Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Central Science: Chapter 21
front 1 All atoms of a given element have the same ________. | back 1 E |
front 2 Atoms containing radioactive nuclei are called ________. | back 2 B |
front 3 What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it undergoes beta decay? | back 3 C |
front 4  Which one of the following is a correct representation of a beta particle? | back 4 D |
front 5  Which one of the following is a correct representation of an alpha particle? | back 5 A |
front 6  Which one of the following is a correct representation of a positron? | back 6 C |
front 7 Which one of the following processes results in an increase in the
atomic number? | back 7 C |
front 8 Of the following processes, which one changes the atomic
number? | back 8 E |
front 9 What radioactive element is used to diagnose medical conditions of
the heart and arteries? | back 9 B |
front 10 In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the
product increase by one? | back 10 B |
front 11 Which type of radioactive decay results in no change in mass number
and atomic number for the starting nucleus? | back 11 E |
front 12 Alpha decay produces a new nucleus whose ________ than those
respectively of the original nucleus. | back 12 C |
front 13  What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 13 B |
front 14 What is the atomic number of a neutron? | back 14 D |
front 15 What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it emits gamma radiation? | back 15 E |
front 16 Atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers
________. | back 16 C |
front 17 How many radioactive decay series exist in nature? | back 17 D |
front 18 At approximately what number of protons, or neutrons, does the 1:1
ratio of protons to neutrons start to produce unstable nuclei? | back 18 B |
front 19 Carbon-11 decays by ________. | back 19 C |
front 20 The formation of krypton from rubidium decay is a result of
________. | back 20 D |
front 21 The mode of decay of 32P is ________. | back 21 B |
front 22 The belt of nuclear stability ends with the element ________. | back 22 E |
front 23  Which of these nuclides is most likely to be radioactive? | back 23 D |
front 24 What is required for a nuclear transmutation to occur? | back 24 C |
front 25  In the nuclear transmutation, [see image], what is the bombarding
particle? | back 25 D |
front 26 Cobalt-60 is produced by a three reaction process involving neutron
capture, beta-emission, and neutron capture. The initial reactant in
the production of cobalt-60 is ________. | back 26 C |
front 27 The product of the nuclear reaction in which 28Si is subjected to
neutron capture followed by alpha emission is ________. | back 27 D |
front 28 Transuranium elements have atomic numbers greater than
________. | back 28 C |
front 29  What is emitted in the nuclear transmutation [see image]? | back 29 A |
front 30  In the nuclear transmutation represented by [see image]? what is the
product? | back 30 C |
front 31  In the nuclear transmutation represented by [see image]?, what is the
emitted particle? | back 31 B |
front 32  What is the product for the nuclear transmutation represented by [see
image]? | back 32 D |
front 33  Which one of the following requires a particle accelerator to occur? | back 33 D |
front 34 Bombardment of uranium-238 with a deuteron (hydrogen-2) generates
neptunium-237 and ________ neutrons. | back 34 C |
front 35  The transmutation in which neptunium-239 is produced via bombardment of uranium-238 with a neutron is represented by ________. | back 35 D |
front 36  The transmutation in which a curium-242 nucleus is bombarded with an alpha particle to produce a californium-245 nucleus is represented by ________. | back 36 E |
front 37 Which one of the following can be done to shorten the half-life of
the radioactive decay of uranium-238? | back 37 E |
front 38 The beta decay of cesium-137 has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many
years must pass to reduce a 25 mg sample of cesium 137 to 8.7
mg? | back 38 A |
front 39 The half-life of 218Po is 3.1 minutes. How much of a 155 gram sample
remains after 0.40 hours? | back 39 C |
front 40 Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent of a cesium-131
sample remains after 60 days? | back 40 C |
front 41 The half-life for beta decay of strontium-90 is 28.8 years. A milk
sample is found to contain 10.3 ppm strontium-90. How many years would
pass before the strontium-90 concentration would drop to 1.0
ppm? | back 41 D |
front 42 The half-life of carbon-11 is 20.3 minutes. How much of a 100.0 mg
sample remains after 1.50 hours? | back 42 B |
front 43 The half-life of 131I is 0.220 years. How much of a 500.0 mg sample
remains after 24 hours? | back 43 A |
front 44 The half-life of 223Ra is 11.4 days. How much of a 200.0 mg sample
remains after 600 hours? | back 44 D |
front 45 The half-life of 222Rn is 3.80 days. If a sample contains 36.0 g of
Rn-222, how many years will it take for the sample to be reduced to
1.00 mg of Rn-222? | back 45 B |
front 46 The carbon-14 dating method can be used to determine the age of a
________. | back 46 B |
front 47 The basis for the carbon-14 dating method is that ________. | back 47 C |
front 48 Pb has a half-life of 22.3 years and decays to produce 206Hg. If you
start with 7.50 g of 210Pb, how many grams of 206Hg will you have
after 17.5 years? | back 48 B |
front 49 The half-life of a radionuclide ________. | back 49 A |
front 50 The curie is a measure of the ________. | back 50 A |
front 51  What is the rate constant (in min-1) for the decay of this
radionuclide? | back 51 E |
front 52  What is the half-life (in min) of this radionuclide? | back 52 C |
front 53 Cesium-137 undergoes beta decay and has a half-life of 30.0 years.
