All atoms of a given element have the same ________.
A) mass
number
B) number of nucleons
C) atomic mass
D) number
of neutrons
E) atomic number
E
Atoms containing radioactive nuclei are called ________.
A)
radionuclides
B) radioisotopes
C) nucleons
D)
nuclides
E) radioisophores
B
What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it undergoes beta decay?
A) Neither the mass number nor the
atomic number changes.
B) The mass number decreases by 4 and the
atomic number decreases by 2.
C) The mass number does not change
and the atomic number increases by 1.
D) The mass number does not
change and the atomic number decreases by 2.
E) The mass number
increases by 2 and the atomic number increases by 1.
C

Which one of the following is a correct representation of a beta particle?
D

Which one of the following is a correct representation of an alpha particle?
A

Which one of the following is a correct representation of a positron?
C
Which one of the following processes results in an increase in the
atomic number?
A) gamma emission
B) positron
emission
C) beta emission
D) alpha emission
E) corrosion
C
Of the following processes, which one changes the atomic
number?
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C) electron
capture
D) positron emission
E) All of these processes
change the atomic numbers.
E
What radioactive element is used to diagnose medical conditions of
the heart and arteries?
A) cobalt-60
B) thallium-201
C)
radium-226
D) radon-222
E) thorium-234
B
In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the
product increase by one?
A) alpha
B) beta
C)
gamma
D) positron emission
E) electron capture
B
Which type of radioactive decay results in no change in mass number
and atomic number for the starting nucleus?
A) alpha
B)
beta
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma
E
Alpha decay produces a new nucleus whose ________ than those
respectively of the original nucleus.
A) atomic number is 2 less
and mass number is 2 less
B) atomic number is 1 less and mass
number is 2 less
C) atomic number is 2 less and mass number is 4
less
D) atomic number is 2 more and mass number is 4 more
E)
atomic number is 2 more and mass number is 2 less
C

What is the missing product from this reaction?
B
What is the atomic number of a neutron?
A) 3
B) 1
C)
2
D) 0
E) 4
D
What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it emits gamma radiation?
A) The mass number remains
unchanged while the atomic number decreases by one.
B) The mass
number decreases by four and the atomic number decreases by
two.
C) The mass number increases by four and the atomic number
increases by two.
D) The mass number remains unchanged while the
atomic number increases by one.
E) The mass number and atomic
numbers remain unchanged.
E
Atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers
________.
A) do not exist
B) are isomers
C) are
isotopes
D) are allotropes
E) are resonance structures
C
How many radioactive decay series exist in nature?
A) 0
B)
1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 10
D
At approximately what number of protons, or neutrons, does the 1:1
ratio of protons to neutrons start to produce unstable nuclei?
A)
10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 50
E) 80
B
Carbon-11 decays by ________.
A) alpha emission
B) beta
emission
C) positron emission
D) photon emission
E)
neutron capture
C
The formation of krypton from rubidium decay is a result of
________.
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C)
positron emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron capture
D
The mode of decay of 32P is ________.
A) alpha emission
B)
beta emission
C) positron emission
D) electron
capture
E) neutron capture
B
The belt of nuclear stability ends with the element ________.
A)
lead
B) polonium
C) radon
D) astatine
E) bismuth
E

Which of these nuclides is most likely to be radioactive?
D
What is required for a nuclear transmutation to occur?
A) very
high temperature
B) a corrosive environment
C) a particle to
collide with a nucleus or neutron
D) spontaneous nuclear
decay
E) gamma emission
C

In the nuclear transmutation, [see image], what is the bombarding
particle?
A) an alpha particle
B) a beta particle
C) a
gamma photon
D) a proton
E) a phosphorus nucleus
D
Cobalt-60 is produced by a three reaction process involving neutron
capture, beta-emission, and neutron capture. The initial reactant in
the production of cobalt-60 is ________.
A) 59Co
B)
56Fe
C) 58Fe
D) 61Co
E) 60Fe
C
The product of the nuclear reaction in which 28Si is subjected to
neutron capture followed by alpha emission is ________.
A)
31S
B) 33S
C) 23Mg
D) 25Mg
E) 25Al
D
Transuranium elements have atomic numbers greater than
________.
A) 90
B) 91
C) 92
D) 93
E) 94
C

