Which of the following are classified as pyrimidines?
thymine and cytosine
What type of bond is formed between the hydroxyl group of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of an adjacent nucleotide, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
phosphodiester bond
What types of bonds are formed between complementary DNA bases?
hydrogen bonds
Based on the following replication bubble, which of these statements is true?
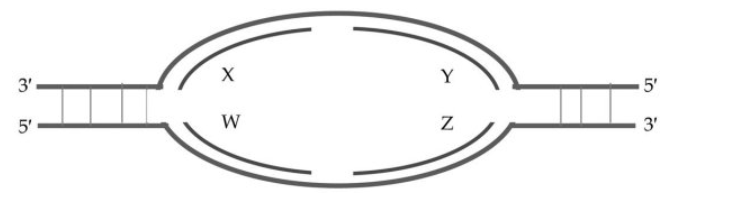
W and Y are leading strands, X and Z are lagging strands
In E. coli, replication begins at which chromosome site?
oriC
What is the DNA replication fork?
It is the site where the DNA helix opens to two single DNA strands.
Okazaki fragments form on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
True
DNA replication in eukaryotes
initiates at multiple origins
DNA replication proceeds
semiconservatively
DNA replication occurs by adding
dNTPs to the 3′ end of the daughter strand
What are two distinguishing features of RNA?
RNA has a ribose sugar and uracil nitrogenous base.
What is the role of a promoter region of a gene?
Recruit transcription factors that form the initiation complex.
Which region(s) of a gene are not found within the mRNA transcript?
promoter and termination region
you want to design a drug that prevents transcription of eukaryotic mRNAs but does not affect transcription of other RNAs. What enzyme would you target?
RNA polymerase II
Which of the following is part of a DNA molecule?
Promoter
Which enzyme is required to initiate 5′ capping of eukaryotic mRNA transcripts by removing the terminal phosphate group?
guanylyl transferase
Which of the following bacterial RNA polymerase subunits is found in the holoenzyme, but not the core enzyme?
σ (sigma)
What is the general name for the components of the spliceosome, which removes introns from mRNAs?
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
snRNA
What are catalytically active RNAs that can activate processes such as self-splicing?
ribozymes
What is the purpose of alternative splicing in eukaryotic cells?
Produce multiple polypeptide sequences from a single primary transcript.
Frederick Griffith studied how Pneumococcus causes fatal pneumonia in mice, focusing on the role of the capsule in the virulence of the bacteria. He found that heat-killed S bacteria somehow donated a molecule that was incorporated into living RII bacteria, which were converted from R to S capsules. He concluded that the basis of heredity was what?
a transforming factor
The antibiotic rifamycin is known to inhibit DNA polymerases in bacteria. What effect would this drug have on the structure of DNA?
It would be unable to form phosphodiester bonds between the 3′ hydroxyl group of one nucleotide and the 5′ phosphate group of an adjacent nucleotide.
How does base stacking contribute to the structure of DNA?
Nucleotide base pairs are spaced 3.4 Å apart, creating a twist to the double helix and two grooves within the backbone.
If Meselson and Stahl had used CsCl gradient analysis and identified DNA molecules with two distinct densities after generation 1, which model of DNA replication would have been supported by these data?
conservative
After how many replication generations were Meselson and Stahl able to distinguish semiconservative replication and dispersive replication.
2
Using pulse-chase labeling, Huberman and Riggs provided the first experimental evidence of bidirectional replication. What results would have supported the hypothesis that plasmid replication was actually unidirectional?
Alternating light and dark tracks in one direction from the replication origin
Which of the following is true regarding the Hershey Chase experiment?
The tagged phosphorus was present in the infected E.coli proving DNA is genetic information.
If a DNA sequence is made up of 30% Thymine, what percent of the DNA should be Cytosine?
20
If a DNA Sequence is 40% Guanine, what percent of the DNA sequence is Uracil?
0 (DNA does not have uracil)
Base pairs are covalently bonded together, adding structure to the DNA helix
false
What is a major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication?
DNA replication in prokaryotes is bidirectional from one origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic replication is bidirectional from multiple origins of replication on each chromosome.
In E. coli, what is the function of the DnaB enzyme?