How many beta particles are emitted by a 14.0-g sample of cesium-137
in three minutes? | back 53 E |
front 54 What is a phosphor? | back 54 D |
front 55 Which one of the following devices converts radioactive emissions to
light for detection? | back 55 C |
front 56 Which one of the following is used as a radiotracer to study
blood? | back 56 A |
front 57 Which one of the following is true? | back 57 C |
front 58 The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10-24 g. The mass of a
neutron is 1.675 × 10-24 g. The mass of the nucleus of an
56Fe atom is 9.289 × 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding
energy (in J) for a 56Fe nucleus? (c = 3.00 x 108
m/s) | back 58 D |
front 59 When two atoms of 2H are fused to form one atom of 4He, the total
energy evolved is 3.83 x 10-12J. What is the total change
in mass (in kg) for this reaction? (c = 3.00 x 108
m/s) | back 59 E |
front 60 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu. Speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.) | back 60 D |
front 61 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy per nucleon (in J) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu. Speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.) | back 61 A |
front 62 What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60
28Ni nucleus if the nuclear mass is 59.9308 amu? The mass
of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. | back 62 B |
front 63 In terms of binding energy per nucleon, what element divides fission
and fusion processes? | back 63 D |
front 64 What type of reaction is known as a thermonuclear reaction? | back 64 B |
front 65 The main scientific difficulty in achieving a controlled fusion
process is the ________. | back 65 A |
front 66 What exposure level to radiation is fatal to most humans? | back 66 C |
front 67 Which one of the following natural radionuclides is the most
abundant? | back 67 A |
front 68 Which one of the following forms of radiation can penetrate the
deepest into body tissue? | back 68 C |
front 69 What percentage of electricity generated in the U.S. is from
commercial nuclear plants? | back 69 C |
front 70 By what process does thorium-230 decay to radium-226? | back 70 B |
front 71 The alpha decay of what isotope of what element produces
lead-206? | back 71 A |
front 72  In balancing the nuclear reaction [see image], the identity of
element E is ________. | back 72 E |
front 73  What is the identity of element E in the nuclear reaction [see
image]? | back 73 D |
front 74  In balancing the nuclear reaction [see image], the identity of
element E is ________. | back 74 D |
front 75  This reaction is an example of ________. A) alpha decay | back 75 A |
front 76  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 76 D |
front 77  The missing reactant from this reaction is ________. | back 77 C |
front 78  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 78 B |
front 79  The missing reactant from this reaction is ________. | back 79 A |
front 80  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 80 A |
front 81  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 81 B |
front 82  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 82 E |
front 83  The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 83 B |
front 84 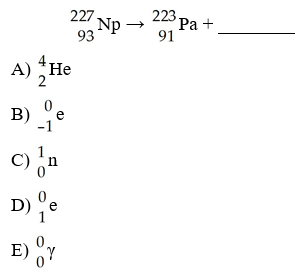 The missing product from this reaction is ________. | back 84 A |
front 85  This reaction is an example of ________. A) alpha decay | back 85 C |
front 86  This reaction is an example of ________. A) alpha decay | back 86 B |
front 87  This reaction is an example of ________. A) alpha decay | back 87 C |
front 88  This reaction is an example of ________. A) alpha decay | back 88 D |
front 89  The missing product in this reaction would be found in which group of the periodic table? A) 1A | back 89 B |
front 90  The missing product in this reaction combines with oxygen to form a compound with the formula ________. A) M2O | back 90 B |
front 91 Radium undergoes alpha decay. The product of this reaction also
undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay
reaction? | back 91 A |
front 92 41Ca decays by electron capture. The product of this reaction
undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay
reaction? | back 92 D |
front 93 What is the mass number of a neutron? | back 93 B |
front 94 Nuclei above the belt of stability can lower their neutron-to-proton
ratio by ________. | back 94 A |
front 95 What is the largest number of protons that can exist in a nucleus and
still be stable? | back 95 D |
front 96 The three radioactive series that occur in nature end with what
element? | back 96 D |
front 97 The largest number of stable nuclei have an ________ number of
protons and an ________ number of neutrons. | back 97 A |
front 98 In the nuclear transmutation represented by 16
8O(p, α) 13
7N, the emitted particle is ________. | back 98 B |
front 99 Bombardment of uranium-235 with a neutron generates tellurium-135, 3
neutrons, and ________. | back 99 A |
front 100  The reaction shown below is responsible for creating 14C in the