What is emitted in the nuclear transmutation [see image]?
A) an
alpha particle
B) a beta particle
C) a neutron
D) a
proton
E) a gamma photon
A

In the nuclear transmutation represented by [see image]? what is the
product?
A) uranium-242
B) curium-245
C)
curium-242
D) uranium-245
E) uranium-243
C

In the nuclear transmutation represented by [see image]?, what is the
emitted particle?
A) neutron
B) proton
C)
positron
D) alpha particle
E) electron
B

What is the product for the nuclear transmutation represented by [see
image]?
A) carbon-12
B) carbon-16
C)
nitrogen-16
D) carbon-14
E) nitrogen-15
D

Which one of the following requires a particle accelerator to occur?
D
Bombardment of uranium-238 with a deuteron (hydrogen-2) generates
neptunium-237 and ________ neutrons.
A) 1
B) 2
C)
3
D) 4
E) 5
C

The transmutation in which neptunium-239 is produced via bombardment of uranium-238 with a neutron is represented by ________.
D

The transmutation in which a curium-242 nucleus is bombarded with an alpha particle to produce a californium-245 nucleus is represented by ________.
E
Which one of the following can be done to shorten the half-life of
the radioactive decay of uranium-238?
A) freeze it
B) heat
it
C) convert it to UF6
D) oxidize it to the +2 oxidation
state
E) none of the above
E
The beta decay of cesium-137 has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many
years must pass to reduce a 25 mg sample of cesium 137 to 8.7
mg?
A) 46
B) 32
C) 3.2
D) 50
E) 52
A
The half-life of 218Po is 3.1 minutes. How much of a 155 gram sample
remains after 0.40 hours?
A) 0.00067 g
B) 0.0072 g
C)
0.72 g
D) 0.0047 g
E) none of the above
C
Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent of a cesium-131
sample remains after 60 days?
A) 100
B) 0
C)
1.4
D) 98.6
E) more information is needed to solve the problem
C
The half-life for beta decay of strontium-90 is 28.8 years. A milk
sample is found to contain 10.3 ppm strontium-90. How many years would
pass before the strontium-90 concentration would drop to 1.0
ppm?
A) 92.3
B) 0.112
C) 186
D) 96.9
E) 131
D
The half-life of carbon-11 is 20.3 minutes. How much of a 100.0 mg
sample remains after 1.50 hours?
A) 8.48 mg
B) 4.63
mg
C) 12.9 mg
D) 22.6 mg
E) 7.70 mg
B
The half-life of 131I is 0.220 years. How much of a 500.0 mg sample
remains after 24 hours?
A) 496 mg
B) 560 mg
C) 219
mg
D) 405 mg
E) 337 mg
A
The half-life of 223Ra is 11.4 days. How much of a 200.0 mg sample
remains after 600 hours?
A) 0.219 mg
B) 21.9 mg
C)
.0302 mg
D) 43.8 mg
E) 6.04 mg
D
The half-life of 222Rn is 3.80 days. If a sample contains 36.0 g of
Rn-222, how many years will it take for the sample to be reduced to
1.00 mg of Rn-222?
A) 19.7
B) 0.1575
C) 8.53
D)
0.0234
E) none of the above
B
The carbon-14 dating method can be used to determine the age of a
________.
A) flint arrowhead
B) papyrus scroll
C) stone
axe head
D) clay pot
E) rock
B
The basis for the carbon-14 dating method is that ________.
A)
the amount of carbon-14 in all objects is the same
B) carbon-14
is very unstable and is readily lost from the atmosphere
C) the
ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in the atmosphere is a
constant
D) living tissue will not absorb carbon-14 but will
absorb carbon-12
E) All of the above are correct.
C
Pb has a half-life of 22.3 years and decays to produce 206Hg. If you
start with 7.50 g of 210Pb, how many grams of 206Hg will you have
after 17.5 years?
A) 4.35
B) 3.15
C) 3.09
D)
0.0600
E) 1.71
B
The half-life of a radionuclide ________.
A) is constant
B)
gets shorter with passing time
C) gets longer with passing
time
D) gets shorter with increased temperature
E) gets
longer with increased temperature
A
The curie is a measure of the ________.
A) number of
disintegrations per second of a radioactive substance
B) total
energy absorbed by an object exposed to a radioactive source
C)
lethal threshold for radiation exposure
D) number of alpha
particles emitted by exactly one gram of a radioactive
substance
E) None of the above is correct.
A