DnaB is a helicase protein that uses ATP energy to hydrolyze hydrogen bonds, which separates the DNA strands and unwinds the double helix.
DNA polymerase III initiates strand elongation by adding a new nucleotide to the 3′ end of a short primer sequence. Where does this short primer come from?
RNA polymerase
During DNA replication, one daughter strand has a 5′-to-3′ direction of elongation that runs opposite to the direction of movement of the replication fork. These daughter strands are elongated discontinuously, in short segments called Okazaki fragments. Which enzyme is involved in annealing these fragments together, once the RNA primers have been removed and replaced with DNA, to form a continuous, newly replicated strand?
DNA ligase
For the DNA strands of a circular chromosome, unwinding creates torsional stress that accumulates as the unwound region gets larger and as DNA replication progresses. The accumulating stress could break the molecule at random locations, potentially leading to a breakdown of DNA replication. How does the cell prevent this stress?
Through the action of topoisomerases, which catalyze a controlled cleavage and rejoining of DNA, thus enabling over-twisted strands to unwind
DNA polymerase I has a 5′-to-3′ polymerase activity, as well as both 5′-to-3′ and 3′-to-5′ exonuclease activities. Suppose a cell has acquired a mutation that eliminates only the 5′-to-3′ exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I. What would be the effect on DNA replication?
RNA primers required for initiation of replication cannot be removed by DNA polymerase I.
Which of the following is the main function of DNA polymerase III
Main replication enzyme
Which of the following is NOT true regarding the formation of telomeres?
They are formed from a DNA template added by telomerase
Prokaryotic DNA does not replicate semiconservatively
false
DNA Polymerase requires a primer
true
If you were to design an antibiotic, which of these molecular features of transcription/translation would you NOT want to target? (Hint: you would want to target bacteria)
transcription factors
Which type of RNA is translated in a cell
mRNA
What are the only types of functional RNA observed in prokaryotes?
tRNA and rRNA
Which type of RNA regulates protein production through RNA interference
miRNA
How does RNA polymerase use DNA to synthesize an mRNA strand during transcription?
The polymerase uses one strand of DNA as the template strand to assemble a complementary, antiparallel strand of ribonucleotides.
Which DNA segment controls the access of RNA polymerase to the gene?
promoter
In bacteria, what structure triggers intrinsic termination of transcription?
Inverted repeats and a string of adenines
In eukaryotes, which enzyme is responsible for transcribing messenger RNAs that encode polypeptides, as well as for most small nuclear RNA genes?
RNA Polymerase II
The TATA box is an important conserved sequence within a gene. What is its primary function?
The TATA box acts as a highly conserved sequence within the eukaryotic promoter, which is located just upstream of the transcriptional start site.
Cancer cells often make their own transcription factors (TFs), which accounts for their increased growth rate. What effect would you expect to see when TF levels are increased in a cell?
Transcription would increase.
Which DNA sequence binds activator proteins and associated coactivator proteins to form a protein "bridge" that bends the DNA and links the complete initiation complex at the promoter to the activator-coactivator complex, ultimately causing an increase in transcription?
enhancer
Pre-mRNA must undergo 5′ capping to increase stability of the transcript. What two steps occur during 5′ capping?
Addition of guanine to the transcript and subsequent methylation
Introns are removed from mRNA by the spliceosome, a complex made up of protein and what type of RNA?
snRNAs
In posttranscriptional processing in Eukaryotes, the poly-A tail is encoded in the actual gene code
false
In prokaryotic intrinsic termination, the poly A tail is encoded by the gene code
true
Which of the following statements is false?
DNA always determines the final mature mRNA nucleotide sequence.
know how to code template strands?
kkk
What is this consensus sequence called?
Pribnow Box
Is this DNA prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic
Where is it located relative to the start of transcription?
10 Nucleotides upstream
Which strand is the template strand?
5'-3'
Which of the following is true regarding sigma subunits?
They bind to prokaryotic RNA polymerase to initiate transcription
Producing multiple proteins from one gene is a direct result of:
alternative splicing
Which of the following RNA sequences could form a hairpin loop?
AAAAAAAAUUUUUUUU
RNA polymerase will attach to the TATA box after it has been signaled to by the sigma subunit
false
Which would most likely effect the formation of a lariat?
Mutations in the branch point