atmosphere. What is the bombarding particle? | back 100 C |
front 101 How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98)
is bombarded with a carbon-12 nucleus to produce a 257
104Rf nucleus? | back 101 D |
front 102 How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98)
is bombarded with a nitrogen-15 nucleus to produce a 260
105Db nucleus? | back 102 C |
front 103 What order process is radioactive decay? | back 103 B |
front 104 Due to the nature of the positron, ________ is actually detected in
positron emission tomography. | back 104 C |
front 105 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu.) | back 105 B |
front 106 What is the typical percent of uranium-235 in the enriched UO2
pellets used in nuclear reactors? | back 106 C |
front 107 On average, ________ neutrons are produced by every fission of a
uranium-235 nucleus. | back 107 D |
front 108 What drives the turbine in a nuclear power plant? | back 108 B |
front 109 Who is credited with first achieving fission of uranium-235? | back 109 A |
front 110 When ionizing radiation enters the body, what is the predominant free
radical produced? | back 110 D |
front 111 A ________ is a highly reactive substance that contains one or more
unpaired electrons. | back 111 B |
front 112 What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it undergoes alpha decay? | back 112 A |
front 113  Which one of the following is a correct representation of beta particle? | back 113 A |
front 114 Which one of the following processes results in a decrease in the
number of neutrons? | back 114 A |
front 115 In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the
product decrease by one? | back 115 A |
front 116  What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 116 A |
front 117 When an atom of an element undergoes beta decay, its proton count
will change by ________ and its neutron count will change by
________. | back 117 A |
front 118 What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 118  A |
front 119  What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 119 A |
front 120  What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 120 A |
front 121  What is the missing product from this reaction? | back 121 A |
front 122 The product of the nuclear reaction in which 40Ar is subjected to
neutron capture followed by alpha emission is ________. | back 122 A |
front 123 The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.20 yr. How many milligrams of a
2.000-mg sample remain after 9.50 years? | back 123 A |
front 124 What percentage of a radioactive sample remains after 175.0 yr if it
has a of 28.8 years? | back 124 E |
front 125 What percentage of a sample remains after 50.0 min if it has a
half-life of 20.4 min.? | back 125 D |
front 126 A rock contains 0.153 mg of lead-206 for each milligram of
uranium-238. The half-life for the decay of uranium-238 to lead-206 is
4.5 × 109 yr. The rock was formed ________ years
ago. | back 126 D |
front 127 131I has a half-life of 8.04 days. Assuming you start with a 1.03 mg
sample of 131I, how many mg will remain after 13.0 days? | back 127 E |
front 128 The decay of a radionuclide with a half-life of 3.3 × 105
years has a rate constant (in yr-1) equal to
________. | back 128 B |
front 129 What is the age in years of a mineral sample that has a mass ratio of
40Ar to 40K of 0.330? Potassium-40 decays to argon-40 with a half-life
of 1.27 × 109 yr. | back 129 B |
front 130 If we start with 1.000 g of strontium-90, 0.805 g will remain after
9.00 yr. This means that the half-life of strontium-90 is ________
yr. | back 130 C |
front 131 If we start with 1.000 g of cobalt-60, 0.400 g will remain after 7.00
yr. This means that the half-life of cobalt-60 is ________ yr. | back 131 D |
front 132 A freshly prepared sample of curium-243 undergoes 3312
disintegrations per second. After 8.00 yr, the activity of the sample
declines to 2591 disintegrations per second. What is the half-life in
years of curium-243? | back 132 A |
front 133 The beta decay of cesium-137 has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many
years must pass to reduce a 30 mg sample of cesium 137 to 5.2
mg? | back 133 A |
front 134 The half-life of 218Po is 3.1 minutes. How much of a 170 gram sample
remains after 0.64 hours? | back 134 A |
front 135 Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent of a cesium-131
sample remains after 62 days? | back 135 A |
front 136 The half-life of carbon-11 is 20.3 minutes. How much of a 100.0 mg
sample remains after 1.6 hours? | back 136 A |
front 137 210Pb has a half-life of 22.3 years and decays to produce 206Hg. If
you start with of 210Pb, how many grams of 206Hg will you have after
15.8 years? | back 137 D |
front 138 Carbon-11 decays by positron emission. The decay occurs with a
release of 2.87 × 1011 J per mole of carbon-11. What mass
(g) is converted to energy when 5.00 g of carbon-11 undergoes this
radioactive decay? | back 138 D |
front 139 How much energy (in J) is produced when 0.067 g of matter is
converted to energy? | back 139 B |