What is the rate constant (in min-1) for the decay of this
radionuclide?
A) 45
B) 32
C) 0.024
D)
0.032
E) 0.022
E

What is the half-life (in min) of this radionuclide?
A)
0.024
B) 0.022
C) 32
D) 0.032
E) 45
C
Cesium-137 undergoes beta decay and has a half-life of 30.0 years.
How many beta particles are emitted by a 14.0-g sample of cesium-137
in three minutes?
A) 6.1 × 1013
B) 6.2 × 1022
C) 8.4 × 1015
D) 1.3 × 10-8
E) 8.1 × 1015
E
What is a phosphor?
A) an oxide of phosphorus
B) a
substance that thermally reduces to phosphorus
C) a
bioluminescent substance
D) a substance that emits light when
excited by radiation
E) an alkali metal phosphide
D
Which one of the following devices converts radioactive emissions to
light for detection?
A) Geiger counter
B) photographic
film
C) scintillation counter
D) radiotracer
E) none
of the above
C
Which one of the following is used as a radiotracer to study
blood?
A) iron-59
B) technetium-99
C) sodium-23
D)
iodine-131
E) phosphorus-32
A
Which one of the following is true?
A) Some spontaneous nuclear
reactions are exothermic.
B) Some spontaneous nuclear reactions
are endothermic.
C) All spontaneous nuclear reactions are
exothermic.
D) There is no relationship between exothermicity and
spontaneity in nuclear reactions.
E) All spontaneous nuclear
reactions are endothermic.
C
The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10-24 g. The mass of a
neutron is 1.675 × 10-24 g. The mass of the nucleus of an
56Fe atom is 9.289 × 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding
energy (in J) for a 56Fe nucleus? (c = 3.00 x 108
m/s)
A) 2.57 × 10-16
B) 7.72 × 10-8
C) 8.36 × 10-9
D) 7.72 × 10-11
E) 6.07 × 106
D
When two atoms of 2H are fused to form one atom of 4He, the total
energy evolved is 3.83 x 10-12J. What is the total change
in mass (in kg) for this reaction? (c = 3.00 x 108
m/s)
A) 1.28 × 10-17
B) 4.26 × 10-26
C) 3.45 × 108
D) 1.15
E) 4.26 × 10-29
E
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu. Speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.)
A) 2.74 × 10-19
B) 9.12 × 10-28
C) 4.94 × 10-13
D) 8.20 × 10-11
E) 2.74 × 10-16
D
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy per nucleon (in J) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu. Speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.)
A) 1.37 × 10-12
B) 2.49 × 10-12
C) 3.04 × 10-12
D) 9.43 × 10-13
E) 7.01 × 10-14
A
What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60
28Ni nucleus if the nuclear mass is 59.9308 amu? The mass
of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu.
A) 0.5449
B) 0.5505
C) 1.2374
D)
1.3066
E) 28.7930
B
In terms of binding energy per nucleon, what element divides fission
and fusion processes?
A) H
B) He
C) C
D)
Fe
E) U
D
What type of reaction is known as a thermonuclear reaction?
A)
fission
B) fusion
C) transmutation
D) beta
emission
E) neutron emission
B
The main scientific difficulty in achieving a controlled fusion
process is the ________.
A) enormous repulsion between nuclei
being fused
B) enormous repulsion between the electrons of atoms
being fused
C) very large number of positrons emitted
D)
very large number of x-rays emitted
E) very large number of gamma
rays emitted
A
What exposure level to radiation is fatal to most humans?
A) 100
rem
B) 200 rem
C) 600 rem
D) 300 rem
E) 1000 rem
C
Which one of the following natural radionuclides is the most
abundant?
A) Potassium-40
B) Rubidium-87
C)
Thorium-232
D) Uranium-238
A
Which one of the following forms of radiation can penetrate the
deepest into body tissue?
A) alpha
B) beta
C)
gamma
D) positron
E) proton
C
What percentage of electricity generated in the U.S. is from
commercial nuclear plants?
A) 1%
B) 10%
C) 19%
D)
50%
E) 90%
C
By what process does thorium-230 decay to radium-226?
A) gamma
emission
B) alpha emission
C) beta emission
D) electron
capture
E) positron emission
B
The alpha decay of what isotope of what element produces
lead-206?
A) polonium-210
B) radon-222
C)
mercury-202
D) bismuth-208
E) thallium-204
A

