces, Okazaki fragment.
mutation
a change in the DNA
mutagen
anything that causes a mutation