front 140 The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10-24g. The mass of a
neutron is 1.675 × 10-24g. The mass of the nucleus of an
59Fe atom is 9.787 × 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding
energy (in J) for A 59Fe nucleus? (c = 3.00 x
108m/s) | back 140 A |
front 141 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 62Co nucleus? | back 141 A |
front 142 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy per nucleon (in J) of a 59Co
nucleus? | back 142 A |
front 143 The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 57Ni nucleus? | back 143 A |
front 144 What happens in the nucleus of an atom that undergoes positron emission? | back 144 A proton is converted to a neutron and a positron. |
front 145 What is the predominant isotope of uranium? | back 145 238U |
front 146 What happens to the atomic mass number and the atomic number of a radioisotope when it undergoes alpha emission? | back 146 The mass number drops by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2. |
front 147 What are beta particles? | back 147 high speed electrons emitted by an unstable nucleus |
front 148 4 2He represents ________. | back 148 an alpha particle |
front 149 What isotope of what element is produced if uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay? | back 149 Answer: thorium-234 |
front 150 Stable nuclei with low atomic numbers, up to ________, have a neutron to proton ratio of approximately 1:1. | back 150 20 |
front 151 The first nuclear transmutation resulted in the conversion of nitrogen-14 to ________. | back 151 oxygen-17 |
front 152 Conversion of one nucleus into another was first demonstrated in 1919 by ________. | back 152 Rutherford |
front 153 The initial element used to make cobalt-60 for cancer radiation therapy is ________. | back 153 iron; Fe |
front 154 What is the rate constant for the decay of some unknown radioactive compound if the half-life for the beta decay is 1.3 × 109 years? | back 154 5.3 × 10-10 year-1 |
front 155 ________ discovered radioactivity. | back 155 Becquerel |
front 156 Carbon-11, fluorine-18, oxygen-15 and nitrogen-13 are all used in the clinical diagnostic technique known as ________. | back 156 positron emission tomography; PET |
front 157 The conversion of matter to energy and mass loss occurs in ________ reactions? | back 157 nuclear |
front 158 Control rods in a nuclear reactor are composed of boron and ________. | back 158 an alloy of silver, indium, and cadmium |
front 159 The amount of fissionable material necessary to maintain a chain reactions is called the ________. | back 159 critical mass |
front 160 What was the purpose of the Manhattan project? | back 160 to build a bomb based on nuclear fission |
front 161 When living tissue is irradiated most of the energy is absorbed by ________. | back 161 water |
front 162 The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of beta rays, gamma rays, and alpha rays are ________, respectively. | back 162 1,1,10 |
front 163 The major type of cancer caused by radiation is ________. | back 163 leukemia |
front 164 Radioactive seeds that are implanted into a tumor are coated with ________ to stop alpha and beta ray penetration. | back 164 platinum |
front 165 Gamma radiation only changes the atomic number but not the mass number of a nucleus. | back 165 false |
front 166 Positron emission causes an increase of one in the atomic number. | back 166 false |
front 167 The neutron/proton ratio of stable nuclei increases with increasing atomic number. | back 167 true |
front 168 Charged particles are accelerated because the faster they move there is a greater chance of producing a nuclear reaction. | back 168 true |
front 169 Radioactive decay is a first order kinetic process. | back 169 true |
front 170 In radioactive dating, the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 is related to the time of death of the animal or plant under investigation. | back 170 false |
front 171 In the formula k = 0.693/t1/2, k is the decay constant. | back 171 true |
front 172 The energy produced by the sun is the result of nuclear fusion. | back 172 true |
front 173 The SI unit of an absorbed dose of radiation is the gray. | back 173 true |
front 174 The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) is tenfold greater for gamma radiation than for alpha radiation. | back 174 false |
front 175 Electrons do not exist in the nucleus, yet beta emission is ejection of electrons from the nucleus. How does this happen? | back 175 A neutron breaks apart to produce a proton and an electron in the nucleus. The proton remains in the nucleus and the electron is ejected. |
front 176 List the common particles and their symbols used in descriptions of radioactive decay and nuclear transformations. | back 176  |
front 177 When an isotope undergoes electron capture, what happens to the captured electron? | back 177 It combines with a proton in the nucleus to form a neutron. |
front 178 The use of radioisotopes in tracing metabolism is possible because ________. | back 178 all isotopes of an element have identical chemical properties |