In balancing the nuclear reaction [see image], the identity of
element E is ________.
A) Pu
B) Np
C) U
D)
Pa
E) Th
E

What is the identity of element E in the nuclear reaction [see
image]?
A) B
B) C
C) O
D) N
E) none of the above
D

In balancing the nuclear reaction [see image], the identity of
element E is ________.
A) Kr
B) Br
C) U
D)
Se
E) none of the above
D

This reaction is an example of ________.
A) alpha decay
B) beta emission
C) gamma emission
D)
positron emission
E) electron capture
A

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
D

The missing reactant from this reaction is ________.
C

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
B

The missing reactant from this reaction is ________.
A

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
A

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
B

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
E

The missing product from this reaction is ________.
B
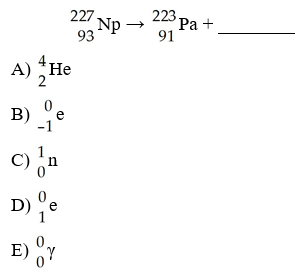
The missing product from this reaction is ________.
A

This reaction is an example of ________.
A) alpha decay
B) beta decay
C) positron decay
D)
electron capture
E) gamma emission
C

This reaction is an example of ________.
A) alpha decay
B) beta decay
C) positron decay
D)
electron capture
E) gamma emission
B

This reaction is an example of ________.
A) alpha decay
B) beta decay
C) positron decay
D)
electron capture
E) gamma emission
C

This reaction is an example of ________.
A) alpha decay
B) beta decay
C) positron decay
D)
electron capture
E) gamma emission
D

The missing product in this reaction would be found in which group of the periodic table?
A) 1A
B) 2A
C) 3A
D) 8A
E) 7A
B

The missing product in this reaction combines with oxygen to form a compound with the formula ________.
A) M2O
B) MO
C) M
D) M2O3
E) M3O2
B
Radium undergoes alpha decay. The product of this reaction also
undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay
reaction?
A) Po
B) Rn
C) U
D) Th
E) Hg
A
41Ca decays by electron capture. The product of this reaction
undergoes alpha decay. What is the product of this second decay
reaction?
A) Ti
B) Ca
C) Ar
D) Cl
E) Sc
D
What is the mass number of a neutron?
A) 2
B) 1
C)
3
D) 4
E) 0
B
Nuclei above the belt of stability can lower their neutron-to-proton
ratio by ________.
A) beta emission
B) gamma
emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E)
Any of the above processes will lower the neutron-to-proton ratio.
A
What is the largest number of protons that can exist in a nucleus and
still be stable?
A) 206
B) 50
C) 92
D) 83
E) 84
D
The three radioactive series that occur in nature end with what
element?
A) Bi
B) U
C) Po
D) Pb
E) Hg
D
The largest number of stable nuclei have an ________ number of
protons and an ________ number of neutrons.
A) even, even
B)
odd, odd
C) even, odd
D) odd, even
E) even, equal
A
In the nuclear transmutation represented by 16
8O(p, α) 13
7N, the emitted particle is ________.
A) a beta
particle
B) an alpha particle
C) a proton
D) a
positron
E) a neutron
B
Bombardment of uranium-235 with a neutron generates tellurium-135, 3
neutrons, and ________.
A) zirconium-98
B)
krypton-101
C) krypton-103
D) strontium-99
E) zirconium-99
A

The reaction shown below is responsible for creating 14C in the
atmosphere. What is the bombarding particle?
A) alpha
particle
B) electron
C) neutron
D) positron
E) proton
C
How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98)
is bombarded with a carbon-12 nucleus to produce a 257
104Rf nucleus?
A) one
B) three
C)
two
D) four
E) zero
D
How many neutrons are emitted when a californium-249 nucleus (Z=98)
is bombarded with a nitrogen-15 nucleus to produce a 260
105Db nucleus?
A) two
B) three
C)
four
D) one
E) zero
C
What order process is radioactive decay?
A) zeroth
B)
first
C) second
D) third
E) fourth
B
Due to the nature of the positron, ________ is actually detected in
positron emission tomography.
A) alpha radiation
B) beta
radiation
C) gamma radiation
D) x-ray emission
E)
neutron emission
C
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 60
27Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338
amu.)
A) 27.7830
B) 0.5489
C) 0.5405
D)
0.0662
E) 0.4827
B
What is the typical percent of uranium-235 in the enriched UO2
pellets used in nuclear reactors?
A) 0.7
B) 1
C)
3
D) 10
E) 14
C
On average, ________ neutrons are produced by every fission of a
uranium-235 nucleus.
A) 4
B) 3.5
C) 1
D)
2.4
E) 2
D
What drives the turbine in a nuclear power plant?
A) the
moderator
B) steam
C) the control rods
D) the primary
coolant
E) UF6 gas
B
Who is credited with first achieving fission of uranium-235?
A)
Fermi
B) Rutherford
C) Curie
D) Dalton
E) Faraday
A
When ionizing radiation enters the body, what is the predominant free
radical produced?
A) H
B) H3O
C) protein
D)
OH
E) H2O
D
A ________ is a highly reactive substance that contains one or more
unpaired electrons.
A) cation
B) free radical
C)
anion
D) protein
B
What happens to the mass number and the atomic number of an element
when it undergoes alpha decay?
A) The mass number decreases by 4
and the atomic number decreases by 2.
B) The mass number does not
change and the atomic number increases by 1.
C) The mass number
increases by 4 and the atomic number does not change.
D) The mass
number increases by 2 and the atomic number decreases by 1.
E)
The mass number does not change and the atomic number increases by 2.
A

Which one of the following is a correct representation of beta particle?
A
Which one of the following processes results in a decrease in the
number of neutrons?
A) alpha emission
B) gamma
emission
C) positron emission
D) corrosion
E) electron capture
A
In what type of radioactive decay does the atomic number of the
product decrease by one?
A) positron emission
B)
corrosion
C) alpha
D) beta
E) gamma
A

What is the missing product from this reaction?
A
When an atom of an element undergoes beta decay, its proton count
will change by ________ and its neutron count will change by
________.
A) +1, -1
B) 0, 0
C) -1, +1
D) -2,
-2
E) -1, -1
A
What is the missing product from this reaction?

A

What is the missing product from this reaction?
A

What is the missing product from this reaction?
A

What is the missing product from this reaction?
A
The product of the nuclear reaction in which 40Ar is subjected to
neutron capture followed by alpha emission is ________.
A)
37S
B) 41Ar
C) 36S
D) 45Ca
E) 35Ar
A
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.20 yr. How many milligrams of a
2.000-mg sample remain after 9.50 years?
A) 0.565
B) 7.03 ×
10-22
C) 7.076
D) 1.095
E) 1.435
A
What percentage of a radioactive sample remains after 175.0 yr if it
has a of 28.8 years?
A) 84.8
B) 0.230
C) 16.5
D)
6.08
E) 1.48
E
What percentage of a sample remains after 50.0 min if it has a
half-life of 20.4 min.?
A) 8.62
B) 66.5
C) 40.8
D)
18.3
E) 2.45
D
A rock contains 0.153 mg of lead-206 for each milligram of
uranium-238. The half-life for the decay of uranium-238 to lead-206 is
4.5 × 109 yr. The rock was formed ________ years
ago.
A) 6.89 × 108
B) 5.60 × 108
C) 7.33 × 108
D) 1.06 × 109
E) 8.08 × 108
D
131I has a half-life of 8.04 days. Assuming you start with a 1.03 mg
sample of 131I, how many mg will remain after 13.0 days?
A)
0.326
B) 0.268
C) 0.422
D) 0.0781
E) 0.336
E
The decay of a radionuclide with a half-life of 3.3 × 105
years has a rate constant (in yr-1) equal to
________.
A) 4.8 × 105
B) 2.1 × 10-6
C) 4.2 × 10-6
D) 2.8 × 103
E) 5.9 × 10-8
B
What is the age in years of a mineral sample that has a mass ratio of
40Ar to 40K of 0.330? Potassium-40 decays to argon-40 with a half-life
of 1.27 × 109 yr.
A) 3.85 × 109
B) 5.23 × 108
C) 1.77 × 109
D) 3.62 × 108
E) 2.55 × 109
B
If we start with 1.000 g of strontium-90, 0.805 g will remain after
9.00 yr. This means that the half-life of strontium-90 is ________
yr.
A) 7.74
B) 11.2
C) 28.8
D) 7.25
E) 41.6
C
If we start with 1.000 g of cobalt-60, 0.400 g will remain after 7.00
yr. This means that the half-life of cobalt-60 is ________ yr.
A)
12.1
B) 17.5
C) 2.80
D) 5.30
E) 7.65
D
A freshly prepared sample of curium-243 undergoes 3312
disintegrations per second. After 8.00 yr, the activity of the sample
declines to 2591 disintegrations per second. What is the half-life in
years of curium-243?
A) 22.6
B) 6.26
C) 10.2
D)
1.36
E) 32.6
A
The beta decay of cesium-137 has a half-life of 30.0 years. How many
years must pass to reduce a 30 mg sample of cesium 137 to 5.2
mg?
A) 76 years
B) -76 years
C) 38 years
D) 0.040
years
E) 25 years
A
The half-life of 218Po is 3.1 minutes. How much of a 170 gram sample
remains after 0.64 hours?
A) 0.032 g
B) 150 g
C) 31
g
D) 4.7 × 10-10 g
E) None of the original sample
will remain.
A
Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent of a cesium-131
sample remains after 62 days?
A) 1.2 %
B) 100 %
C) 0
%
D) 99 %
E) 62%
A
The half-life of carbon-11 is 20.3 minutes. How much of a 100.0 mg
sample remains after 1.6 hours?
A) 3.77 mg
B) 0.0377
mg
C) 94.7 mg
D) 1.75 × 10-89 mg
E) 99.9 mg
A
210Pb has a half-life of 22.3 years and decays to produce 206Hg. If
you start with of 210Pb, how many grams of 206Hg will you have after
15.8 years?
A) 4.60 g
B) 2.83 g
C) 9.20 g
D) 2.30
g
E) 12.5 g
D
Carbon-11 decays by positron emission. The decay occurs with a
release of 2.87 × 1011 J per mole of carbon-11. What mass
(g) is converted to energy when 5.00 g of carbon-11 undergoes this
radioactive decay?
A) 1.45 × 10-6
B) 4.35 ×
105
C) 6.90 × 102
D) 1.45 ×
10-3
E) 1.59 × 10-2
D
How much energy (in J) is produced when 0.067 g of matter is
converted to energy?
A) 6.0 × 1018
B) 6.0 × 1012
C) 2.0 × 104
D)
6.0 × 1015
E) 2.0 × 107
B
The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10-24g. The mass of a
neutron is 1.675 × 10-24g. The mass of the nucleus of an
59Fe atom is 9.787 × 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding
energy (in J) for A 59Fe nucleus? (c = 3.00 x
108m/s)
A) 8.13 × 10-11 J
B) 2.71 ×
10-19 J
C) 8.13 × 10-8 J
D) 4.00 ×
10-9 J
E) -9.74 × 10-10 J
A
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 62Co nucleus?
(The
mass of a cobalt-62 nucleus is 61.9341 amu. The speed of light is 3.00
x 108m/s.)
A) 8.46 × 10-11 J
B) 8.46 ×
10-19 J
C) 4.15 × 10-9 J
D) 5.09 ×
1016 J
E) -1.12 × 10-9 J
A
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the binding energy per nucleon (in J) of a 59Co
nucleus?
(The mass of a cobalt-59 nucleus is 58.9332 amu. The
speed of light is 3.00 x 108m/s.)
A) 8.46 ×
10-12 J
B) 8.46 × 1013 J
C) 4.15 ×
1034 J
D) 5.09 × 1012 J
E) -1.12 ×
1010 J
A
The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867
amu. What is the mass defect (in amu) of a 57Ni nucleus?
(The
mass of a nickel-57 nucleus is 56.938 amu. )
A) 0.5155
amu
B) 28.76 amu
C) -0.4932 amu
D) 0.5141 amu
E)
1.031 amu
A
What happens in the nucleus of an atom that undergoes positron emission?
A proton is converted to a neutron and a positron.
What is the predominant isotope of uranium?
238U
What happens to the atomic mass number and the atomic number of a radioisotope when it undergoes alpha emission?
The mass number drops by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2.
What are beta particles?
high speed electrons emitted by an unstable nucleus
4 2He represents ________.
an alpha particle
What isotope of what element is produced if uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay?
Answer: thorium-234
Stable nuclei with low atomic numbers, up to ________, have a neutron to proton ratio of approximately 1:1.
20
The first nuclear transmutation resulted in the conversion of nitrogen-14 to ________.
oxygen-17
Conversion of one nucleus into another was first demonstrated in 1919 by ________.
Rutherford
The initial element used to make cobalt-60 for cancer radiation therapy is ________.
iron; Fe
What is the rate constant for the decay of some unknown radioactive compound if the half-life for the beta decay is 1.3 × 109 years?
5.3 × 10-10 year-1
________ discovered radioactivity.
Becquerel
Carbon-11, fluorine-18, oxygen-15 and nitrogen-13 are all used in the clinical diagnostic technique known as ________.
positron emission tomography; PET
The conversion of matter to energy and mass loss occurs in ________ reactions?
nuclear
Control rods in a nuclear reactor are composed of boron and ________.
an alloy of silver, indium, and cadmium
The amount of fissionable material necessary to maintain a chain reactions is called the ________.
critical mass
What was the purpose of the Manhattan project?
to build a bomb based on nuclear fission
When living tissue is irradiated most of the energy is absorbed by ________.
water
The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of beta rays, gamma rays, and alpha rays are ________, respectively.
1,1,10
The major type of cancer caused by radiation is ________.
leukemia
Radioactive seeds that are implanted into a tumor are coated with ________ to stop alpha and beta ray penetration.
platinum
Gamma radiation only changes the atomic number but not the mass number of a nucleus.
false
Positron emission causes an increase of one in the atomic number.
false
The neutron/proton ratio of stable nuclei increases with increasing atomic number.
true
Charged particles are accelerated because the faster they move there is a greater chance of producing a nuclear reaction.
true
Radioactive decay is a first order kinetic process.
true
In radioactive dating, the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 is related to the time of death of the animal or plant under investigation.
false
In the formula k = 0.693/t1/2, k is the decay constant.
true
The energy produced by the sun is the result of nuclear fusion.
true
The SI unit of an absorbed dose of radiation is the gray.
true
The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) is tenfold greater for gamma radiation than for alpha radiation.
false
Electrons do not exist in the nucleus, yet beta emission is ejection of electrons from the nucleus. How does this happen?
A neutron breaks apart to produce a proton and an electron in the nucleus. The proton remains in the nucleus and the electron is ejected.
List the common particles and their symbols used in descriptions of radioactive decay and nuclear transformations.

When an isotope undergoes electron capture, what happens to the captured electron?
It combines with a proton in the nucleus to form a neutron.
The use of radioisotopes in tracing metabolism is possible because ________.
all isotopes of an element have identical chemical properties